INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Cell culture
Tissue preparation
The atlas of non-coding RNA in cancer (TANRIC) analysis
Subcellular fraction
Lentivirus transduction and cell transfection
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay
Lactate production assay
Extracellular acidification rate (ECAR)
Biotin pull down assay
qRT-PCR
Western blotting
Immunoprecipitation (IP)-semiquantitative PCR
Luciferase reporter assay
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Increased level of lncRNA-SNHG7 was detected in breast cancer tissue and cell lines
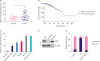 | Figure 1Elevated expression of lncRNA-SNHG7 in breast cancer. (A) qRT-PCR for the abundance of lncRNA-SNHG7 in 30 pairs of breast cancer samples. (B) The correlation between overall survival and lncRNA-SNHG7 level in breast cancer obtained by TANRIC. (C) qRT-PCR for the abundance of lncRNA-SNHG7 in normal breast cells and various breast cancer cell lines. (D) Western-blot analysis for PARP and β-actin in the nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively, in MCF-7 cells. Data shown represent 3 independent experiments. (E) Nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of MCF-7 cells were subjected to qRT-PCR analysis.Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation.
lncRNA = long non-coding RNA; qRT-PCR = quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; PARP = poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase.
*p < 0.05, †p < 0.01, ‡p < 0.001.
|
LncRNA-SNHG7 promoted proliferation of breast cancer cells
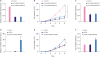 | Figure 2LncRNA-SNHG7 promotes proliferation of breast cancer cells. (A, B) MCF-7 cells were transduced with sh-ctrl or sh-lncRNA-SNHG7 lentivirus. LncRNA-SNHG7 level was assessed by qRT-PCR, and then cells were subjected to cell proliferation analysis. (C) MCF-7 cells were transduced with sh-ctrl or sh-lncRNA-SNHG7 lentivirus and then subjected to cell viability assays. (D, E) MCF-7 cells were transduced with pCDH or pCDH-lncRNA-SNHG7 lentivirus. LncRNA-SNHG7 level was assessed by qRT-PCR, and then the cells were subjected to cell proliferation analysis. (F) MCF-7 cells were transduced with pCDH or pCDH-lncRNA-SNHG7 lentivirus, and then subjected to cell viability assays.Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation.
lncRNA = long non-coding RNA; qRT-PCR = quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; sh = short hairpin.
*p < 0.05, †p < 0.01.
|
Knockdown of lncRNA-SNHG7 inhibited glycolysis in breast cancer cells
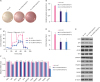 | Figure 3Knocking down lncRNA-SNHG7 inhibits glycolysis in breast cancer cells. (A) MCF-7 cells expressing either control shRNA or lncRNA-SNHG7 shRNA were cultured for 24 hours. Acidification of the culture medium was evaluated by visually inspecting the color of the medium. (B) MCF-7 cells expressing either control shRNA or lncRNA-SNHG7 shRNA were cultured for 24 hours. Levels of lactate in the culture medium were then measured and normalized to cell number. (C, D) ECAR was measured in MCF-7 cells expressing either control shRNA or lncRNA-SNHG7 shRNA by Seahorse XF assays. (E, F) Western blotting and qRT-PCR analysis of glycolysis enzymes in MCF-7 cells expressing either control shRNA or lncRNA-SNHG7 shRNA.Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation.
lncRNA = long non-coding RNA; sh = short hairpin; ECAR = extracellular acidification rate; qRT-PCR = quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
*p < 0.01.
|
LncRNA-SNHG7 regulated LDHA level by targeting miR-34a-5p
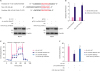 | Figure 4LncRNA-SNHG7 acts as a target of miR-34a-5p to increase LDHA level. (A) Illustration of the base pairing between miR-34a-5p and lncRNA-SNHG7. The base pairing between miR-34a-5p and LDHA 3′UTR is also shown. (B) Lysates from MCF-7 cells were incubated with in vitro-synthesized biotin-labeled sense or antisense DNA probes against lncRNA-SNHG7 for biotin pull-down assay, followed by qRT-PCR analysis to examine miR-34a-5p and lncRNA-SNHG7 level. (C) MCF-7 were transduced with sh-ctrl or sh-lncRNA-SNHG7 lentivirus followed by miR-34a-5p inhibitor or negative control transfection. Western blot analysis of LDHA and β-actin. (D) MCF-7 were transduced with pCDH or pCDH-lncRNA-SNHG7 lentivirus followed by miR-34a-5p mimics or negative control transfection. Western blot analysis of LDHA and β-actin. (E, F) MCF-7 cells were transduced with sh-ctrl or sh-lncRNA-SNHG7 lentivirus followed by miR-34a-5p inhibitor or negative control transfection. ECAR was measured by Seahorse XF assays.Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation.
lncRNA = long non-coding RNA; sh = short hairpin; ECAR = extracellular acidification rate; qRT-PCR = quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; ns = not significant; LDHA = lactate dehydrogenase A; 3′UTR = 3′ untranslated region.
*p < 0.01.
|
LncRNA-SNHG7 is a direct transcriptional target of c-Myc
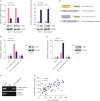 | Figure 5LncRNA-SNHG7 is a direct transcriptional target of c-Myc. (A, B) MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells were transduced with sh-ctrl or sh-c-Myc lentivirus, pCDH or pCDH-c-Myc lentivirus. Western blot analysis of c-Myc and β-actin. LncRNA-SNHG7 level was assessed by quantitative RT-PCR. (C) Schematic illustration of the consensus c-Myc binding sites in lncRNA-SNHG7 gene promoter. The wild-type and mutant binding sites are shown in the open boxes. The corresponding pGL3-based luciferase reporter constructs generated are shown. (D, E) MCF-7 were transduced with sh-ctrl or sh-c-Myc lentivirus, pCDH or pCDH-c-Myc lentivirus followed by transfection with the indicated pGL3-based luciferase reporter constructs. The reporter activity was measured 24 hours post-transfection, and plotted after normalizing with the Renilla luciferase activity. Western blot analysis of c-Myc and β-actin. (F) MCF-7 cells lysates were analyzed by ChIP assay using anti-c-Myc or IgG rabbit antibody. The ChIP products were amplified by semi-quantitative RT-PCR. (G) Correlation analyses conducted between c-Myc and lncRNA-SNHG7 in breast cancers (n = 50 biologically independent samples). Pearson correlation coefficients (r) and p-values.Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation.
lncRNA = long non-coding RNA; sh = short hairpin; RT-PCR = real-time polymerase chain reaction; NS = not significant; GAPDH = glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IgG = immunoglobulin G.
*p < 0.05, † p < 0.01.
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download