INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
AD mouse model
Antibiotic treatment of the mice
Feces preparation and transplantation
Probiotics preparation
Clinical scoring
Assessment of epidermal permeability barrier function
Histology
Quantitation of immunoglobulin E (IgE) serum levels
Real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Cell isolation and flow cytometry
Measurement of fecal SCFAs
RESULTS
Oral antibiotic administration aggravates the clinical signs of AD in the mouse
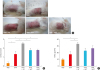 | Fig. 1Oral antibiotic administration aggravates clinical signs in a mouse model of AD. (A) Clinical features (erythema and swelling) in the AD mice treated as indicated. (B) TEWL levels. (C) Estimated clinical scores in AD mice treated as indicated.PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; OVA, ovalbumin; AT, oral antibiotic administration; TEWL, transepidermal water loss; AFT, antibiotics + orally administered fecal matter; APT, antibiotics + oral probiotics; AD, atopic dermatitis.
*P < 0.05, †P < 0.01, and ‡P < 0.001 by analysis of variance with Tukey's multiple comparison test.
|
Oral antibiotic administration up-regulates the systemic immune allergic response and Th2 cytokine levels in the skin
 | Fig. 2Oral antibiotic treatment increases the systemic immune allergic response and Th2 cytokine levels in the skin of AD mice. (A) Total IgE levels in the AD mice treated as indicated. (B) Measurement of IL4 expression in the skin of treated AD mice by real-time polymerase chain reaction.IgE, immunoglobulin E; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; OVA, ovalbumin; AT, oral antibiotic administration; AFT, antibiotics + fecal administration orally; APT, antibiotics + oral probiotics; IL4, interleukin 4; AD, atopic dermatitis.
*P < 0.05, †P < 0.01, and ‡P < 0.001 by analysis of variance with Tukey's multiple comparison test.
|
Oral antibiotic administration suppresses the intestinal metabolites processed by the microbiota leading to reduced SCFA levels
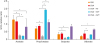 | Fig. 3Oral antibiotic treatment suppresses the production of intestinal metabolites and SCFAs by microbiota. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry SCFA measurements in atopic dermatitis mice treated as indicated.SCFA, short-chain fatty acid; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; OVA, ovalbumin; AT, oral antibiotic administration; AFT, antibiotics + oral fecal administration; APT, antibiotics + oral probiotics.
*P < 0.05, †P < 0.01, and ‡P < 0.001 by analysis of variance with Tukey's multiple comparison test.
|
Oral antibiotic administration up-regulates inflammation associated with ILC3s and IL17+ cells and suppresses the levels of CD4+FOXP3+ cells in the gut
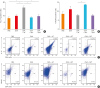 | Fig. 4Oral antibiotic treatment increases IL-17+ cell-related inflammation and suppresses CD4+FOXP3+ cell levels in the gut of AD mice. (A, C) Population of CD4+IL-17+ cells in the small intestine of treated AD mice as determined by FACS. (B, D) Population of CD4+FOXP3+ cells in the small intestine of treated AD mice as determined by FACS.IL17, interleukin 17; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; OVA, ovalbumin; AT, oral antibiotic administration; AFT, antibiotics + oral fecal administration; APT, antibiotics + oral probiotics; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; AD, atopic dermatitis.
*P < 0.05 and †P < 0.01 by analysis of variance with Tukey's multiple comparison test.
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download