Abstract
Background and Objectives
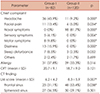
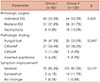
Magnetic resonance imaging is commonly used in neurologic examination of intracranial problems. Incidental abnormalities in the sinonasal area without clinical symptoms have been reported in about 38% of patients.
Subjects and Method
The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical characteristics of sinonasal surgical patients transferred from neurologists. Two hundred two patients were enrolled and divided into two groups. Group I patients had been directly transferred from the Neurology Department within 1 month after neurologic evaluation. Group II patients directly visited the Rhinology Department without a neurologic evaluation within the prior year. Both groups had received sinonasal endoscopic surgery or septal surgery. Clinical characteristics, pathologic findings, and surgical results were compared between groups.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Patel K. , Chavda SV, Violaris N, Pahor AL. Incidental paranasal sinus inflammatory changes in a British population. J Laryngol Otol. 1996; 110:649–651.

2. Wani MK, Ruckenstein MJ, Parikh S. Magnetic resonance imaging of the paranasal sinuses: incidental abnormalities and their relationship to patient symptoms. J Otolaryngol. 2001; 30:257–262.

3. Zinreich SJ, Kennedy DW, Malat J, Curtin HD, Epstein JI, Huff LC, et al. Fungal sinusitis: diagnosis with CT and MR imaging. Radiology. 1988; 169:439–444.

4. Fawaz SA, Ezzat WF, Salman MI. Sensitivity and specificity of computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of isolated sphenoid sinus diseases. Laryngoscope. 2011; 121:1584–1589.

5. Lin SH, Ho CY. Paranasal sinus pathologies in patients presenting with headache as the primary symptom. Cephalalgia. 2006; 26:423–427.

6. Lal D, Rounds AB, Rank MA, Divekar R. Clinical and 22-item Sino-Nasal Outcome Test symptom patterns in primary headache disorder patients presenting to otolaryngologists with “sinus” headaches, pain or pressure. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015; 5:408–416.

7. Welge-Luessen A, Hauser R, Schmid N, Kappos L, Probst R. Endonasal surgery for contact point headaches: a 10-year longitudinal study. Laryngoscope. 2003; 113:2151–2156.

8. Yazici ZM, Cabalar M, Sayin I, Kayhan FT, Gurer E, Yayla V. Rhinologic evaluation in patients with primary headache. J Craniofac Surg. 2010; 21:1688–1691.

9. Mohebbi A, Memari F, Mohebbi S. Endonasal endoscopic management of contact point headache and diagnostic criteria. Headache. 2010; 50:242–248.

10. Tosun F, Gerek M, Ozkaptan Y. Nasal surgery for contact point headaches. Headache. 2000; 40:237–240.

11. Cho JH, Jeong YS, Lee YJ, Hong SC, Yoon JH, Kim JK. The Korean version of the Sniffin’ stick (KVSS) test and its validity in comparison with the cross-cultural smell identification test (CC-SIT). Auris Nasus Larynx. 2009; 36:280–286.

12. Senocak D, Senocak M. Sinonasal pathology and headaches. Rhinology. 2004; 42:8–14.
13. Eweiss AZ, Lund VJ, Barlow J, Rose G. Do patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps suffer with facial pain? Rhinology. 2013; 51:231–235.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download