Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
REFERENCES
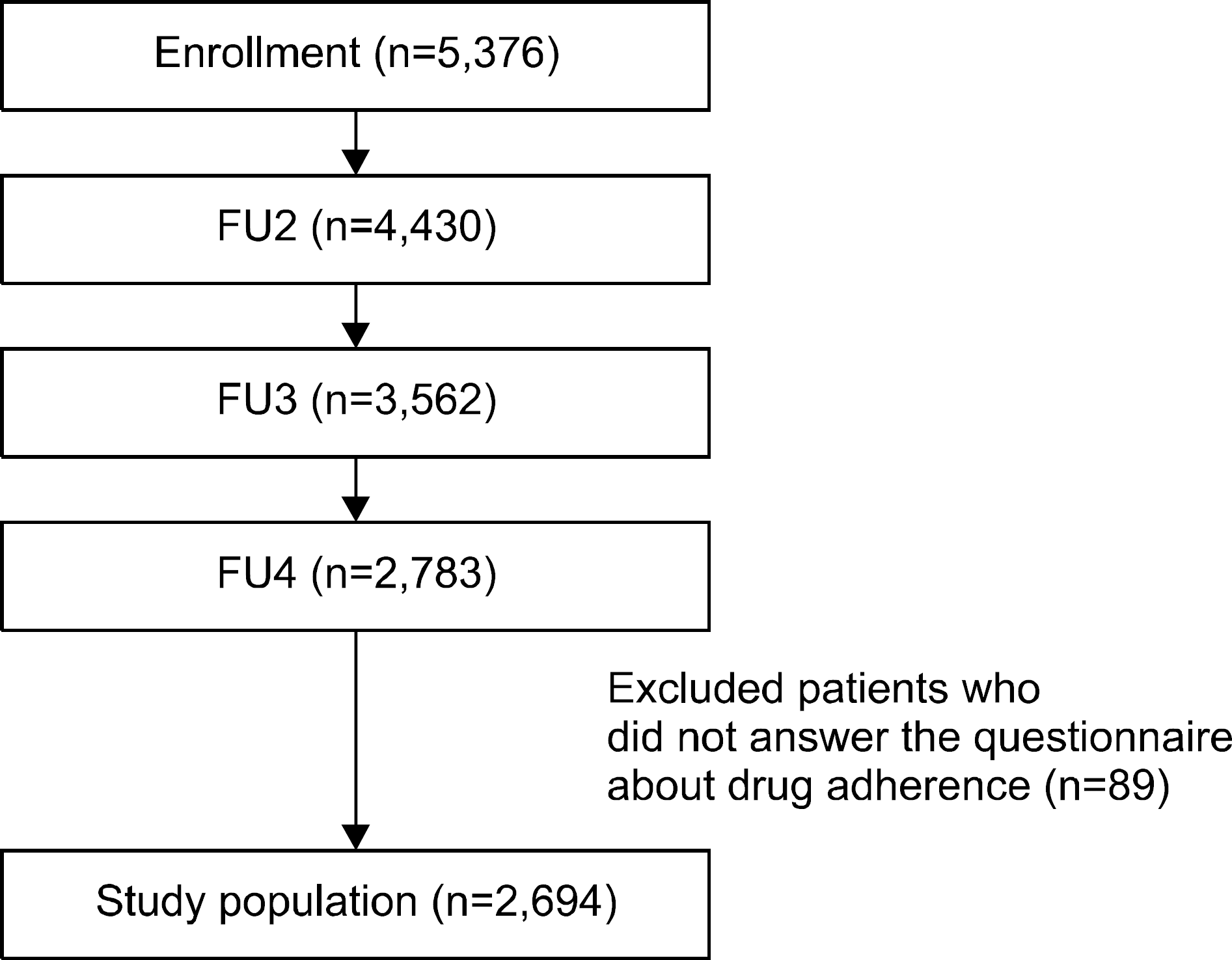 | Figure 1.Patient selection flow chart. FU2: second follow-up, FU3: third follow-up, FU4: fourth follow-up. |
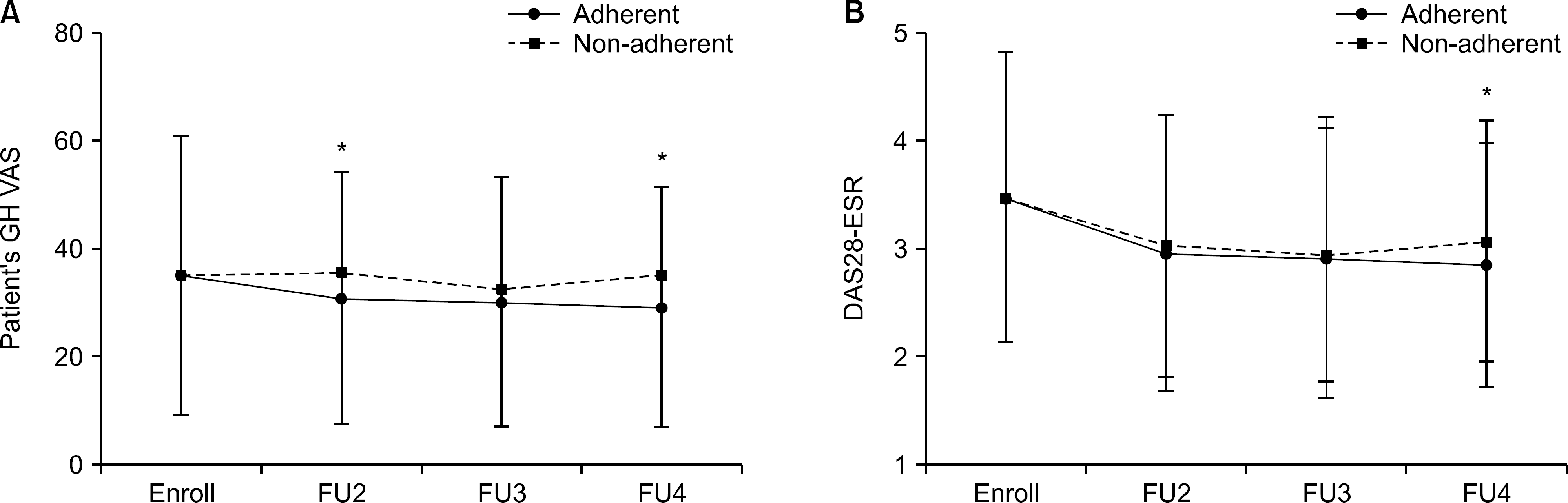 | Figure 2.The change of patient's (A) GH VAS and (B) DAS28-ESR between two groups in early RA patients (mean±standard deviation). GH VAS: global health visual analogue scale, DAS: disease activity score, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, FU2: second follow-up, FU3: third follow-up, FU4: fourth follow-up. *p-value <0.05. |
Table 1.
| Variable | Before PSM | After PSM | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adherent (n=2,161) | Non-adherent (n=533) | p-value | Adherent (n=1,447) | Non-adherent (n=522) | p-value | |
| Age (yr) | 54.14±10.98 | 50.26±12.01 | <0.01* | 51.57±10.85 | 50.49±11.94 | 0.07 |
| Sex, female | 1,852 (85.7) | 473 (88.7) | 0.06 | 1,265 (87.4) | 462 (88.5) | 0.54 |
| BMI | 22.77±3.22 | 22.56±3.07 | 0.19 | 22.62±3.21 | 22.56±3.06 | 0.71 |
| Disease duration (mo) | 84.59±64.97 | 74.91±57.41 | <0.01* | 77.11±61.07 | 75.46±57.54 | 0.59 |
| ACR criteria number | ||||||
| <4 | 101 (4.7) | 22 (4.1) | 0.36 | 63 (4.4) | 21 (4.0) | 0.74 |
| ≥4 | 2,060 (95.3) | 511 (95.9) | 1,384 (95.6) | 501 (96.0) | ||
| Current smoker | 146 (6.8) | 38 (7.1) | 0.26 | 97 (6.7) | 37 (7.1) | 0.96 |
| Side effects | 715 (33.1) | 229 (43.0) | <0.01* | 556 (38.4) | 220 (42.1) | 0.18 |
| Income (USD/mo) | ||||||
| <2,000 | 1,430 (66.5) | 297 (55.8) | <0.01* | 876 (60.5) | 296 (56.7) | 0.09 |
| 2,000∼4,990 | 574 (26.7) | 184 (34.6) | 466 (32.2) | 180 (34.5) | ||
| ≥5,000 | 145 (6.7) | 51 (9.6) | 105 (7.3) | 46 (8.8) | ||
| Education | ||||||
| Middle school or less | 950 (44.2) | 1,201 (55.8) | <0.01* | 541 (37.4) | 173 (33.1) | 0.09 |
| High school or more | 174 (32.6) | 359 (67.4) | 906 (62.6) | 349 (66.9) | ||
| Rheumatoid factor | 1,493 (69.1) | 386 (72.4) | 0.14 | 1,042 (72.0) | 375 (71.8) | 0.96 |
| ACPA | 1,486 (68.8) | 352 (66.0) | 0.23 | 976 (67.4) | 344 (65.9) | 0.52 |
| Medication | ||||||
| MTX | 1,867 (86.4) | 460 (86.3) | 0.94 | 1,250 (86.4) | 450 (86.2) | 0.94 |
| NSAID | 1,795 (83.1) | 444 (83.3) | 0.95 | 1,203 (83.1) | 434 (83.1) | 1.00 |
| Steroid | 1,805 (83.5) | 444 (83.3) | 0.90 | 1,191 (82.3) | 433 (83.0) | 0.79 |
| Biologics | 170 (7.9) | 26 (4.9) | <0.05* | 77 (5.3) | 26 (5.0) | 0.82 |
| Physician's VAS score | 24.42±18.17 | 22.05±16.39 | <0.01* | 22.55±17.09 | 22.11±16.45 | 0.61 |
| Patient's GH VAS score | 37.86±25.64 | 37.65±25.23 | 0.86 | 37.06±25.61 | 37.44±25.23 | 0.77 |
| DAS28-ESR | 3.67±1.30 | 3.57±1.30 | <0.05* | 3.58±1.28 | 3.57±1.30 | 0.85 |
| EQ5D | 0.69±0.23 | 0.72±0.23 | <0.05* | 0.71±0.22 | 0.72±0.23 | 0.67 |
| HAQ | 0.66±0.62 | 0.56±0.58 | <0.01* | 0.58±0.56 | 0.56±0.58 | 0.53 |
| ESR | 29.93±24.34 | 27.40±22.10 | <0.05* | 28.06±23.03 | 27.55±22.18 | 0.67 |
| CRP | 0.82±1.39 | 0.71±1.50 | 0.12 | 0.74±1.18 | 0.72±1.52 | 0.68 |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%). PSM: propensity score matching, BMI: body mass index, ACR: American college of rheumatology, USD: United States dollar, ACPA: anti-citrullinated peptide antibody, MTX: methotrexate, NSAID: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, VAS: visual analog scale, GH: global health, DAS: disease activity score, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, EQ5D: EuroQol-5D, HAQ: health assessment questionnaire, CRP: C-reactive protein.
Table 2.
| Variable | Total population | Early RA | Late RA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adherent (n=1,447) | Non-adherent (n=522) | p-value | Adherent (n=483) | Non-adherent (n=186) | p-value | Adherent (n=894) | Non-adherent (n=332) | p-value | |
| EULAR response | |||||||||
| Good | 302 (20.9) | 93 (17.8) | 0.14 | 135 (28.0) | 38 (20.4) | <0.05* | 160 (17.9) | 53 (16.0) | 0.45 |
| Moderate | 322 (22.3) | 105 (20.1) | 0.32 | 103 (21.3) | 42 (22.6) | 0.75 | 200 (22.4) | 65 (19.6) | 0.31 |
| None | 823 (56.9) | 324 (62.1) | <0.05* | 245 (50.7) | 106 (57.0) | 0.17 | 534 (59.7) | 214 (64.5) | 0.15 |
| Disease flare | |||||||||
| FU2 flare | 253 (17.5) | 108 (20.7) | 0.11 | 70 (14.5) | 32 (17.2) | 0.40 | 160 (17.9) | 74 (22.3) | 0.09 |
| FU3 flare | 265 (18.3) | 102 (19.5) | 0.56 | 79 (16.4) | 32 (17.2) | 0.82 | 158 (17.7) | 69 (20.8) | 0.22 |
| FU4 flare | 245 (16.9) | 107 (20.5) | 0.07 | 65 (13.5) | 32 (17.2) | 0.22 | 161 (18.0) | 74 (22.3) | 0.10 |
| Any flare | 511 (35.3) | 203 (38.9) | 0.15 | 147 (30.4) | 59 (31.7) | 0.78 | 317 (25.5) | 142 (42.8) | <0.05* |
Values are presented as number (%). Early and advanced RA was classified according to disease duration of 48 months. Flares were defined as any flare occurring during the follow-up period. EULAR: European league against rheumatism, RA: rheumatoid arthritis, FU2: second follow-up, FU3: third follow-up, FU4: fourth follow-up.
Table 3.
| Variable | Total population | Early RA | Late RA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adherent (n=1,447) | Non-adherent (n=522) | p-value | Adherent (n=483) | Non-adherent (n=186) | p-value | Adherent (n=894) | Non-adherent (n=332) | p-value | |
| FU2 | |||||||||
| Physician's | 16.60±15.04 | 16.27±14.32 | 0.67 | 15.26±14.28 | 16.56±15.28 | 0.30 | 17.34±15.40 | 16.15±13.83 | 0.19 |
| VAS score | |||||||||
| Patient's GH | 35.07±24.30 | 36.85±24.13 | 0.15 | 31.05±23.04 | 35.80±25.75 | <0.05* | 37.42±24.42 | 37.30±23.24 | 0.94 |
| VAS score | |||||||||
| DAS28-ESR | 3.25±1.31 | 3.31±1.26 | 0.41 | 2.97±1.27 | 3.04±1.21 | 0.52 | 3.44±1.29 | 3.46±1.26 | 0.77 |
| EQ5D | 0.73±0.22 | 0.72±0.22 | 0.18 | 0.78±0.19 | 0.76±0.19 | 0.16 | 0.71±0.21 | 0.69±0.23 | 0.41 |
| HAQ | 0.52±0.58 | 0.51±0.57 | 0.52 | 0.36±0.46 | 0.37±0.50 | 0.82 | 0.62±0.60 | 0.58±0.59 | 0.26 |
| ESR | 25.77±21.57 | 26.50±23.02 | 0.51 | 23.55±21.02 | 22.73±19.46 | 0.64 | 27.05±21.46 | 28.68±24.49 | 0.26 |
| CRP | 0.72±2.95 | 0.59±1.00 | 0.33 | 0.94±5.11 | 0.55±0.82 | 0.30 | 0.64±1.02 | 0.62±1.10 | 0.83 |
| FU3 | |||||||||
| Physician's | 15.88±13.51 | 15.62±12.81 | 0.70 | 15.54±13.03 | 15.19±12.76 | 0.75 | 16.27±14.02 | 15.62±12.17 | 0.45 |
| VAS score | |||||||||
| Patient's GH | 34.35±23.43 | 35.71±13.17 | 0.25 | 30.30±22.98 | 32.80±23.03 | 0.21 | 36.57±22.79 | 36.94±23.11 | 0.80 |
| VAS score | |||||||||
| DAS28-ESR | 3.19±1.26 | 3.21±1.20 | 0.79 | 2.93±1.20 | 2.96±1.17 | 0.75 | 3.34±1.25 | 3.33±1.19 | 0.87 |
| EQ5D | 0.73±0.22 | 0.75±0.20 | 0.07 | 0.77±0.21 | 0.80±0.20 | 0.10 | 0.71±0.21 | 0.72±0.20 | 0.30 |
| HAQ | 0.53±0.57 | 0.47±0.54 | 0.06 | 0.40±0.45 | 0.33±0.46 | 0.51 | 0.62±0.59 | 0.55±0.57 | 0.08 |
| ESR | 26.25±20.78 | 26.77±22.56 | 0.63 | 24.27±21.15 | 24.05±20.62 | 0.90 | 27.80±20.49 | 28.28±23.39 | 0.73 |
| CRP | 0.58±0.96 | 0.61±1.31 | 0.67 | 0.56±0.99 | 0.67±1.89 | 0.48 | 0.74±3.60 | 0.58±0.57 | 0.42 |
| FU4 | |||||||||
| Physician's | 16.28±13.65 | 15.77±13.72 | 0.47 | 14.68±13.51 | 14.82±13.78 | 0.91 | 16.81±13.87 | 16.49±13.68 | 0.72 |
| VAS score | |||||||||
| Patient's GH | 35.06±23.93 | 33.32±25.79 | 0.13 | 29.40±22.21 | 35.22±24.03 | <0.01* | 38.32±23.83 | 38.18±24.26 | 0.92 |
| VAS score | |||||||||
| DAS28-ESR | 3.17±1.17 | 3.26±1.12 | 0.12 | 2.87±1.12 | 3.08±1.11 | <0.05* | 3.36±1.17 | 3.37±1.11 | 0.87 |
| EQ5D | 0.72±0.23 | 0.73±0.21 | 0.31 | 0.77±0.20 | 0.77±0.21 | 0.61 | 0.69±0.23 | 0.71±0.21 | 0.05 |
| HAQ | 0.57±0.61 | 0.53±0.59 | 0.15 | 0.38±0.47 | 0.38±0.48 | 0.87 | 0.68±0.64 | 0.61±0.63 | 0.11 |
| ESR | 26.26±20.33 | 26.41±18.90 | 0.88 | 23.54±19.04 | 24.85±20.16 | 0.43 | 28.33±21.46 | 27.36±18.30 | 0.43 |
| CRP | 0.78±2.92 | 0.86±4.69 | 0.62 | 0.62±1.17 | 1.25±7.74 | 0.27 | 0.72±1.37 | 0.67±0.99 | 0.54 |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation. Early and advanced RA was classified according to disease duration of 48 months. RA: rheumatoid arthritis, VAS: visual analog scale, GH: global health, DAS: disease activity score, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, EQ5D: EuroQol-5D, HAQ: health assessment questionnaire, CRP: C-reactive protein, FU2: second follow-up, FU3: third follow-up, FU4: fourth follow-up.
Table 4.
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%). RA: rheumatoid arthritis, BMI: body mass index, ACR: American college of rheumatology, USD: United States dollar, ACPA: anti-citrullinated peptide antibody, MTX: methotrexate, NSAID: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, VAS: visual analog scale, GH: global health, DAS: disease activity score, ESR: erythrocyte sedimentation rate, EQ5D: EuroQol-5D, HAQ: health assessment questionnaire, CRP: C-reactive protein.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download