Abstract
Purpose
To determine the clinical features, imaging findings and possible causes of pneumatosis intestinalis (PI) in thoracic disorder patients.
Materials and Methods
From 2005 to 2017, Among 62 PI patients, four of PI related with thoracic disease (6%) were identified. Medical records were reviewed to determine the clinical presentation, laboratory findings and treatment at the time of presentation of PI. Two experienced chest radiologists reviewed all imaging studies and recorded specific findings for each patient.
Results
The causative thoracic diseases for each four patient were severe asthma, emphysema and airway obstruction. The imaging appearance of PI, including the involved bowel segment and pattern of the air, were divided into two mesenteric vascular territories; three of our cases showed linear pattern of PI located in the ascending & proximal transverse colon and the fourth case (lung cancer) had bubbly and cystic PI in the distal transverse and descending colon. All of the remaining 3 patients, except one patient who had not been followed up, improved within 1 month by conservative treatment.
References
1. Keene JG. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis and intramural intestinal gas.J Emerg Med. 1989; 7:645–650.
2. Thompson WM, Ho L, Marroquin C. Pneumatosis intestinalis and pneumoperitoneum after bilateral lung transplantation in adults.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011; 196:W273–W279.
3. Greenstein AJ, Nguyen SQ, Berlin A, Corona J, Lee J, Wong E, et al. Pneumatosis intestinalis in adults: management, surgical indications, and risk factors for mortality.J Gastrointest Surg. 2007; 11:1268–1274.
4. Hawn MT, Canon CL, Lockhart ME, Gonzalez QH, Shore G, Bondora A, et al. Serum lactic acid determines the outcomes of CT diagnosis of pneumatosis of the gastrointestinal tract.Am Surg. 2004; 70:19–23. ; discussion 23–24.
5. Doumit M, Saloojee N, Seppala R. Pneumatosis intestinalis in a patient with chronic bronchiectasis.Can J Gastroenterol. 2008; 22:847–850.
6. Pear BL. Pneumatosis intestinalis: a review.Radiology. 1998; 207:13–19.
7. Choi JY, Cho SB, Kim HH, Lee IH, Lee HY, Kang HS, et al. Pneumatosis intestinalis complicated by pneumoperitoneum in a patient with asthma.Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2014; 77:219–222.
8. Ling FY, Zafar AM, Angel LF, Mumbower AL. Benign pneumatosis intestinalis after bilateral lung transplantation. BMJ Case Rep. 2015; 2015:bcr2015210701.

9. Faria LD, Anjos CH, Fernandes GD, Carvalho IF. Pneumatosis intestinalis after etoposide-based chemotherapy in a patient with metastatic small cell lung cancer: successful conservative management of a rare condition. Einstein (Sao Paulo). 2016; 14:420–422.

10. Iwasaku M, Yoshioka H, Korogi Y, Kunimasa K, Nishiyama A, Nagai H, et al. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis after gefitinib therapy for pulmonary adenocarcinoma.J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7:257.
11. Maeda A, Nakata M, Shimizu K, Yukawa T, Saisho S, Okita R. Pneumatosis intestinalis after gefitinib therapy for pulmonary adenocarcinoma: a case report. World J Surg Oncol. 2016; 14:175.

12. Hsueh KC, Tsou SS, Tan KT. Pneumatosis intestinalis and pneumoperitoneum on computed tomography: beware of non-therapeutic laparotomy. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2011; 3:86–88.

13. St Peter SD, Abbas MA, Kelly KA. The spectrum of pneumatosis intestinalis.Arch Surg. 2003; 138:68–75.
Fig. 1.
A 43-year-old woman with severe asthma. A. Chest X-ray posterior-anterior views shows pneumomediastinum (arrows) with PI (arrowheads) on initial chest radiography. B. These lesions are completely resolved after 1 month with conservative treatment. C, D. Transverse and coronal abdomen CT scans (2.0-mm slice thickness) obtained with lung and wide window show linear patterns of PI involving from the cecum to proximal transverse colon.
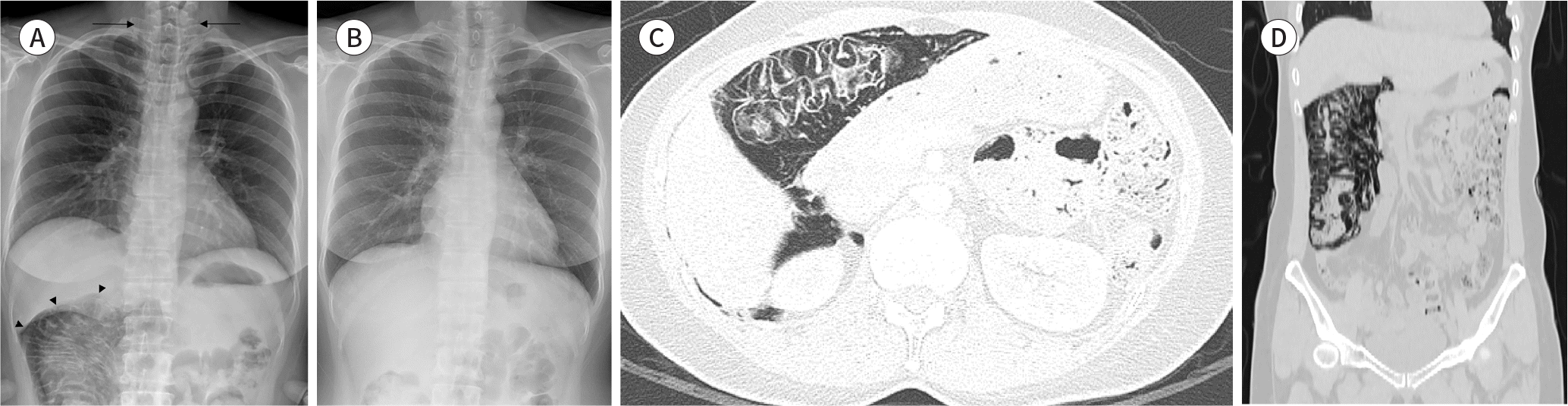
Fig. 2.
A 79-year-old man with lung cancer. A. Chest X-ray posterior-anterior views shows decreased volume of left lung with mass and a nodule in right lower lung zone. B. Transverse contrast-enhanced CT scan obtained with mediastinal window shows a large necrotic mass causing nearly complete stenosis of left main bronchus (arrow). C. Coronal chest CT scan obtained with lung setting shows cystic and bubbly appearance of pneumatosis intestinalis involving distal trans-
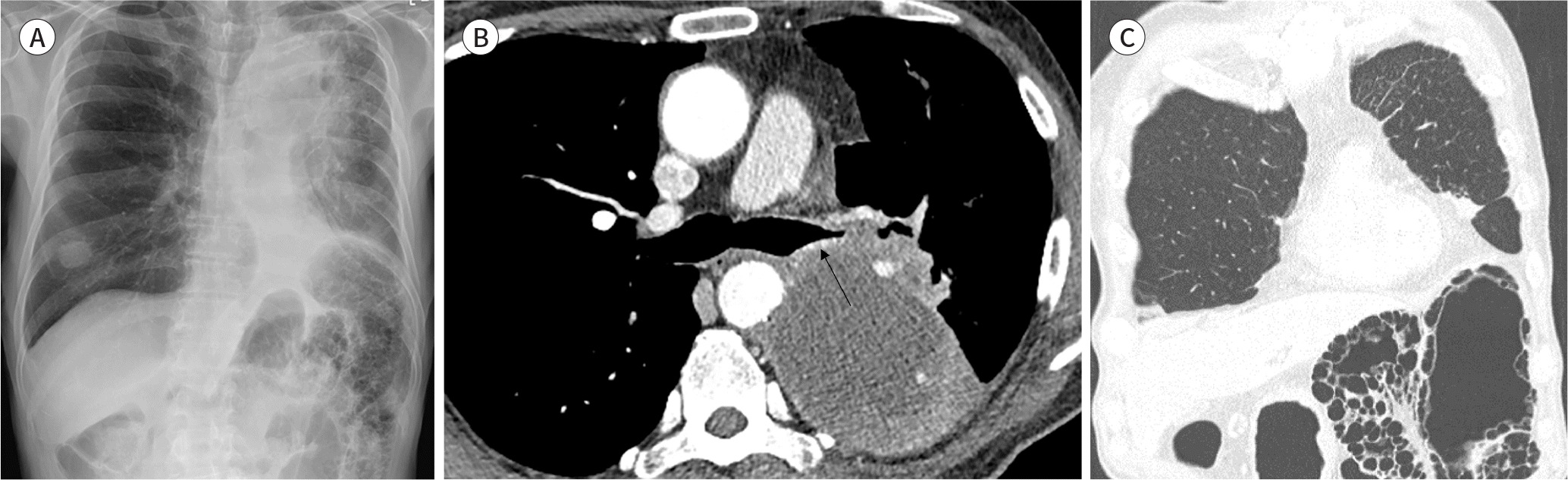
Fig. 3.
A 71-year-old man with choking by food material and aspiration pneumonia. with residual food and mucoid impaction in the left main bronchus. B, C. Transverse and coronal abdomen CT scan with bone window shows a linear pattern of pneumatosis intestinalis in the ascending colon. A. Transverse chest CT scan obtained with lung window taken after removal of aspirated food material shows atelectasis of left lower lobe
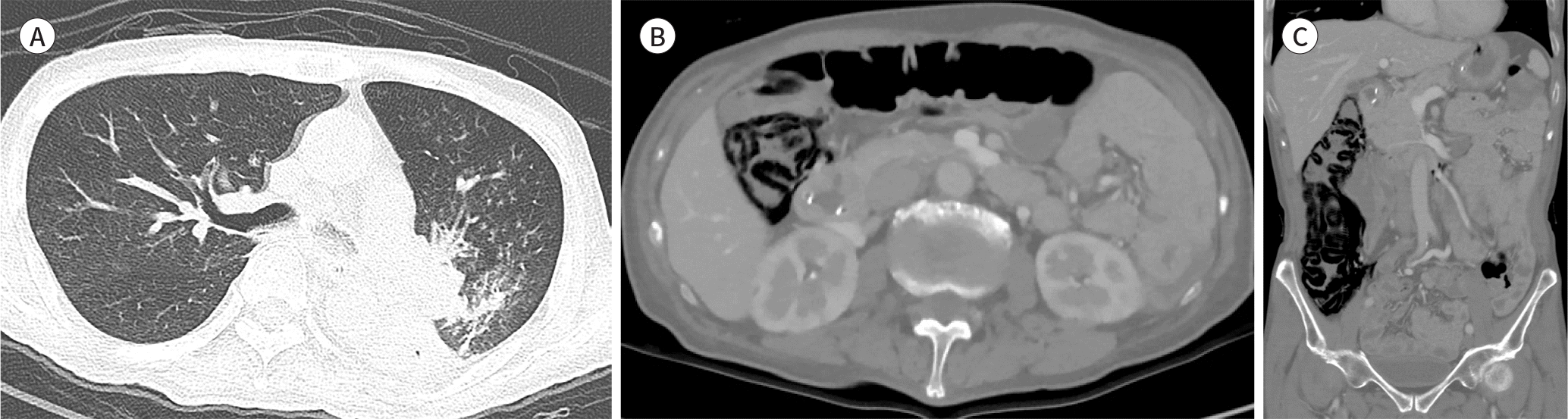
Table 1.
Clinical Findings in Four Patients with Pneumatosis
Table 2.
Radiologic Findings in Four Patients with PI
| No. | Chest | Abdomen CT | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chest X-Ray | CT | Pneumoperitoneum | PI | Distribution | Pattern | Extra-Luminal Gas Distribution | |||
| Thorax | Pneumoperitoneum | PI | |||||||
| 1 | Pneumomediastinum PI | Pneumomediastinum Asthma | Y | Y | Y | Y | Cecum to proximal transverse colon | Linear | Retroperitoneum, liver bare area |
| 2 | Lung mass PI | Lung cancer in left lung Pulmonary emphysema | N | Y | N∗ | Y∗ | Distal transverse colon to descending colon∗ | Bubbly and cystic∗ | N∗ |
| 3 | –PI | Stable TB Pulmonary emphysema | Y | Y | Y | Y | Cecum to hepatic flexure of colon | Linear | Paracolic gutter |
| 4 | Atelectasis in BLLZ PI | Atelectasis in LLL Partial atelectasis in RLL | L N | Y | Y | Y | Cecum to hepatic flexure of colon | Linear | Small bowel mesentery around right psoas muscle, anterior aspect of aorta and IVC |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download