1. Herring ES, Smith MM, Robertson JL. Lymph node staging of oral and maxillofacial neoplasms in 31 dogs and cats. J Vet Dent. 2002; 19:122–126.

2. Théon AP, Rodriguez C, Madewell BR. Analysis of prognostic factors and patterns of failure in dogs with malignant oral tumors treated with megavoltage irradiation. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1997; 210:778–784.
3. Brissot HN, Edery EG. Use of indirect lymphography to identify sentinel lymph node in dogs: a pilot study in 30 tumours. Vet Comp Oncol. 2017; 15:740–753.

4. Langenbach A, McManus PM, Hendrick MJ, Shofer FS, Sorenmo KU. Sensitivity and specificity of methods of assessing the regional lymph nodes for evidence of metastasis in dogs and cats with solid tumors. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2001; 218:1424–1428.

5. Nyman HT, Lee MH, McEvoy FJ, Nielsen OL, Martinussen T, Kristensen AT. Comparison of B-mode and Doppler ultrasonographic findings with histologic features of benign and malignant superficial lymph nodes in dogs. Am J Vet Res. 2006; 67:978–984.

6. Nyman HT, O'Brien RT. The sonographic evaluation of lymph nodes. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract. 2007; 22:128–137.

7. Seiler GS, Griffith E. Comparisons between elastographic stiffness scores for benign versus malignant lymph nodes in dogs and cats. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2018; 59:79–88.

8. Johnson PJ, Elders R, Pey P, Dennis R. Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging features of inflammatory versus neoplastic medial retropharyngeal lymph node mass lesions in dogs and cats. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2016; 57:24–32.

9. Ballegeer EA, Adams WM, Dubielzig RR, Paoloni MC, Klauer JM, Keuler NS. Computed tomography characteristics of canine tracheobronchial lymph node metastasis. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2010; 51:397–403.

10. Grimes JA, Secrest SA, Northrup NC, Saba CF, Schmiedt CW. Indirect computed tomography lymphangiography with aqueous contrast for evaluation of sentinel lymph nodes in dogs with tumors of the head. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2017; 58:559–564.

11. Stahle JA, Larson MM, Rossmeisl JH, Dervisis N, Neelis D. Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging is a feasible method for characterizing regional lymph nodes in canine patients with head and neck disease. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2019; 60:176–183.

12. Bhatia KS, Cho CC, Yuen YH, Rasalkar DD, King AD, Ahuja AT. Real-time qualitative ultrasound elastography of cervical lymph nodes in routine clinical practice: interobserver agreement and correlation with malignancy. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010; 36:1990–1997.

13. Tan R, Xiao Y, He Q. Ultrasound elastography: its potential role in assessment of cervical lymphadenopathy. Acad Radiol. 2010; 17:849–855.
14. Thomas A, Kümmel S, Fritzsche F, Warm M, Ebert B, Hamm B, Fischer T. Real-time sonoelastography performed in addition to B-mode ultrasound and mammography: improved differentiation of breast lesions? Acad Radiol. 2006; 13:1496–1504.

15. Burnside ES, Hall TJ, Sommer AM, Hesley GK, Sisney GA, Svensson WE, Fine JP, Jiang J, Hangiandreou NJ. Differentiating benign from malignant solid breast masses with US strain imaging. Radiology. 2007; 245:401–410.

16. Regner DM, Hesley GK, Hangiandreou NJ, Morton MJ, Nordland MR, Meixner DD, Hall TJ, Farrell MA, Mandrekar JN, Harmsen WS, Charboneau JW. Breast lesions: evaluation with US strain imaging--clinical experience of multiple observers. Radiology. 2006; 238:425–437.

17. Desmots F, Fakhry N, Mancini J, Reyre A, Vidal V, Jacquier A, Santini L, Moulin G, Varoquaux A. Shear wave elastography in head and neck lymph node assessment: image quality and diagnostic impact compared with B-mode and Doppler ultrasonography. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016; 42:387–398.

18. Alam F, Naito K, Horiguchi J, Fukuda H, Tachikake T, Ito K. Accuracy of sonographic elastography in the differential diagnosis of enlarged cervical lymph nodes: comparison with conventional B-mode sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 191:604–610.

19. Belotta AF, Gomes MC, Rocha NS, Melchert A, Giuffrida R, Silva JP, Mamprim MJ. Sonography and sonoelastography in the detection of malignancy in superficial lymph nodes of dogs. J Vet Intern Med. 2019; 33:1403–1413.

20. Moon WK, Choi JW, Cho N, Park SH, Chang JM, Jang M, Kim KG. Computer-aided analysis of ultrasound elasticity images for classification of benign and malignant breast masses. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010; 195:1460–1465.

21. Nakajima T, Inage T, Sata Y, Morimoto J, Tagawa T, Suzuki H, Iwata T, Yoshida S, Nakatani Y, Yoshino I. Elastography for predicting and localizing nodal metastases during endobronchial ultrasound. Respiration. 2015; 90:499–506.

22. Viera AJ, Garrett JM. Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic. Fam Med. 2005; 37:360–363.
23. Nyman HT, Kristensen AT, Skovgaard IM, McEvoy FJ. Characterization of normal and abnormal canine superficial lymph nodes using gray-scale B-mode, color flow mapping, power, and spectral Doppler ultrasonography: a multivariate study. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2005; 46:404–410.

24. De Swarte M, Alexander K, Rannou B, D'Anjou MA, Blond L, Beauchamp G. Comparison of sonographic features of benign and neoplastic deep lymph nodes in dogs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. 2011; 52:451–456.

25. Carlsen JF, Ewertsen C, Sletting S, Talman ML, Vejborg I, Bachmann Nielsen M. Strain histograms are equal to strain ratios in predicting malignancy in breast tumours. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0186230.

26. Chiorean L, Barr RG, Braden B, Jenssen C, Cui XW, Hocke M, Schuler A, Dietrich CF. Current Clinical Applications and Literature Review. Transcutaneous ultrasound: elastographic lymph node evaluation. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016; 42:16–30.
27. Wojcinski S, Dupont J, Schmidt W, Cassel M, Hillemanns P. Real-time ultrasound elastography in 180 axillary lymph nodes: elasticity distribution in healthy lymph nodes and prediction of breast cancer metastases. BMC Med Imaging. 2012; 12:35.

28. Dietrich CF, Cantisani V. Current status and perspectives of elastography. Eur J Radiol. 2014; 83:403–404.

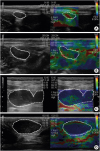

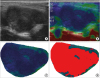



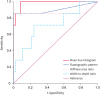




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download