Abstract
초록
Figures and Tables
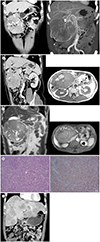 | Fig. 1Gastric paraganglioma in a 61-year-old man.
A. Coronal portal-phase CT shows a large hypervascular mass, with heterogeneous enhancement in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. The large mass from the gastric antrum (arrow) has a tortuous peritumoral and intratumoral vessels (arrowheads) (left image). Coronal maximal intensity projection CT reveals peritumoral and intratumoral vessels arising in the right gastric, gastroduodenal, gastroepiploic (arrowheads), and superior mesenteric arteries (right image).
B. Multiplanar reformatted CT shows that the large mass arises from the gastric antrum (arrow) (left image). Axial T1-weighted in-phase MRI shows hyperintense lesions, which indicate hemorrhage (arrow) (right image).
C. Coronal T2-weighted MRI reveals a large heterogeneous hyperintense mass with internal signal void vessels (arrows). Axial T1-weighted fat-suppressed contrast-enhanced MRI shows a heterogeneous enhancing mass with hypervascularity in the gastric antrum.
D. Photomicrograph shows epithelioid (arrow) and mesenchymal cells (arrowhead) with some portion of nested pattern (dotted circle) (left, hematoxylin and eosin, × 100). Immunohistochemistry shows tumor cells positive for neuron-specific enolase (right, × 200).
E. In the 1-year follow-up, axial portal-phase CT shows multiple enhancing liver masses, confirmed as metastases from the paraganglioma on liver biopsy. Surgical clips after mass excision from the gastric antrum are shown (arrow).
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download