This article has been corrected. See "Corrigendum: Failure of Intramedullary Nailing for Subtrochanteric Atypical Femoral Fractures Caused by Endosteal Cortical Thickening" in Volume 33 on page 63.
Abstract
Purpose
Recent literature has noted incidences of subtrochanteric atypical femoral fractures (AFFs) in patients who have taken long-term bisphosphonates (BPs). Most cases of subtrochanteric AFFs have been treated with intramedullary nailing and cases of delayed union have been reported. On the other hand, there is no data available on the complications associated with endosteal thickening or cortical thickening. This study evaluated the results of surgical treatment according to the endosteal thickening of the lateral cortex in subtrochanteric AFFs.
Materials and Methods
Investigation was performed at the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Jeju National University Hospital. The study consisted of patients with subtrochanteric AFFs, defined by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ASBMR) major criteria, who underwent intramedullary nailing from March 2012 to October 2014. The cases were categorized into two groups based on the presence of endosteal thickening. The evaluation included the demographic data, radiographic data of initial reduction state, and duration of BPs.
Results
The demographic data and duration of BPs were similar in the two groups. On the other hand, varus reduction (Group I: 12.5% vs. Group II: 78.9%; p=0.001), delayed union (Group I: 0% vs. Group II: 70.0%; p=0.003), nonunion (Group I: 0% vs. Group II: 47.4%; p=0.017), and union time (Group I: 5.5 months vs. Group II: 8.3 months; p<0.001) were significantly different in the two groups.
Go to : 
References
1. Lloyd AA, Gludovatz B, Riedel C, et al. Atypical fracture with longterm bisphosphonate therapy is associated with altered cortical composition and reduced fracture resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 114:8722–8727. 2017.

2. Koh A, Guerado E, Giannoudis PV. Atypical femoral fractures related to bisphosphonate treatment: issues and controversies related to their surgical management. Bone Joint J. 99:295–302. 2017.
3. Gedmintas L, Solomon DH, Kim SC. Bisphosphonates and risk of subtrochanteric, femoral shaft, and atypical femur fracture: a systematic review and metaanalysis. J Bone Miner Res. 28:1729–1737. 2013.

4. Shane E, Burr D, Abrahamsen B, et al. Atypical subtrochanteric and diaphyseal femoral fractures: second report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res. 29:1–23. 2014.

5. Schilcher J, Sandberg O, Isaksson H, Aspenberg P. Histology of 8 atypical femoral fractures: remodeling but no healing. Acta Orthop. 85:280–286. 2014.
6. Schilcher J. Epidemiology, radiology and histology of atypical femoral fractures: development of understanding. Acta Orthop. 84:1–26. 2013.
7. Goh SK, Yang KY, Koh JS, et al. Subtrochanteric insufficiency fractures in patients on alendronate therapy: a caution. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 89:349–353. 2007.
8. Koh JS, Goh SK, Png MA, Kwek EB, Howe TS. Femoral cortical stress lesions in longterm bisphosphonate therapy: a herald of impending fracture? J Orthop Trauma. 24:75–81. 2010.

9. Neviaser AS, Lane JM, Lenart BA, Edobor-Osula F, Lorich DG. Low-energy femoral shaft fractures associated with alendronate use. J Orthop Trauma. 22:346–350. 2008.

10. Balach T, Baldwin PC, Intravia J. Atypical femur fractures associated with diphosphonate use. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 23:550–557. 2015.

11. Zheng N, Tang N, Qin L. Atypical femoral fractures and current management. J Orthop Translat. 7:7–22. 2016.

12. Banffy MB, Vrahas MS, Ready JE, Abraham JA. Nonoperative versus prophylactic treatment of bisphosphonateassociated femoral stress fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 469:2028–2034. 2011.

13. Egol KA, Park JH, Rosenberg ZS, Peck V, Tejwani NC. Healing delayed but generally reliable after bisphosphonateassociated complete femur fractures treated with IM nails. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 472:2728–2734. 2014.

14. Owens WD, Felts JA, Spitznagel EL Jr. ASA physical status classifications: a study of consistency of ratings. Anesthesiology. 49:239–243. 1978.
15. LeBlanc ES, Rosales AG, Black DM, et al. Evaluating atypical features of femur fractures: how change in radiological criteria influenced incidence and demography of atypical femur fractures in a community setting. J Bone Miner Res. 32:2304–2314. 2017.

16. Yau WP, Chiu KY, Tang WM, Ng TP. Coronal bowing of the femur and tibia in Chinese: its incidence and effects on total knee arthroplasty planning. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 15:32–36. 2007.

17. Corrales LA, Morshed S, Bhandari M, Miclau T 3rd. Variability in the assessment of fracture-healing in orthopaedic trauma studies. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 90:1862–1868. 2008.

19. Hierholzer C, Sama D, Toro JB, Peterson M, Helfet DL. Plate fixation of ununited humeral shaft fractures: effect of type of bone graft on healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 88:1442–1447. 2006.
20. Shukla S, Johnston P, Ahmad MA, Wynn-Jones H, Patel AD, Walton NP. Outcome of traumatic subtrochanteric femoral fractures fixed using cephalomedullary nails. Injury. 38:1286–1293. 2007.

21. Kraemer WJ, Hearn TC, Powell JN, Mahomed N. Fixation of segmental subtrochanteric fractures. A biomechanical study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 332:71–79. 1996.
23. Einhorn TA, Bogdan Y, Tornetta P 3rd. Bisphosphonate-associated fractures of the femur: pathophysiology and treatment. J Orthop Trauma. 28:433–438. 2014.
24. Phillips HK, Harrison SJ, Akrawi H, Sidhom SA. Retrospective review of patients with atypical bisphosphonate related proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 48:1159–1164. 2017.

25. Lee PC, Hsieh PH, Yu SW, Shiao CW, Kao HK, Wu CC. Biologic plating versus intramedullary nailing for comminuted subtrochanteric fractures in young adults: a prospective, randomized study of 66 cases. J Trauma. 63:1283–1291. 2007.

26. Oh CW, Kim JJ, Byun YS, et al. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis of subtrochanteric femur fractures with a locking plate: a prospective series of 20 fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 129:1659–1665. 2009.

27. Prasarn ML, Ahn J, Helfet DL, Lane JM, Lorich DG. Bisphosphonate-associated femur fractures have high complication rates with operative fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 470:2295–2301. 2012.

28. Spinelli MS, Marini E, Daolio PA, Piccioli A. Atypical diaphyseal femoral fractures: considerations on surgical technique. Injury. 50(Suppl 2):S65–S69. 2019.

29. Errani C, Mavrogenis AF, Cevolani L, et al. Treatment for long bone metastases based on a systematic literature review. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 27:205–211. 2017.

30. Piccioli A, Maccauro G, Spinelli MS, Biagini R, Rossi B. Bone metastases of unknown origin: epidemiology and principles of management. J Orthop Traumatol. 16:81–86. 2015.

31. Yang KH, Kim JR, Park J. Nonisthmal femoral shaft nonunion as a risk factor for exchange nailing failure. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 72:E60–E64. 2012.

32. Bogdan Y, Tornetta P 3rd, Einhorn TA, et al. Healing time and complications in operatively treated atypical femur fractures associated with bisphosphonate use: a multicenter retrospective cohort. J Orthop Trauma. 30:177–181. 2016.
33. Weil YA, Rivkin G, Safran O, Liebergall M, Foldes AJ. The outcome of surgically treated femur fractures associated with longterm bisphosphonate use. J Trauma. 71:186–190. 2011.

34. Teo BJ, Koh JS, Goh SK, Png MA, Chua DT, Howe TS. Postoperative outcomes of atypical femoral subtrochanteric fracture in patients on bisphosphonate therapy. Bone Joint J. 96-B:658–664. 2014.

36. Lim HS, Kim CK, Park YS, Moon YW, Lim SJ, Kim SM. Factors associated with increased healing time in complete femoral fractures after longterm bisphosphonate therapy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 98:1978–1987. 2016.

37. Lenart BA, Neviaser AS, Lyman S, et al. Association of low-energy femoral fractures with prolonged bisphosphonate use: a case control study. Osteoporos Int. 20:1353–1362. 2009.

38. Giusti A, Hamdy NA, Dekkers OM, Ramautar SR, Dijkstra S, Papapoulos SE. Atypical fractures and bisphosphonate therapy: a cohort study of patients with femoral fracture with radiographic adjudication of fracture site and features. Bone. 48:966–971. 2011.

Go to : 
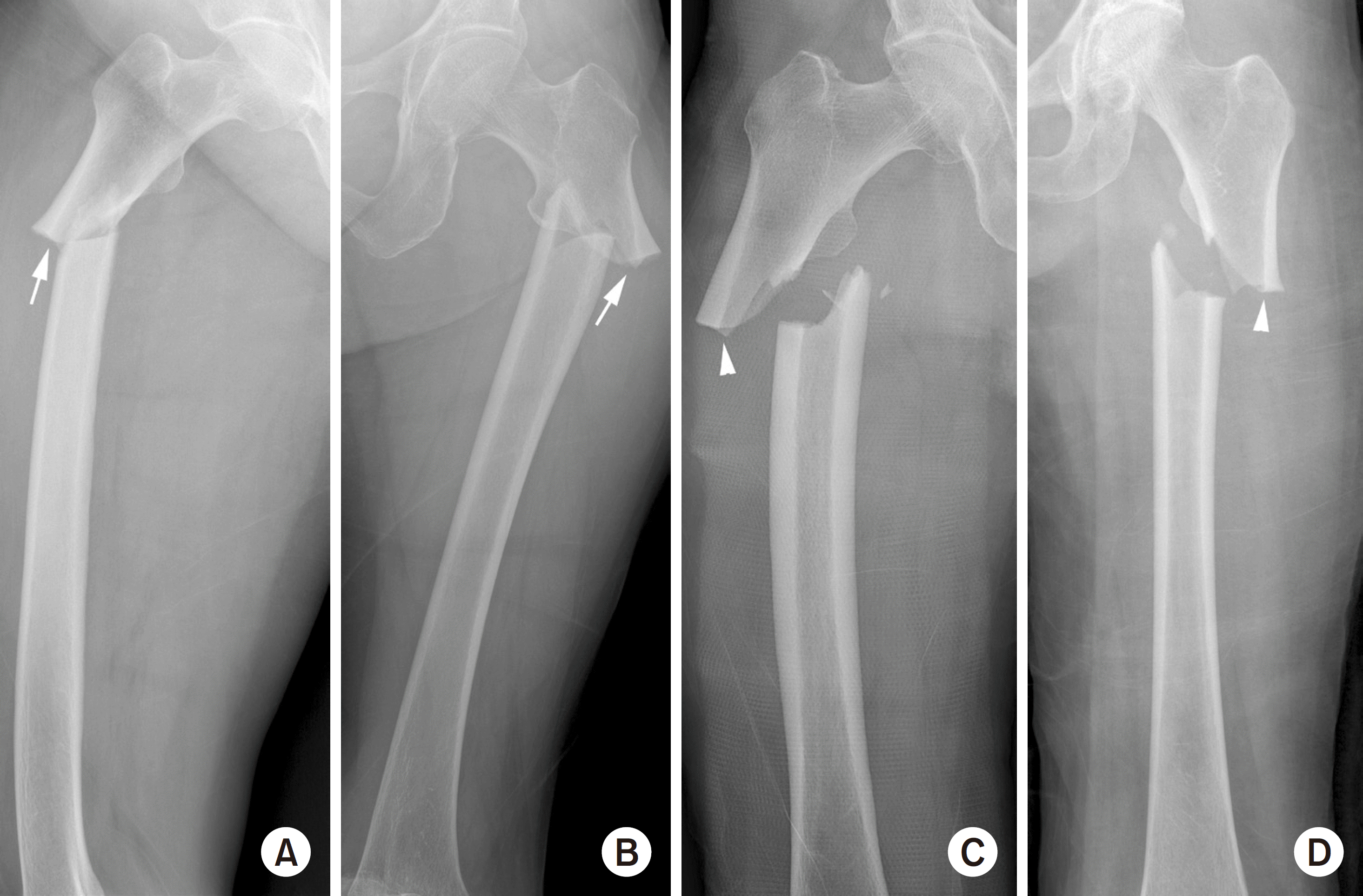 | Fig. 1.(A) Atypical subtrochanteric fracture in the right femur, antero-posterior (AP) view. Endosteal thickening of the lateral cortex at the fracture site is depicted by a white arrow. (B) Atypical subtrochanteric fracture in the left femur, AP view. Endosteal thickening of the lateral cortex at the fracture site is depicted by a white arrow. (C) Atypical subtrochanteric fracture in the right femur, AP view. The lateral cortex thickness at the fracture site does not differ from the distal part (white arrowhead). (D) Atypical subtrochanteric fracture in the left femur AP view. Periosteal thickening of the lateral cortex is observed, but endosteal cortical thickening is not observed (white arrowhead). |
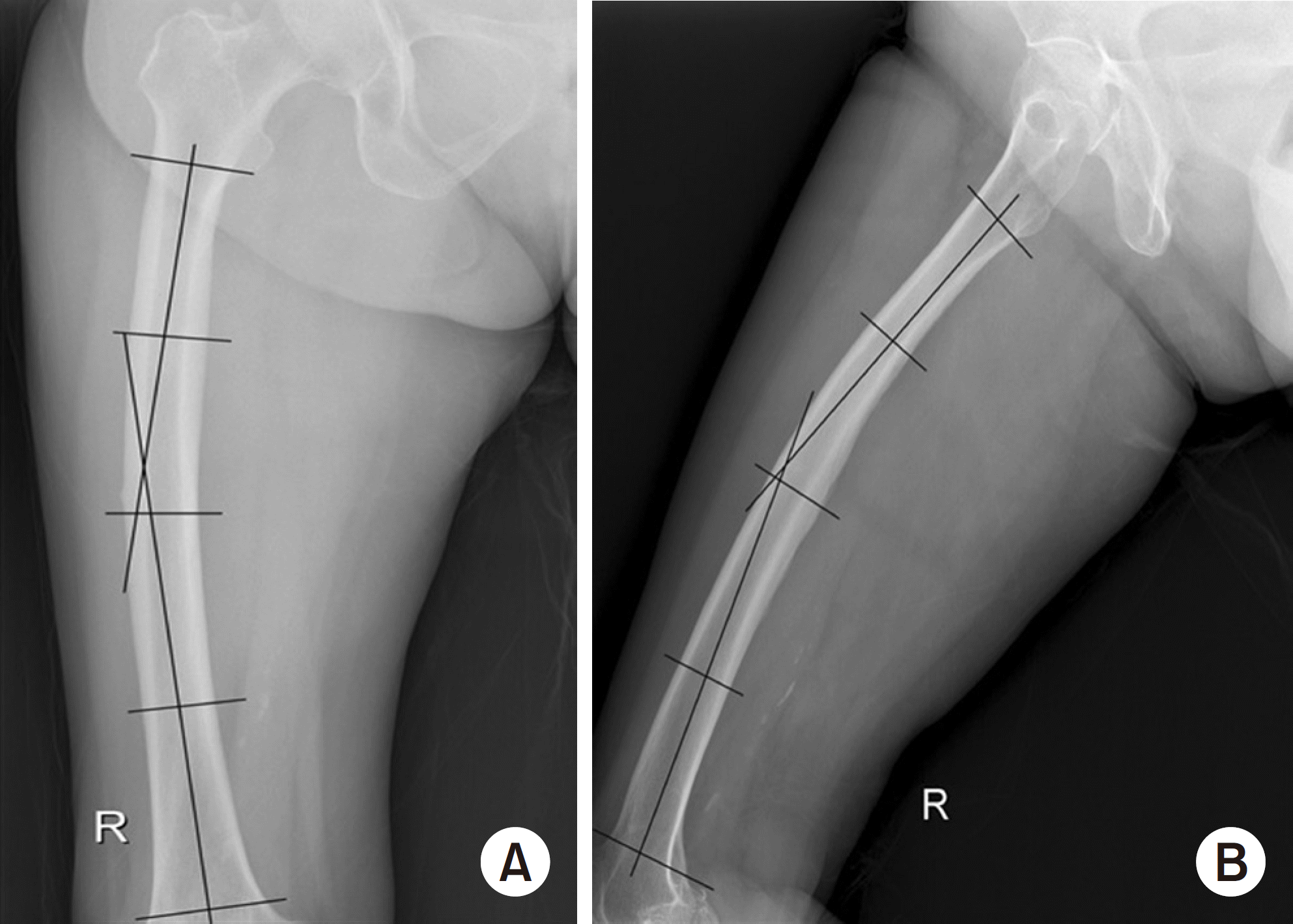 | Fig. 2.(A) Coronal plane femoral bowing was measured as the angulation between the proximal and distal quarters of the femoral diaphysis in the femur antero-posterior view. (B) Sagittal plane femoral bowing was measured as the angulation between the proximal and distal quarters of the femoral diaphysis in the femur lateral view. |
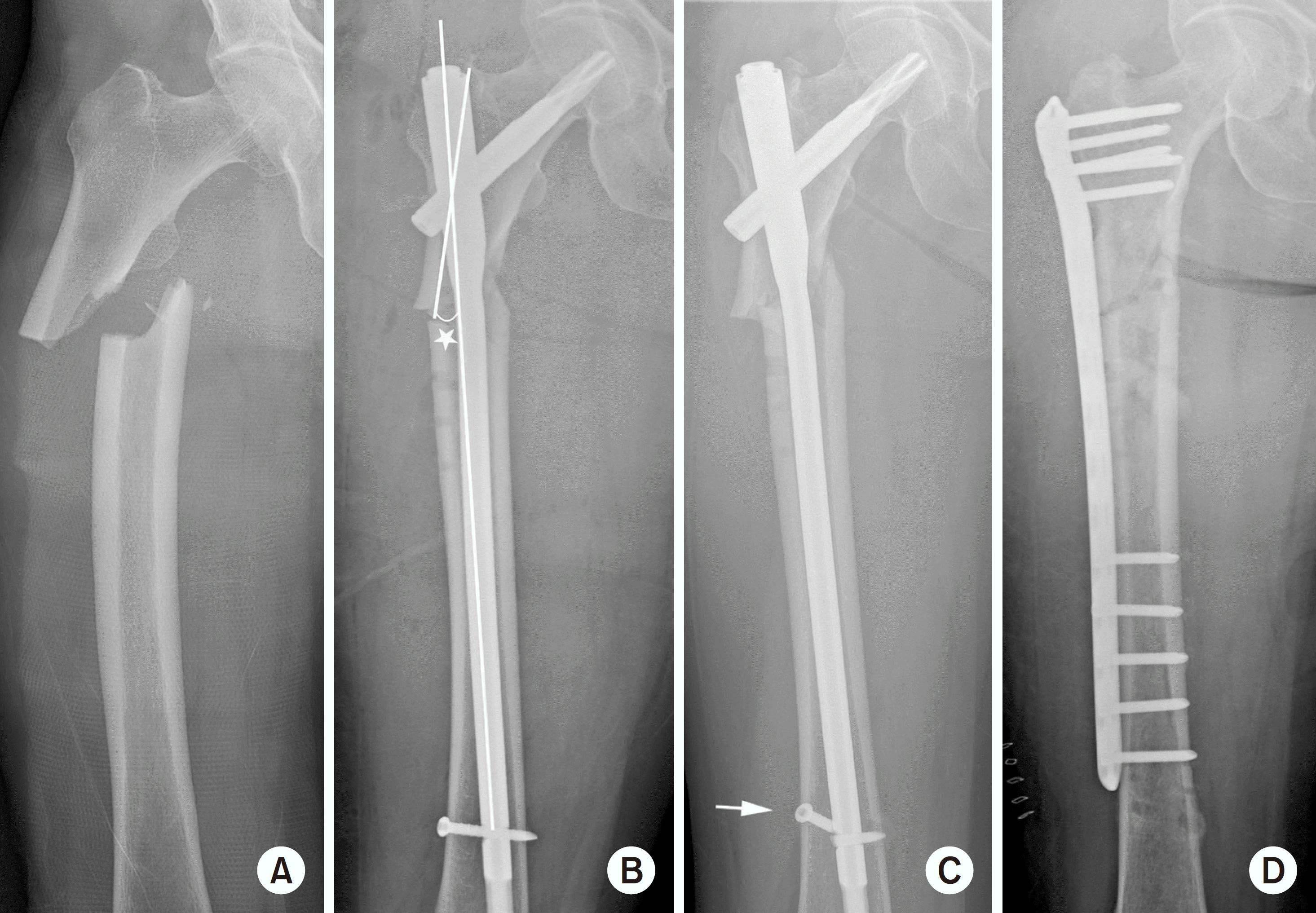
 | Fig. 3.(A, B) Atypical subtrochanteric fracture in the left femur, anteroposterior (AP) and lateral (LAT) views. Shortening, varus deformation, and total displacement of fracture were observed. Endosteal thickening of the lateral cortex at the fracture site is depicted by a white arrowhead. (C, D) These are left femur AP and LAT views taken nine months after surgery. The atypical subtrochanteric fracture was fixed with a long cephalo-medullary nail and cerclage cable. Callus formation was observed at four cortical regions (medial, lateral, anterior and posterior cortex) in the fracture site marked with white arrows. |
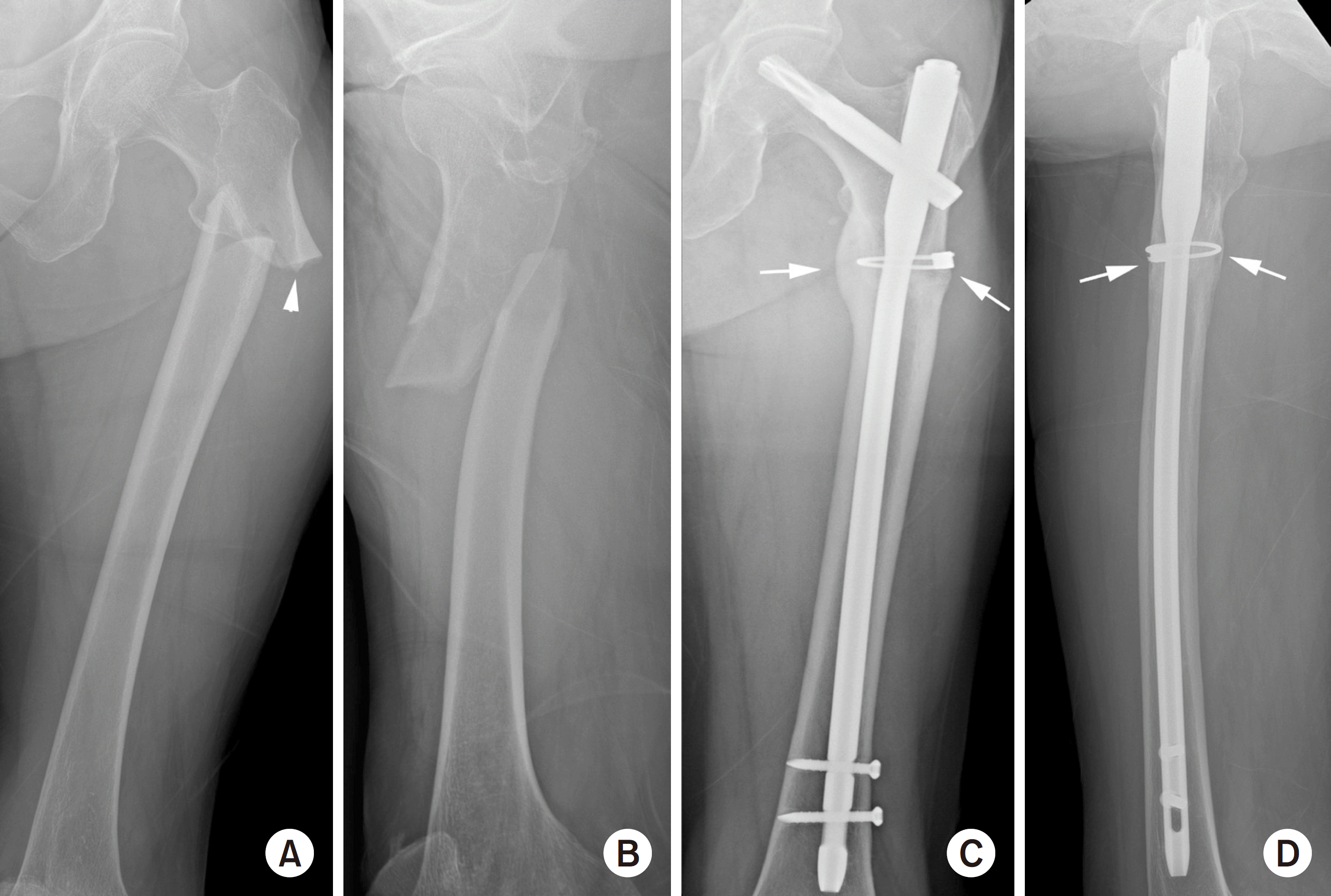
 | Fig. 4.(A) Atypical subtrochanteric fracture in the right femur, antero-posterior (AP) view. (B) This is right femur AP view taken immediately after surgery. The atypical subtrochanteric fracture was fixed with a long cephalo-medullary nail. Compared to the contralateral side, 13 varus reduction was observed (asterisk). (C) This is the right femur AP view taken 12 months after surgery. Breakage of the distal interlocking screw (white arrow) and nonunion of the fracture are observed. (D) This is the right femur AP view after performing re-operation using a plate. |
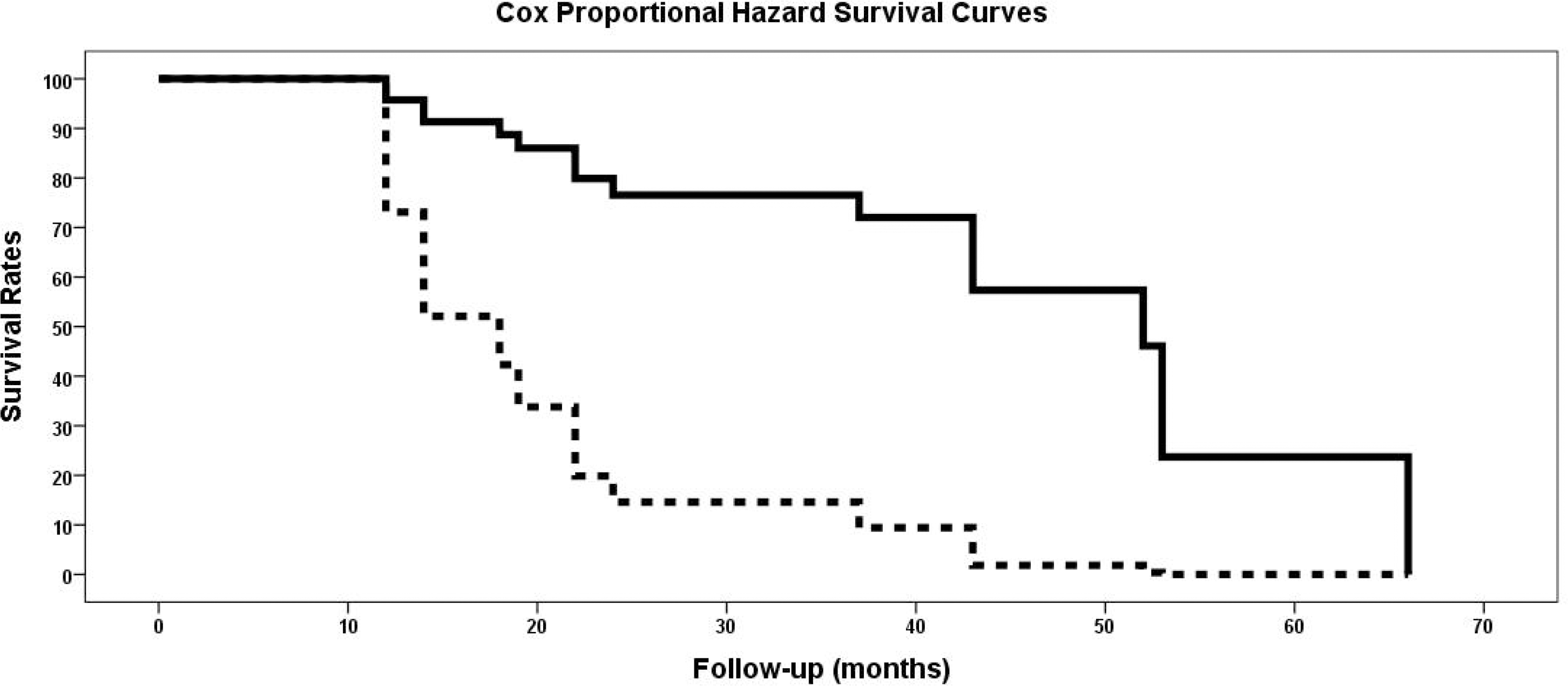 | Fig. 5.Cox proportional hazard survival curve (solid line: Group I, dotted line: Group II). |
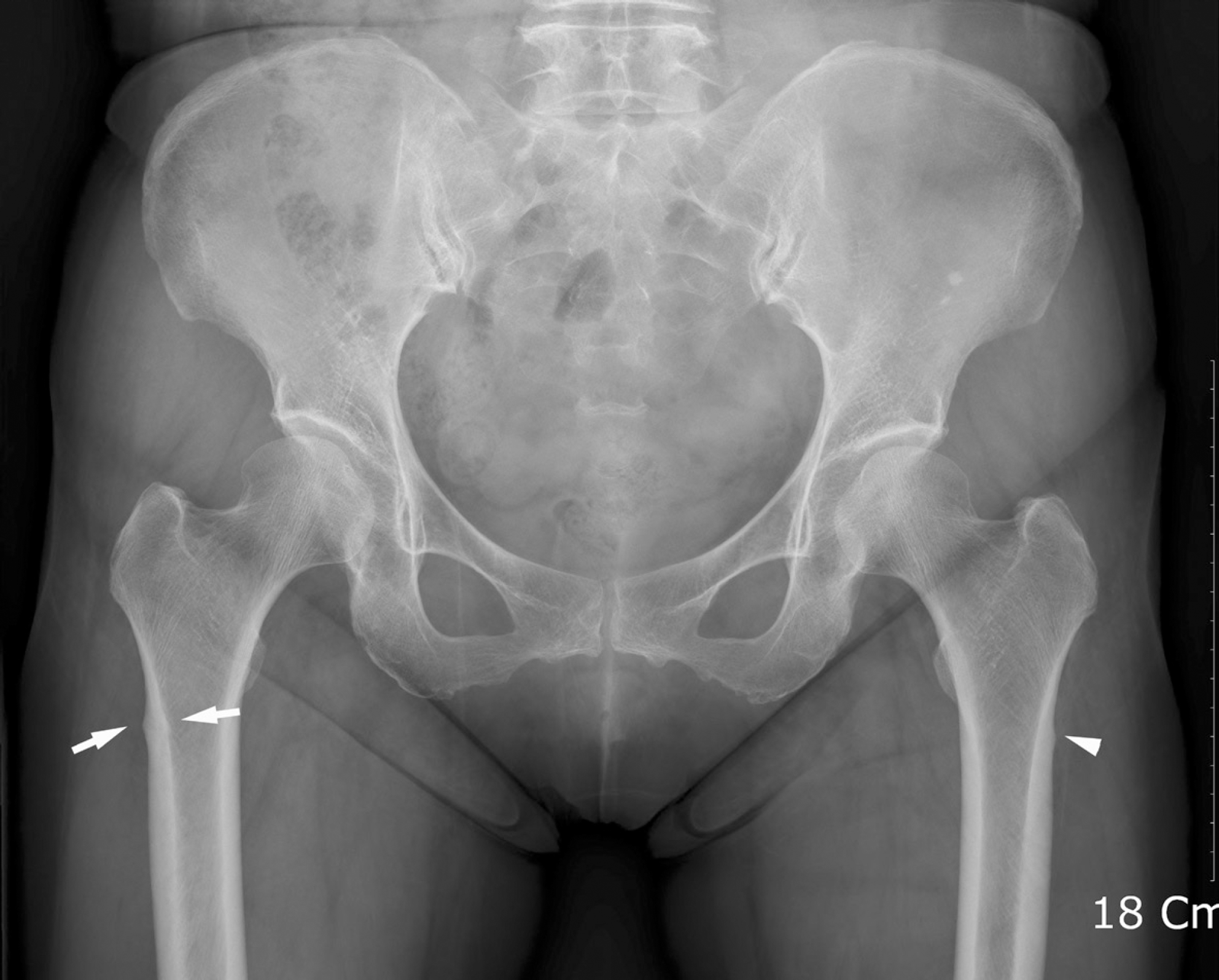 | Fig. 6.Thickening of the lateral cortex in subtrochanteric regions is observed on both sides. On the right side, both endosteal and periosteal cortical thickening are observed (white arrows), whereas only periosteal cortical thickening is observed on the left side (white arrowhead). |
Table 1.
ASBMR Task Force 2013 Case Definition of AFFs Baseline4
Table 2.
Baseline Characteristics Included in This Study
Table 3.
Intra- and Postoperative Variables
Table 4.
Univariate Comparison between the Union and Nonunion Groups




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download