Abstract
Background and Objectives
Most thyroid cancers progress slowly, have high survival rates, and have good prognosis. Therefore, the management of patients with thyroid cancer should be viewed from a long-term perspective, taking into account a return to normal social life. Cancer patients have a higher risk of unemployment than the general population, and so unemployment can be an economic problem for thyroid cancer patients. However, there have been few studies on factors affecting return to work in thyroid cancer patients. The purpose of this study is to investigate occupational changes and the period of leave of absence for patients with thyroid cancer and to identify factors that affect the return to work after surgery.
Materials and Methods
A total of 427 questionnaires of thyroid cancer patients were used for the analysis. The occupational changes and sick leave periods were analyzed according to general characteristics, disease-related characteristics, and side effects.
Results
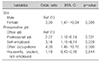
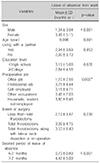
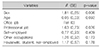
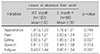
The factors related to occupational change and leave of absence in thyroid cancer patients were sex and type of occupation. Women had more occupational changes and longer leave of absence than men, office workers had the least change in occupation, and professional workers had a longer period of sick leave. Fatigue was the primary side effect that affected the leave of absence.
Figures and Tables
References
1. Kilfoy BA, Zheng T, Holford TR, Han X, Ward MH, Sjodin A, et al. International patterns and trends in thyroid cancer incidence, 1973-2002. Cancer Causes Control. 2009; 20(5):525–531.

2. Lim H, Devesa SS, Sosa JA, Check D, Kitahara CM. Trends in thyroid cancer incidence and mortality in the United States, 1974–2013. JAMA. 2017; 317(13):1338–1348.

3. Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Seo HG, Lee JS. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival and prevalence in 2010. Cancer Res Treat. 2013; 45(1):1–14.

4. National Cancer Center Korea [Internet]. National Cancer Registration Statistics 2014. cited January 17, 2017. Available from: URL: http://ncc.re.kr/cancerStatsView.ncc?bbsnum=397&searchKey=total&searchValue=&pageNum=1.
5. Abdullah MI, Junit SM, Ng KL, Jayapalan JJ, Karikalan B, Hashim OH. Papillary thyroid cancer: genetic alterations and molecular biomarker investigations. Int J Med Sci. 2019; 16(3):450–460.

6. Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Kramer JL, Rowland JH, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016; 66(4):271–289.

7. Wang T, Jiang M, Ren Y, Liu Q, Zhao G, Cao C, et al. Health-related quality of life of community thyroid cancer survivors in Hangzhou, China. Thyroid. 2018; 28(8):1013–1023.

8. Singer S, Husson O, Tomaszewska IM, Locati LD, Kiyota N, Scheidemann-Wesp U, et al. Quality-of-life priorities in patients with thyroid cancer: a multinational European Organisation for research and treatment of cancer phase I study. Thyroid. 2016; 26(11):1605–1613.

9. Tan LG, Nan L, Thumboo J, Sundram F, Tan LK. Health-related quality of life in thyroid cancer survivors. Laryngoscope. 2007; 117(3):507–510.

10. Suzuki M. Quality of life, uncertainty, and perceived involvement in decision making in patients with head and neck cancer. Oncol Nurs Forum. 2012; 39(6):541–548.

11. Lupoli GA, Fonderico F, Colarusso S, Panico A, Cavallo A, Di Micco L, et al. Current management of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Med Sci Monit. 2005; 11(12):RA368–RA373.
12. Yoo SH, Yun YH, Park S, Kim YA, Park SY, Bae DS, et al. The correlates of unemployment and its association with quality of life in cervical cancer survivors. J Gynecol Oncol. 2013; 24(4):367–375.

13. Mols F, Thong MS, Vreugdenhil G, van de Poll-Franse LV. Long-term cancer survivors experience work changes after diagnosis: results of a population-based study. Psychooncology. 2009; 18(12):1252–1260.

14. Buckwalter AE, Karnell LH, Smith RB, Christensen AJ, Funk GF. Patient-reported factors associated with discontinuing employment following head and neck cancer treatment. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007; 133(5):464–470.

15. Verdonck-de Leeuw IM, van Bleek WJ, Leemans CR, de Bree R. Employment and return to work in head and neck cancer survivors. Oral Oncol. 2010; 46(1):56–60.

16. Mehnert A. Employment and work-related issues in cancer survivors. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011; 77(2):109–130.

17. Ross L, Petersen MA, Johnsen AT, Lundstroem LH, Carlsen K, Groenvold M. Factors associated with Danish cancer patients' return to work. A report from the population-based study 'The Cancer Patient's World'. Cancer Epidemiol. 2012; 36(2):222–229.

18. Shin KC. Policy measures for consolidating sickness benefits. Korean Soc Secur Stud. 2011; 27(1):136–156.
19. Bouknight RR, Bradley CJ, Luo Z. Correlates of return to work for breast cancer survivors. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24(3):345–353.

20. Balak F, Roelen CA, Koopmans PC, Ten Berge EE, Groothoff JW. Return to work after early-stage breast cancer: a cohort study into the effects of treatment and cancer-related symptoms. J Occup Rehabil. 2008; 18(3):267–272.

21. Spelten ER, Verbeek JH, Uitterhoeve AL, Ansink AC, van der Lelie J, de Reijke TM, et al. Cancer, fatigue and the return of patients to work-a prospective cohort study. Eur J Cancer. 2003; 39(11):1562–1567.

22. Han KT, Park EC, Kim SJ, Jang SI, Shin J, Kim CO, et al. Factors affecting the quality of life of Korean cancer survivors who return to the workplace. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014; 15(20):8783–8788.

23. Marino P, Teyssier LS, Malavolti L, Le Corroller-Soriano AG. Sex differences in the return-to-work process of cancer survivors 2 years after diagnosis: results from a large French population-based sample. J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31(10):1277–1284.

24. Torp S, Nielsen RA, Fossa SD, Gudbergsson SB, Dahl AA. Change in employment status of 5-year cancer survivors. Eur J Public Health. 2013; 23(1):116–122.

25. Ahn E, Cho J, Shin DW, Park BW, Ahn SH, Noh DY, et al. Impact of breast cancer diagnosis and treatment on work-related life and factors affecting them. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 116(3):609–616.

26. van Muijen P, Weevers NL, Snels IA, Duijts SF, Bruinvels DJ, Schellart AJ, et al. Predictors of return to work and employment in cancer survivors: a systematic review. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2013; 22(2):144–160.

27. Drolet M, Maunsell E, Brisson J, Brisson C, Masse B, Deschenes L. Not working 3 years after breast cancer: predictors in a population-based study. J Clin Oncol. 2005; 23(33):8305–8312.

28. Pryce J, Munir F, Haslam C. Cancer survivorship and work: symptoms, supervisor response, co-worker disclosure and work adjustment. J Occup Rehabil. 2007; 17(1):83–92.

29. Arfi A, Baffert S, Soilly AL, Huchon C, Reyal F, Asselain B, et al. Determinants of return at work of breast cancer patients: results from the OPTISOINS01 French prospective study. BMJ Open. 2018; 8(5):e020276.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download