Abstract
Diabetic foot ulcers can progress to the point where amputation is needed, and so these ulcers require active treatment. Skin grafts or flaps can be performed for coverage of this type of ulcer. Local flap surgery is relatively easy to perform and good results have been previously reported. We performed single-lobed rotation flap on 5 cases of forefoot ulcer around the site of weight bearing. The location of the foot ulcers was the medial part of the first metatarsophalangeal joint in all the patients. The mean size of the defect was 4.70 cm2. Managing of ulcers, controlling of diabetes and infection, and improving of peripheral blood flow were performed before surgery. In two cases, infection progressed to the articular cartilage and so metatarsophalangeal joint fusions were performed simultaneously. All the cases were completely transplanted. There was no recurrence of the ulcers, and all the patients were able to walk.
Figures and Tables
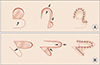 | Figure 1Single-lobed rotation flap. (A) Type 1: the excision of the defect is arranged so that right angle (90-degree angle) is formed at the base of the defect for the start of the flap. (B) Type 2: the excision of the defect is arranged so that 60-degree angle is formed at the base of the defect. |
 | Figure 3(A) Skin closure of round defect. Preoperative photograph showing a round defect on medial side of first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ). (B) Postoperative photograph showing a well covered defect of the MTPJ by single-lobed rotation flap, type 1. (C) Postoperative photograph showing good appearance of the foot at the final follow-up. |
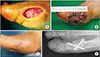 | Figure 4(A) Skin closure of oval defect. Preoperative photograph showing an oval defect on medial side of first metatarsophalangeal joint (MTPJ). (B) Postoperative photograph showing a well covered defect of the MTPJ by single-lobed rotation flap, type 2. (C) Postoperative photograph showing good appearance of the foot at the final follow-up. (D) Plain radiograph showing arthrodesis of the 1st MTPJ with headless screws. |
References
1. Seo DK, Lee HS. Management of diabetic foot ulcer. J Korean Foot Ankle Soc. 2014; 18:1–7. DOI: 10.14193/jkfas.2014.18.1.1.

2. Kwon DJ, Lee YB, Ahn HC. Use of acellular allograft dermal matrix (Alloderm®) and split-thickness skin graft for treatment of diabetic foot ulcer. J Korean Musculoskelet Transplant Soc. 2007; 7:86–91.
3. Wagner FW. A classification and treatment program for diabetics, neuropathic and dysvascular foot problems. Instr Course Lect. 1979; 28:143–165.
4. Schrudde J, Petrovici V. The use of slide-swing plasty in closing skin defects: a clinical study based on 1,308 cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1981; 67:467–481. DOI: 10.1097/00006534-198104000-00008.
5. Kim JM, Kim DY, Woo JT, Kim SW, Yang IM, Kim JW, et al. A clinical study on the diabetic foot lesions. J Korean Diabetes Assoc. 1993; 17:387–394.
6. Song JY, Kim KS, Ko SH, Choi YS, Chung YR, Kim HD, et al. Reconstruction of diabetic foot ulcers by regional flap surgery. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2003; 38:301–304. DOI: 10.4055/jkoa.2003.38.3.301.

7. Kadukammakal J, Yau S, Urbas W. Assessment of partial first-ray resections and their tendency to progress to transmetatarsal amputations: a retrospective study. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2012; 102:412–416. DOI: 10.7547/1020412.

8. Steed DL, Donohoe D, Webster MW, Lindsley L. Effect of extensive debridement and treatment on the healing of diabetic foot ulcers Diabetic Ulcer Study Group. J Am Coll Surg. 1996; 183:61–64.
9. Randon C, Vermassen F, Jacobs B, De Ryck F, Van Landuyt K, Taes Y. Outcome of arterial reconstruction and free-flap coverage in diabetic foot ulcers: long-term results. World J Surg. 2010; 34:177–184. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-009-0250-9.

10. Laing PW, Cogley DI, Klenerman L. Neuropathic foot ulceration treated by total contact casts. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992; 74:133–136. DOI: 10.1302/0301-620X.74B1.1732242.

11. Nam SC, Han SH, Lim SH, Hong YS, Won JH, Bae JI, et al. Factors affecting the validity of ankle-brachial index in the diagnosis of peripheral arterial obstructive disease. Angiology. 2010; 61:392–396. DOI: 10.1177/0003319709348295.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download