Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Induction and identification of adipogenic differentiation in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs). hAMSCs were cultured in adipogenic differentiation medium to induce adipogenic differentiation for the indicated days. (A) Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis of enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPα) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) was conducted. (B) Western blot was used to measure the expression of C/EBPα and PPARγ, and the quantitation was determined with an image analyzer. (C) The expression of miR-138 was assessed by qRT-PCR. Data represent means±standard error of means. *n=3, p<0.05 compared with control hAMSCs on day 0. |
 | Fig. 2Overexpression of miR-138 inhibits adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs). Overexpression of miR-138 in hAMSCs was obtained by transfection of miR-138 mimic (miR-138) for 2 d. (A) Transfection efficiency was determined with quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. (B and C) Expression of enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPα) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) mRNA was monitored after adipogenic differentiation induction. (D–F) Expression of C/EBPα and PPARγ protein was monitored after adipogenic differentiation induction via Western blot assay. Data represent means±standard error of means. *n=3, p<0.05 compared with the miR-NC group at the indicated times. |
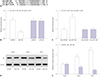 | Fig. 3miRNA-138 (miR-138) targets lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and negatively regulates LPL expression in human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs). (A) The binding sites between miR-138 and the 3′-UTR of LPL predicted by the miRTarBase database and the mutant are shown. (B and C) Dual-luciferase reporter assay was employed to detect the luciferase activity of wild type of LPL 3′UTR (LPL WT 3′UTR) and mutant of LPL 3′UTR (LPL MUT 3′UTR) after co-transfection with miR-138 or miR-NC. (D and E) Western blot was conducted to measure the effect of miR-138 on LPL protein expression during adipogenic differentiation of hAMSCs. Data represent means±standard error of means. *n=3, p<0.05 compared with the miR-NC group at the indicated times. |
 | Fig. 4Silencing of lipoprotein lipase (LPL) suppresses adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs). Silencing of LPL in hAMSCs was obtained by transfection with si-LPL for 2 d. (A and B) Expression of LPL was determined through quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot assay. (C and D) The mRNA expression of enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPα) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) was examined after adipogenic differentiation induction via qRT-PCR. (E–G) Expression of C/EBPα and PPARγ protein was analyzed after adipogenic differentiation induction utilizing Western blot assay. Data represent means±standard error of means. *n=3, p<0.05 compared with the si-LPL group at the indicated times. |
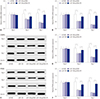 | Fig. 5Overexpression of lipoprotein lipase (LPL) partly reverses the inhibitory effect of miRNA-138 (miR-138) on adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAMSCs). Four transfection groups were used to study adipogenic differentiation: miR-NC mimic, miR-138 mimic, miR-138 mimic+pcDNA, and miR-138 mimic+pcDNA-LPL. (A and B) Expression of enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPα) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) mRNA was evaluated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. (C–F) Protein expression of C/EBPα and PPARγ was tested with Western blot assay. Data represent means±standard error of means. *n=3, p<0.05 compared with the si-LPL group or miR-138 mimic+pcDNA group at the indicated times. |
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: Lixin Lin.
Data curation: Lixin Lin and Peng Wang.
Formal analysis: Yuting Wang and Junjun Sun.
Funding acquisition: Xueming Wang.
Investigation: Yong Huang and Xueming Wang.
Methodology: Yuting Wang and Yong Huang.
Project administration: Yuting Wang.
Resources: Lixin Lin and Yong Huang.
Software: Peng Wang.
Supervision: Yuting Wang and Lixin Lin.
Validation: Yuting Wang and Lixin Lin.
Visualization: Yong Huang and Junjun Sun.
Writing—original draft: Yuting Wang and Lixin Lin.
Writing—review & editing: Lixin Lin and Yong Huang.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download