Abstract
Figures and Tables
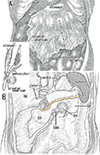 | Fig. 1Schematic representation of the greater omentum, duodenum and transverse colon in adults. Panel A is an anterior view showing an apron-like extension of the greater omentum. The transverse colon appears as a transparent image under the omentum. Panel B displays topographical anatomy after removal of the liver, stomach, jejunum and ileum, as well as entire parts of the colon. An attachment of the transverse mesocolon (red color) crosses the pancreas (P) longitudinally. The left and right kidneys (LK, RK) are located behind the transparent peritoneum. An insert on the left-hand side shows a logical lamination of the peritoneum. Specifically, the greater omentum, consisting of four layers, is attached to two layers of the transverse mesocolon. D3, horizontal or third portion of the duodenum; D4, ascending or fourth portion of the duodenum; SMA, superior mesentery artery. |
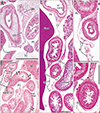 | Fig. 2Sagittal sections of midterm fetuses. Panel A shows a specimen of crown-rump length (CRL) 32 mm (gestational age [GA] 8 weeks); panels B and D show a specimen of CRL 36 mm (GA 9 weeks); and panels C and E show a specimen of CRL 61 mm (GA 10 weeks). Panel B and C were prepared at the same magnification, and panels D and E are higher magnification views of the squares in panels B and C, respectively. (A) The greater omentum (GO) is separated from the transverse mesocolon. (B, C) The GO extends inferiorly from the stomach and is fused to the transverse mesocolon. However, the fusion plane cannot be identified (stars in panels D and E). (B) The mesocolon (arrows) is separated from the retroperitoneal structures below the pancreas (P). Scale bars=1 mm. AD, adrenal; J, jejunum; LO, lesser omentum; LY, lymph node; P, pancreas; PC, peritoneal cavity; SMV, superior mesentery vein; ST, stomach; TC, transverse colon. |
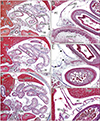 | Fig. 3Horizontal sections of a specimen of crown-rump length 48 mm. Panels A and C show the uppermost and lowermost sites in the figure, respectively. Intervals are 0.4 mm between panels A and B and 1.8 mm between panels B and C. Panels D and E are higher magnification views of squares in panel A, and panel F is a higher magnification of the square in panel C. The transverse colon (TC) is attached to the anterior surface of the pylorus as well as the superior or first portion of the duodenum (D1; A, B). The TC pushes up the greater omentum (GO; A, D), and the jejunum (J) pushes up the transverse mesocolon (A, E). The omentum is fused with the mesocolon (stars in panel E), and double laminae of the omentum extend anteriorly into the liver and enclose the umbilical vein (C, F). Panels A–C (D–E) were prepared at the same magnifications. Scale bars=1 mm. AC, ascending colon; AD, adrenal; AO, aorta; AP, appendix; CL, caudate lobe of the liver; D2, descending or second portion of the duodenum; DC, descending colon; GB, gallbladder; IVC, inferior vena cava; LK, left kidney; P, pancreas; PC, peritoneal cavity; SMA, superior mesentery artery; ST, stomach; UV, umbilical vein. |
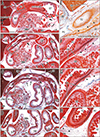 | Fig. 4Horizontal sections of a specimen of crown-rump length 90 mm. Panels A and D show the uppermost and lowermost sites in the figure, respectively. Intervals between panels A and B, B and C, and C and D are 1.3 mm, 0.7 mm and 1.0 mm, respectively. Panels E–H are higher magnification views of squares in panels A–D, respectively. The transverse colon (TC) is attached to the anterior surface of the stomach (ST) as well as the superior or first portion of the duodenum (A, E). The jejunum (J) pushes up the transverse mesocolon (A). The greater omentum (GO) extends widely along the liver (B, C). The TC is tightly attached to the pylorus, the descending portion of the duodenum (D2), the pancreas (P) and the right kidney (RK) without specific borders (triangles in panels E–H). The transverse mesocolon is indicated by arrows (A–D). The arrowheads in panels A–C indicate a hole in the mesocolon. Panels A–D (E–H) were prepared at the same magnifications. Scale bars=1 mm. AD, adrenal; AO, aorta; D1, superior or first portion of the duodenum; D4, ascending or fourth portion or the duodenum; DC, descending colon; GB, gallbladder; LK, left kidney; P, pancreas; papilla, major duodenal papilla; PC, peritoneal cavity; SMA, superior mesentery artery; TC, transverse colon. |
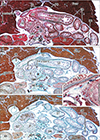 | Fig. 5Horizontal sections of a specimen of crown-rump length 97 mm. Panels A and C show the uppermost and lowermost sites in the figure, respectively. Intervals between panels A and B and B and C are 0.8 mm and 1.6 mm, respectively. The insert between panels B and C displays a higher magnification view of the irregular square in panel B. The transverse colon (TC) is attached to the anterior surface of the stomach (ST) as well as the superior or first portion of the duodenum (D1; A, B). The jejunum (J) pushes up the transverse mesocolon (panel B and inset). The greater omentum (GO) is fused with the mesocolon (stars in the inset and panel C) and the colon is tightly attached to the stomach without any specific borders (triangles in the insert). A major part of the GO is present along the left lobe of the liver (A–C). Panels A–C were prepared at the same magnification. Scale bars=1 mm. AD, adrenal; AO, aorta; D2, descending or second portion or the duodenum; D4, ascending or fourth portion of the duodenum; DC, descending colon; GB, gallbladder; LK, left kidney; P, pancreas; papilla, major duodenal papilla; PC, peritoneal cavity; RK, right kidney; SMA, superior mesentery artery; TC, transverse colon. |
 | Fig. 6Inter-individual differences in the macroscopic morphologies of the greater omentum. Panels A (of a fetus of crown-rump length [CRL] 258 mm) and B (of a fetus of CRL 264 mm) display the greater omentum (GO) extending leftward and inferiorly. The morphology of the wavy jejunum and ileum was similar in these fetuses. Panel C (of a fetus of CRL 272 mm) shows rightward shifting of the omentum, with the asterisk in panel C indicating an injury during dissection. RK, right kidney; ST, stomach; TC, transverse colon; UV, umbilical vein. |
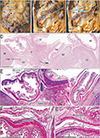 | Fig. 7Macroscopic and histologic observations of a specimen of crown-rump length 274 mm. Panel A shows the greater omentum (GO) extending inferiorly from the stomach and covering almost the entire jejunum and ileum. The transverse colon (TC) is located under the transparent omentum, and the right part of the TC appears wavy (star) near the pylorus. Panel B shows the transverse mesocolon reflected upward after removal of most parts of the ileum and jejunum ( J). Panel C shows a cut line of the transverse mesocolon (arrows). The mesocolon is attached to the inferior aspect of the pylorus. Panel D shows the topographic anatomy of the upper abdomen, including the TC adjacent to the stomach (ST); this sectional plane is indicated by a blue line in panel C. Panel E shows the right anterior part of panel D, and panels F and G are higher magnification views of squares in panel E. The GO appears to cover the transverse mesocolon from the anterior side, with both separated by a narrow space (circles in panels F and G). Similarly, the mesocolon is separated from the peritoneum covering the second portion of the duodenum (D2; G). Scale bars=5 mm (D), 1 mm (E–G). AC, ascending colon; AD, adrenal; AP, appendix; DC, descending colon; LK, left kidney; P, pancreas; papilla, major duodenal papilla; RK, right kidney; SMA, superior mesentery artery; UV, umbilical vein. |
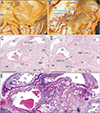 | Fig. 8Macroscopic and histologic observations of a specimen of crown-rump length 262 mm. Panel A is an anterior view after removal of major parts of the liver and greater omentum (GO), showing an attachment between the transverse colon (TC) and the stomach (ST). Panel B displays a cut surface of the transverse mesocolon (arrows) along the pancreas (P) after removal of major parts of the ST, TC, jejunum ( J) and ileum. Panels C and D are views along the horizontal planes indicated by the two blue lines in panel B. Panel C shows attachment of the TC to the anterior aspects of the pylorus and duodenum, and panel D shows attachment of the TC to the duodenum and right kidney (RK). Panel E is a higher magnification view of the central part of panel C. The TC is separated from the duodenum by a narrow peritoneal space (small circles). The duodenum, from the descending (D2) to the ascending (D4) portion, is seen in a single horizontal section (D). Scale bars=1 mm. AC, ascending colon; AO, aorta; AP, appendix; D3, horizontal or third portion of the duodenum; DC, descending colon; IVC, inferior vena cava; SMA, superior mesentery artery; UV, umbilical vein. |
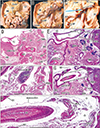 | Fig. 9Macroscopic and histologic observations of a specimen of crown-rump length 282 mm. Panels A displays the upper abdomen after removal of almost the entire liver and cutting of the greater omentum (GO). Panel B exhibits the transverse colon (TC) reflected upward after removal of most parts of the ileum and jejunum (J). Panel C shows partial removal of the TC. Panel D shows the topographical anatomy of the upper abdomen, including the TC, between the descending portion of the duodenum (D2) and the stomach (ST); this sectional plane is indicated by a blue line in panel C. Panel E shows the anterior part of panel E, panel F shows a higher magnification view of the square in panel E, and panel G shows a plane 1 mm above panel E. A comparison of panels E and G shows that the TC appears to push upward the superior portion of the duodenum (D1). Panel H is a higher magnification view of the square in panel G. Panels F and H both contain branches of the colic and gastric arteries (MCA, RGEA). The circles in panels F and H indicate a border between the GO and the mesocolon. The duodenum, from the descending to the ascending portion, is seen in a single horizontal section (D). Scale bars=5 mm (D), 1 mm (E–H). AC, ascending colon; AD, adrenal; AP, appendix; D3, horizontal or third portion of the duodenum; DC, descending colon; GDA, gastroduodenal artery; IVC, inferior vena cava; LK, left kidney; MCA, middle colonic artery; P, pancreas; papilla, major duodenal papilla; RGEA, right gastroepiploic artery; RK, right kidney; SMA, superior mesentery artery; UV, umbilical vein. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download