Abstract
Background and Objectives
Recently, the prevalence of olfactory dysfunction has increased with pollution and population adequate. Treatment by olfactory training has been suggested as an alternative method, but there is no protocol for olfactory training with odorants familiar to Koreans. Also, no studies have analyzed the effects of individual preference in terms of personalized medicine. This study compared the effectiveness of olfactory training according to patient odor preference.
Materials and Methods
The prospective study was performed in patients with olfactory dysfunction and used 8 total odorants. After a survey of preference for the odorants, patients were divided into two groups, one group performed olfactory training with 3 preferred odorants, whereas the other group performed training with odorants they did not prefer. Also, the effects of olfactory training in the two groups were compared by KVSS threshold, discrimination, identification score, and subjective VAS score of olfaction. Olfactory testing was performed before and after training for 4 and 12 weeks.
Results
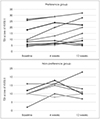
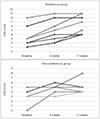
There was no demographic difference between the two groups. After olfactory training, the preference group showed statistically significant improvement in threshold, identification, TDI score, and VAS score. Conversely, there was no significant change of olfactory function in the non-preference group.
Figures and Tables
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean Government (NRF-2017R1C1B1007454).
References
1. Hummel T, Rissom K, Reden J, Hahner A, Weidenbecher M, Huttenbrink KB. Effects of olfactory training in patients with olfactory loss. The Laryngoscope. 2009; 119:496–499.

2. Lee WH, Wee JH, Kim DK, Rhee CS, Lee CH, Ahn S, et al. Prevalence of subjective olfactory dysfunction and its risk factors: korean national health and nutrition examination survey. PloS one. 2013; 8:e62725.

3. Upadhyay UD, Holbrook EH. Olfactory loss as a result of toxic exposure. Otolaryngologic Clinics of North America. 2004; 37:1185–1207.

6. Schriever VA, Merkonidis C, Gupta N, Hummel C, Hummel T. Treatment of smell loss with systemic methylprednisolone. Rhinology. 2012; 50:284–289.

7. Henkin RI, Velicu I, Schmidt L. An open-label controlled trial of theophylline for treatment of patients with hyposmia. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 2009; 337:396–406.

8. Heilmann S, Just T, Goktas O, Hauswald B, Huttenbrink KB, Hummel T. [Effects of systemic or topical administration of corticosteroids and vitamin B in patients with olfactory loss]. Laryngo-Rhino-Otologie. 2004; 83:729–734.
9. Lyckholm L, Heddinger SP, Parker G, Coyne PJ, Ramakrishnan V, Smith TJ, et al. A randomized, placebo controlled trial of oral zinc for chemotherapy-related taste and smell disorders. Journal of Pain & Palliative Care Pharmacotherapy. 2012; 26:111–114.

10. Choi SH, Kim ST, Park HM, Moon KH, Jung JH, Cha HE. Analysis of Characteristics and Steroid Effects in Olfactory Dysfunction Patients. Journal of Rhinology. 2016; 23:39.

11. Damm M, Pikart LK, Reimann H, Burkert S, Göktas Ö, Haxel B, et al. Olfactory training is helpful in postinfectious olfactory loss: a randomized, controlled, multicenter study. The Laryngoscope. 2014; 124:826–831.

12. Pekala K, Chandra RK, Turner JH. Efficacy of olfactory training in patients with olfactory loss: a systematic review and meta-analysis. International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology. 2016; 6:299–307.

13. Sorokowska A, Drechsler E, Karwowski M, Hummel T. Effects of olfactory training: a meta-analysis. Rhinology. 2017; 55:17–26.

14. Haehner A, Tosch C, Wolz M, Klingelhoefer L, Fauser M, Storch A, et al. Olfactory training in patients with Parkinson's disease. PloS one. 2013; 8:e61680.

15. Wang L, Chen L, Jacob T. Evidence for peripheral plasticity in human odour response. The Journal of Physiology. 2004; 554:236–244.

16. Soudry Y, Lemogne C, Malinvaud D, Consoli SM, Bonfils P. Olfactory system and emotion: common substrates. European Annals of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Diseases. 2011; 128:18–23.

17. Storbeck J, Maswood R. Happiness increases verbal and spatial working memory capacity where sadness does not: Emotion, working memory and executive control. Cognition & Emotion. 2016; 30:925–938.

18. Konstantinidis I, Tsakiropoulou E, Constantinidis J. Long term effects of olfactory training in patients with post-infectious olfactory loss. Rhinology. 2016; 54:170–175.

19. Ajou. Olfactory training video, Youtube. 2017. Accessed 28 March 2019. https://www.youtu.be/3BofTli6itg.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download