Abstract
Intussusception is a rare disease in adults. A demonstrable etiology is found in approximately 85% of all cases, and approximately 40% of them are caused by malignant tumors. A 65-year-old patient visited the outpatient department with mild abdominal pain without other symptoms. The initial laboratory test and simple X-ray showed normal findings. CT revealed intussusception in the ileocecal area. The initial colonoscopic biopsy revealed atypical cells. Follow up colonoscopy showed spontaneous reduction of the intussusception. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma was suspected in the second colonoscopic biopsy. An elective operation was performed. This case reports a case of a spontaneous reduction of adult intussusception with a brief review of literature.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
(A) A mass like lesion with mild contrast enhancement (white arrow) is observed in the cecum. The proximal ileocecal valve shows a crescent shape. (B) Enlarged lymph node (white arrow) is observed adjacent to the ileocecal area.

Fig. 2
(A) The normal cecum and the intussuscepted ileocecal valve are observed like a mass. The upper part of the intussuscepted region (white arrow) was firm and showed mucosal erythema. At the lower part, a normal ileal mucosa is observed. (B) Other side view of the intussuscepted lesion. (C, D) Biopsies were done at the marked area (white arrows).
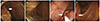
Fig. 3
(A) The normal cecum and the ileocecal valve are observed. (B–D) Two fungating masses were observed (B, C: proximal terminal ileum; D: distal terminal ileum).

Fig. 4
(A) Micrograph of the ileal mass. The submucosal layer is invaded by atypical cells (H&E, ×20). (B) The nuclei of atypical cells are three times larger than normal lymphocytes and scattered diffusely (H&E, ×200). (C) Tumor cells can be diagnosed as a diffuse large B-cell lymphoma when the findings of (B) demonstrate a strong positive for CD20 immunostaining, a B-cell marker (CD20 immunohistochemical, ×200). (D) Tumor cells are positive for CD10 and correspond to the germinal center B type according to the Hans classification (CD20 immunohistochemical, ×20).

References
1. Nestorović M, Stanojević G, Brzacki V, et al. Ileocolic intussusception as a presenting sign of primary lymphoma of the colon. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 2011; 139:673–676.
2. Azar T, Berger DL. Adult intussusception. Ann Surg. 1997; 226:134–138.
3. Hong KD, Kim J, Ji W, Wexner SD. Adult intussusception: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Tech Coloproctol. 2019; 23:315–324.
4. Onkendi EO, Grotz TE, Murray JA, Donohue JH. Adult intussusception in the last 25 years of modern imaging: is surgery still indicated? J Gastrointest Surg. 2011; 15:1699–1705.
5. Gupta RK, Agrawal CS, Yadav R, Bajracharya A, Sah PL. Intussusception in adults: Institutional review. Int J Surg. 2011; 9:91–95.
6. Cochran AA, Higgins GL 3rd, Strout TD. Intussusception in traditional pediatric, nontraditional pediatric, and adult patients. Am J Emerg Med. 2011; 29:523–527.
7. Valentini V, Buquicchio GL, Galluzzo M, et al. Intussusception in adults: the role of MDCT in the identification of the site and cause of obstruction. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016; 2016:5623718.
8. Karakus SC, Ozokutan BH, Ceylan H. Diseases mimicking intussusception: diagnostic dilemma. Pediatr Int. 2014; 56:768–771.
9. Aledavood A, Nasiri MR, Memar B, et al. Primary gastrointestinal lymphoma. J Res Med Sci. 2012; 17:487–490.
10. Vobořil R, Fanta J, Bačkovský P, Ehrenberger D, Vobořilová J. Transient and non-transient intussusceptions of the large bowel in adults: two case reports. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2015; 58:66–68.
11. Lai J, Ramai D, Murphy T, Kasher F. Transient adult jejunojejunal Intussusception: a case of conservative management vs. surgery. Gastroenterology Res. 2017; 10:369–371.
12. Khan Z, Darr U, Renno A, Alkully T, Rafiq E, Sodeman T. Transient descending colocolonic intussusception due to a large fecaloma in an adult. ACG Case Rep J. 2017; 4:e94.
13. Kim JH, Kim YB, Kwak ST, Kim HY, Park CK, Yoo JY. Two cases of malignant lymphomas in the terminal ileum causing intussusception: diagnosis and reduction of intussusception by colonoscopy. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 19:650–655.
14. Park JH, Kim HW, Part WI, et al. A Case of ileocecal Burkitt’s lymphoma with intussusception in an adult. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 29:94–98.
15. Chung KW, Sun HS, Park SH, et al. Primary malignant lymphoma of the small intestine causing adult intussusception as an initial symptom. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1994; 14:100–104.
16. Park DK, Ahn IK. Primary lymphoma of the ileum manifested as ileocolic intussusception. J Korean Surg Soc. 1996; 50:137–143.
17. Nam S, Kang J, Park H, Lee KY, Sohn SK. Adult ileocecal intussusception caused by malignant lymphoma. Korean J Clin Oncol. 2014; 10:46–48.
18. Lee JJ, Sim MS, Kang JK. Primary lymphoma of the lieum manifested as Ileocecal intussusception: a case report. J Korean Surg Soc. 1994; 47:892.
19. Chung GO, Kang DB, Jo HJ, Oh JT. Primary malignant lymphoma of the terminal ileum causing intussusception in adults. J Korean Surg Soc. 2007; 72:244–249.
20. Park IH, Roh JH, Yu JH, et al. Two cases of cecal lymphoma causing intussusception. Korean J Med. 2008; 74:315–320.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download