INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cells
Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) method
Plasmids
Dual luciferase assay method
Western blot analysis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Expression profiles of prv-miR-LLT11a during PRV infection
 | Fig. 1PRV infection affects prv-miR-LLT11a expression. PK15 cells were infected with PRV (MOI = 1) and harvested at 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h post-transfection. (A) The expression levels of prv-miR-LLT11a were detected by using a stem-loop qRT-PCR method. (B) One-step growth curve for PRV replication in PK15 cells. The fold changes in the mRNA levels were calibrated to the level of U6 using a 2−ddCt method. The data are representative of 3 independent experiments (mean ± standard deviation). Statistical significance of differences is indicated by ns.PRV, pseudorabies virus; MOI, multiplicity of infection; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; ns, not significant.
*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
|
Overexpression of prv-miR-LLT11a causes inhibition of PRV replication
 | Fig. 2Effects of prv-miR-LLT11a on PRV replication. PK15 cells were transfected with prv-miR-LLT11a or NC mimics for 24 h and then infected with PRV at an MOI of 1. The supernatants were then harvested at different times and (A) viral titers were detected by using a plaque assay method. (B) Cell viability was determined by using a cell counting kit-8. The data are representative of 3 independent experiments (mean ± standard deviation).NC, negative control; hpi, hours post infection; PRV, pseudorabies virus; MOI, multiplicity of infection.
Statistically significant differences are indicated by *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
|
SLA-1 mRNA as the target gene of prv-miR-LLT11a
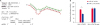 | Fig. 3Prv-miR-LLT11a targets the 3′UTR of SLA-1. (A) Predicted target sites of prv-miR-LLT11a in the 3′UTR of SLA-1; the SLA-1 miRNA sequences are labeled in red; (B) PK15 cells were transfected with SLA-1-3′UTR or SLA-1-3′UTR-mut luciferase reporters and 40 pmol of prv-miR-LLT11a or miR-NC mimics for 36 h. The cell lysates were harvested to determine reporter activity levels by using a luciferase assay method. The data are expressed as relative firefly luciferase activity normalized to Renilla luciferase activity. The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation values from 3 independent experiments.SLA, swine leukocyte antigen; NC, negative control.
Statistically significant values are indicated by *p < 0.05.
|
SLA-1 expressions downregulated by the prv-miR-LLT11a
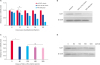 | Fig. 4Overexpression of prv-miR-LLT11a reduces the mRNA and protein levels of SLA-1. (A, B) PK15 cells were transfected with 120 pmol of prv-miR-LLT11a or miR-NC mimics or infected with PRV at an MOI of 1. The mRNA (A) and protein (B) levels of SLA-1 were measured at different times after transfection or infection by using qRT-PCR and western blot methods, respectively. (C, D) PK15 cells were transfected with different doses of prv-miR-LLT11a mimics for 48 h. The mRNA (C) and protein (D) levels of SLA-1 were measured by using qRT-PCR and western blot methods, respectively and β-actin was used as the internal reference control. The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation values from three independent experiments.SLA, swine leukocyte antigen; MOI, multiplicity of infection; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; PRV, pseudorabies virus; ns, not significant.
Statistically significant values are indicated by *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
|
TAP1 transcriptions downregulated by prv-miR-LLT11a
Table 1
The sequences of primers used in this study

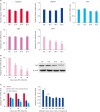 | Fig. 5Overexpression of prv-miR-LLT11a downregulated TAP1 expression. (A) PK15 cells were transfected with prv-miR-LLT11a or miR-NC mimics. The mRNA (A) levels of tapasin, ERp44, CRT, TAP1, and CNX were measured at different times after transcription by using a qRT-PCR method. (B, C) PK15 cells were infected with PRV or transfected with different doses of prv-miR-LLT11a mimics for 48 h. The mRNA (B) level of TAP1 was measured by using a qRT-PCR method; (C) the effects of PRV infection on the TAP1 expression levels were evaluated by using qRT-PCR with β-actin used as the internal reference control. The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation values from three independent experiments.NC, negative control; TAP, transporter associated with antigen processing; CRT, calreticulin; CNX, calnexin; ns, not significant; qRT-PCR, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.
Statistically significant values are indicated by *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download