Introduction
Materials and Methods
 is the HA mass attenuation coefficient at energy E, and (ρHA)[µ(E)ρ]
is the HA mass attenuation coefficient at energy E, and (ρHA)[µ(E)ρ] is the linear attenuation coefficient of the HA.317
is the linear attenuation coefficient of the HA.317
Journal List > Imaging Sci Dent > v.49(4) > 1139930
 is the HA mass attenuation coefficient at energy E, and (ρHA)[µ(E)ρ]
is the HA mass attenuation coefficient at energy E, and (ρHA)[µ(E)ρ] is the linear attenuation coefficient of the HA.317
is the linear attenuation coefficient of the HA.317
 | Fig. 1A bone density calibration phantom (QRM, Moehrendorf, Germany) contained 3 inserts of different densities (0, 100, and 200 mg of hydroxyapatite [HA]/cm3). As a base material for the 3 inserts, CTWATER® (QRM, Moehrendorf, Germany) was used. CTWATER® is a solid water-equivalent plastic offering the same X-ray attenuation properties as water. In this study, CTWATER® represents 0 mg of HA/cm3. HA 100 and HA 200 represent 100 mg and 200 mg, respectively, of HA/cm3. |
 | Fig. 2On the cross-sectional image of the phantom, the mean Hounsfield (HU) is measured via placing a circular region of interests (ROIs) in the center of the HA 100 insert. Min: minimum value, Max: maximum value, Avg: average value, SD: standard deviation. |
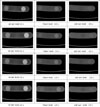 | Fig. 3Virtual monochromatic images of hydroxyapatite inserts of various densities obtained with dual-energy computed tomography show the differences in the image contrast and image noise depending on energy level, reconstruction kernel, and rotation time (seconds). |
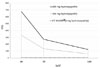 | Fig. 4Hounsfield units (HU) for CTWATER® (0 mg), 100, and 200 mg of hydroxyapatite/cm3 according to energy level (40, 70, or 140 keV) with a body regular 40 kernel and a 0.5 second tube rotation time. Virtually no difference in HU is observed according to the energy level of CTWATER®. The HU value increases with hydroxyapatite density, but decreases markedly with increasing energy levels. |
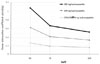 | Fig. 5Linear attenuation coefficient µ (cm2/g) of CTWATER® (0), 100, and 200 mg of hydroxyapatite/cm3 according to energy level (40, 70, or 140 keV). Virtually no difference is observed in the linear attenuation coefficient according to the energy level of CTWATER®. The linear attenuation coefficient increases with hydroxyapatite density but decreases with increasing energy level. |


Dae-Kyo Jeong 
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8102-5119
Sam-Sun Lee 
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7223-9262
Jo-Eun Kim 
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0218-5304
Kyung-Hoe Huh 
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8771-0392
Won-Jin Yi 
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5977-6634
Min-Suk Heo 
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3406-0645
Soon-Chul Choi 
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9846-9936