Abstract
Ultrasonography is used for making the diagnosis and treatment decisions for those patients who complain of shoulder pain related with sports activity. Ultrasonography is especially helpful for diagnosing issues with the rotator cuff, the long head of biceps tendon and the acromio-clavicular joint. The medical decisions about shoulder pain can be promptly made when portable ultrasonography is used in the field of sports.
References
1. Park JY, Lee SJ, Kim YI, Heo GY. Shoulder and elbow injury rates and patterns in Korean rookie professional baseball pitchers. Clin Should Elbow. 2016. 19:15–9.

2. Lin CL, Lee JS, Su WR, Kuo LC, Tai TW, Jou IM. Clinical and ultrasonographic results of ultrasonographically guided percutaneous radiofrequency lesioning in the treatment of recalcitrant lateral epicondylitis. Am J Sports Med. 2011. 39:2429–35.

3. Lesniak BP, Loveland D, Jose J, Selley R, Jacobson JA, Bedi A. Use of ultrasonography as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool in sports medicine. Arthroscopy. 2014. 30:260–70.

4. Yablon CM, Bedi A, Morag Y, Jacobson JA. Ultrasonography of the shoulder with arthroscopic correlation. Clin Sports Med. 2013. 32:391–408.

5. Erickson SJ. High-resolution imaging of the musculoskeletal system. Radiology. 1997. 205:593–618.

6. Yim ES, Corrado G. Ultrasound in athletes: emerging techniques in point-of-care practice. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2012. 11:298–303.
7. Roy JS, Braën C, Leblond J. . Diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography, MRI and MR arthrography in the characterisation of rotator cuff disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2015. 49:1316–28.

8. Teefey SA, Middleton WD, Bauer GS, Hildebolt CF, Yamaguchi K. Sonographic differences in the appearance of acute and chronic full-thickness rotator cuff tears. J Ultrasound Med. 2000. 19:377–8; quiz 383.

9. Middleton WD, Teefey SA, Yamaguchi K. Sonography of the rotator cuff: analysis of interobserver variability. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004. 183:1465–8.
10. van Holsbeeck MT, Kolowich PA, Eyler WR. . US depiction of partial-thickness tear of the rotator cuff. Radiology. 1995. 197:443–6.
11. Soble MG, Kaye AD, Guay RC. Rotator cuff tear: clinical experience with sonographic detection. Radiology. 1989. 173:319–21.

12. Iannotti JP, Ciccone J, Buss DD. . Accuracy of office-based ultrasonography of the shoulder for the diagnosis of rotator cuff tears. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005. 87:1305–11.

13. Farin PU, Jaroma H, Harju A, Soimakallio S. Shoulder impingement syndrome: sonographic evaluation. Radiology. 1990. 176:845–9.

14. Mack LA, Gannon MK, Kilcoyne RF, Matsen RA 3rd. Sonographic evaluation of the rotator cuff. Accuracy in patients without prior surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. 234:21–7.

15. Seo JB, Lee JY, Bahng SC. Efficacy of ultrasonogram for the diagnosis of biceps tendon pathology. J Korean Shoulder Elbow Soc. 2008. 11:90–5.

16. Hammar MV, Wintzell GB, Aström KG, Larsson S, Elvin A. Role of us in the preoperative evaluation of patients with anterior shoulder instability. Radiology. 2001. 219:29–34.

17. Krzyżanowski W. The use of ultrasound in the assessment of the glenoid labrum of the glenohumeral joint. Part I: ultrasound anatomy and examination technique. J Ultrason. 2012. 12:164–77.
18. Borsa PA, Scibek JS, Jacobson JA, Meister K. Sonographic stress measurement of glenohumeral joint laxity in collegiate swimmers and age-matched controls. Am J Sports Med. 2005. 33:1077–84.

Figure 1.
Ultrasonography of the short axis of the SSP showing hyperechoic fluid in the tear (arrow). RT, right; SSP, supraspinatus.
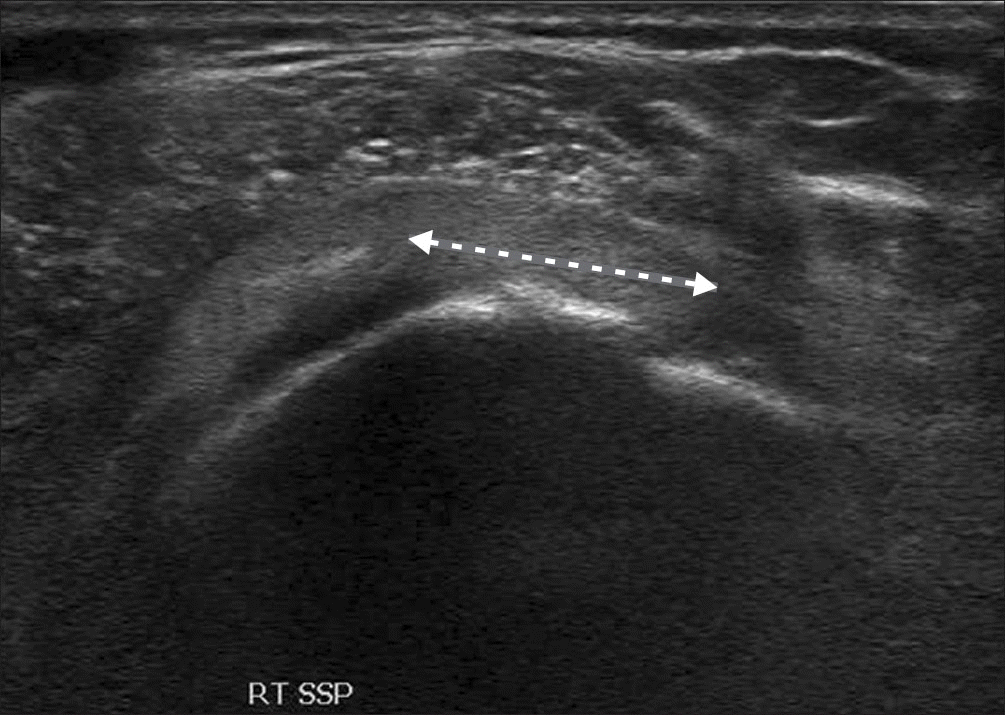
Figure 2.
Ultrasonography of the long axis of the SSP showing a medially retracted torn edge (arrow). RT, right; SSP, supraspinatus.
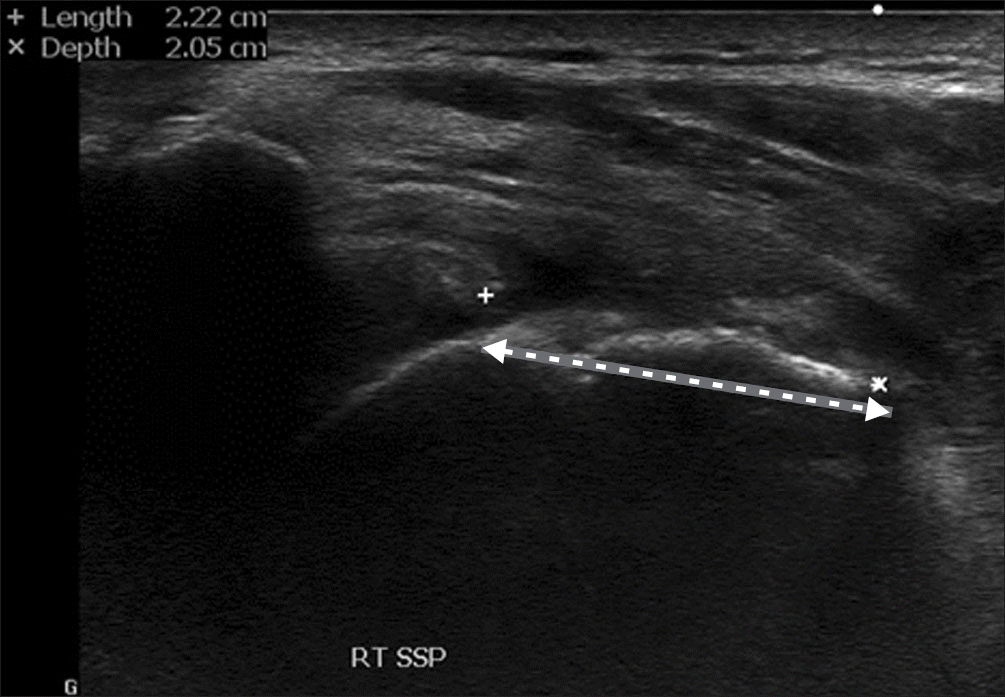
Figure 3.
Ultrasonography of the short axis of the SPP showing cartilage interface sign’ with the hyperechoic line of the articular cartilage (arrows). LT, left; SSP, supraspinatus.
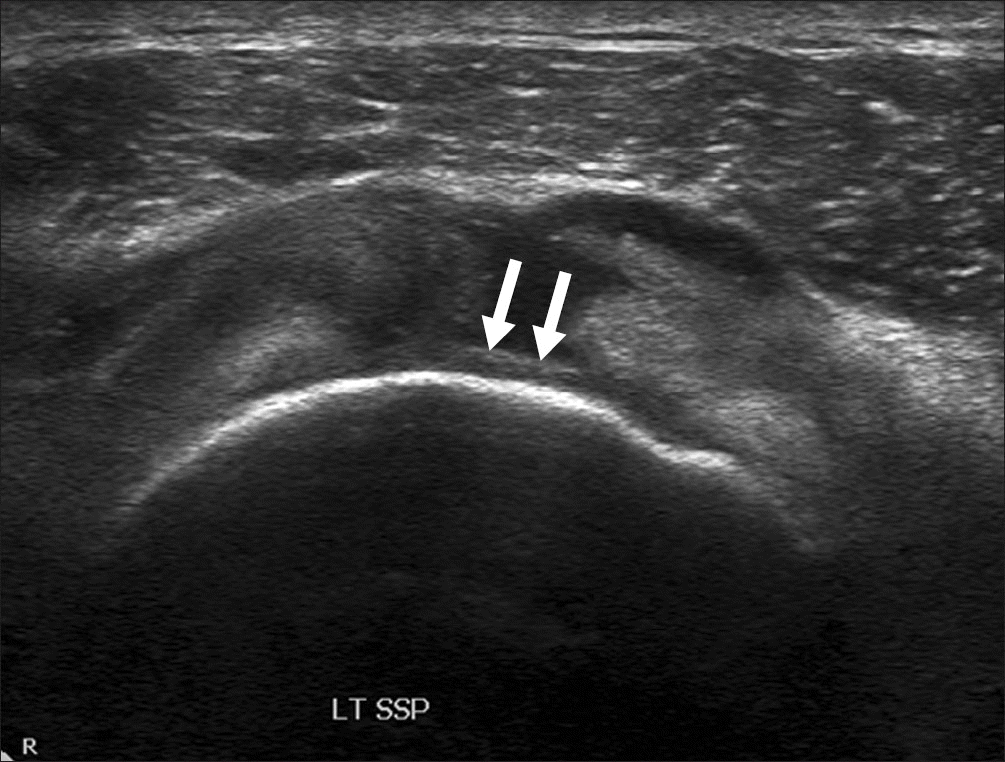
Figure 4.
Ultrasonography of the long axis of the supraspinatus showing the ‘peribursal sagging sign’ (between two crosses) at the lateral corner of the greater tuberosity.
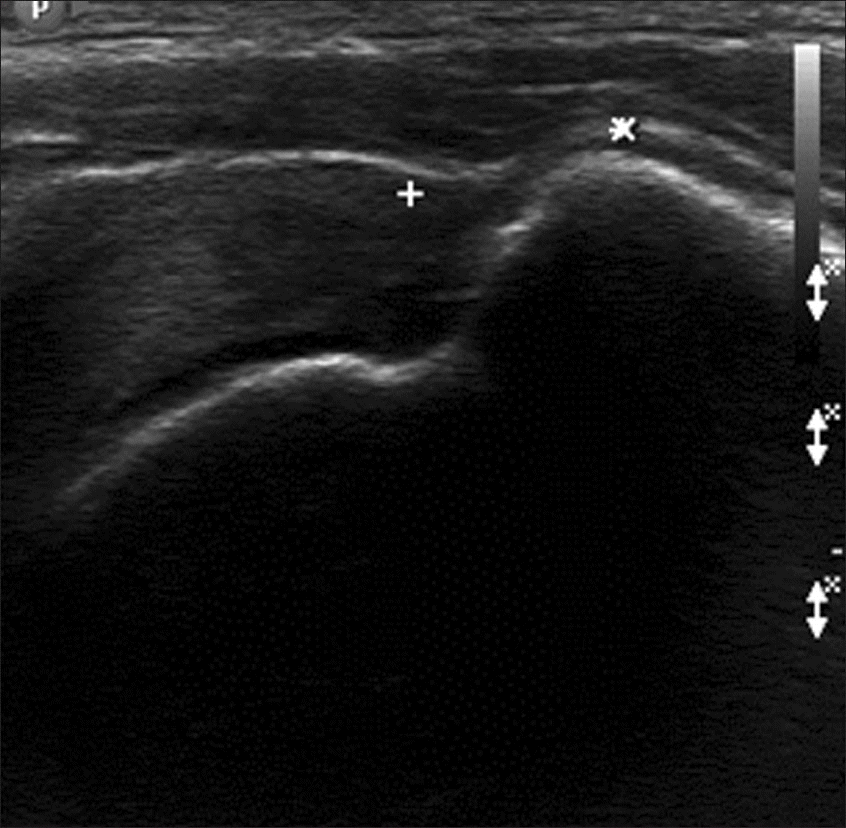
Figure 5.
Partial thickness articular side supraspinatus tear. (A) Ultrasonography of the short axis of the supraspinatus showing the partial thickness tear with a hypoechoic defect (arrow). (B) Arthroscopic photo showing a partial thickness tear (arrow).
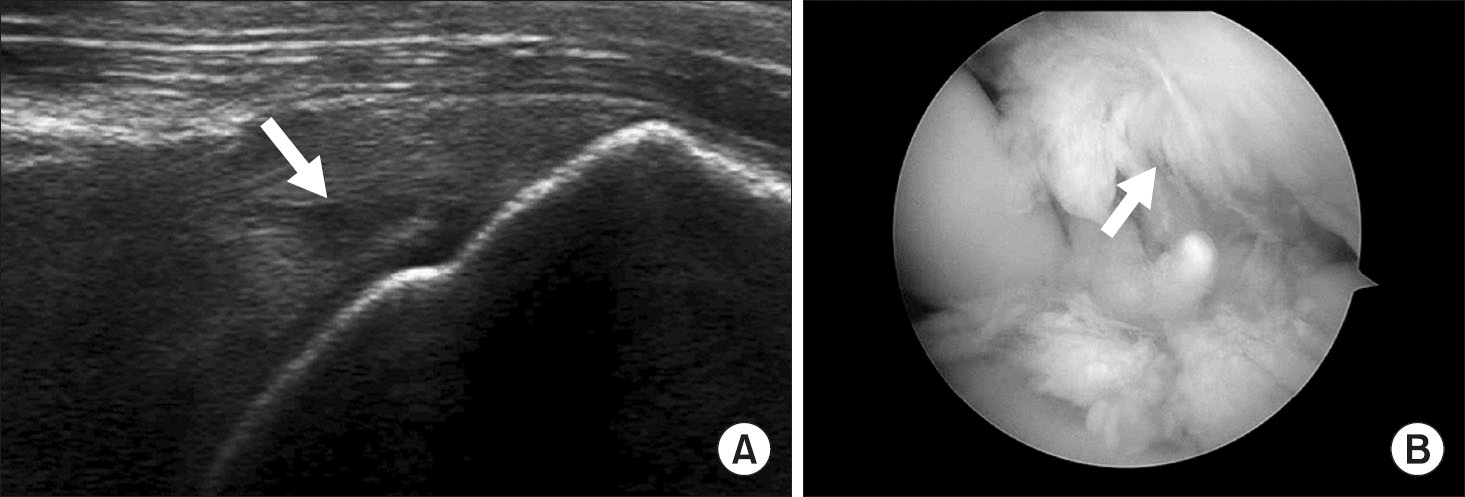
Figure 6.
Ultrasonography of the long axis of the SSC showing hypoechoic defects (arrows). RT, right; SSC, subscapularis.
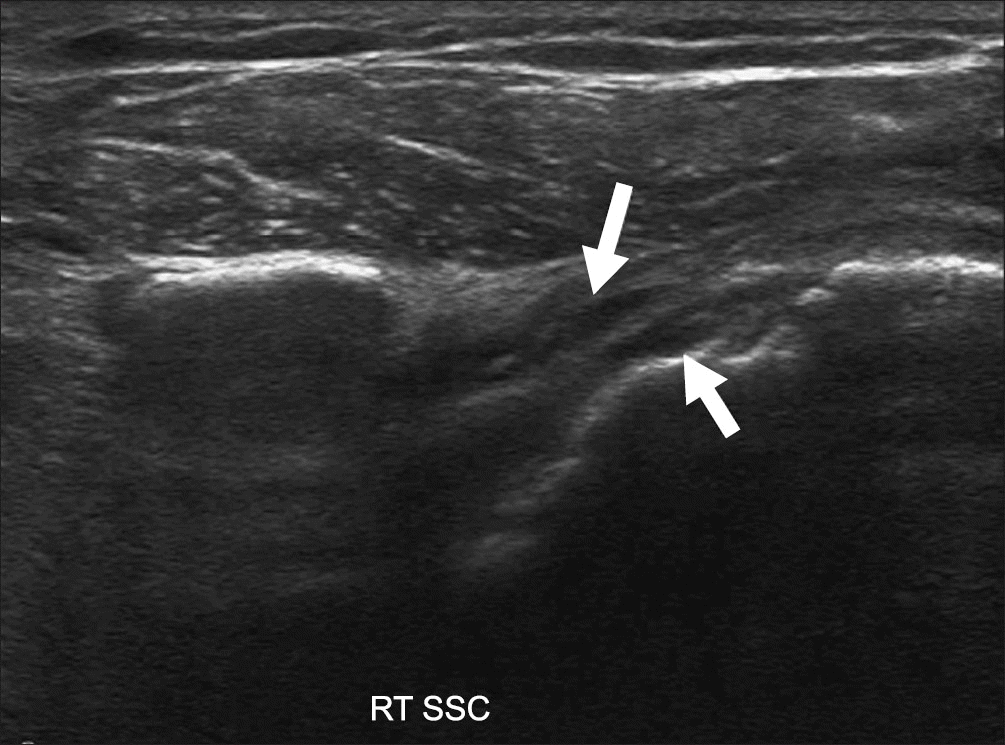
Figure 7.
Ultrasonography of the long axis of the SSC showing a normal insertion pattern (LT) (A) and the parallel pattern of tear (RT) (B). Dotted lines show the fiber pattern. LT, left; RT, right; SSC, subscapularis.
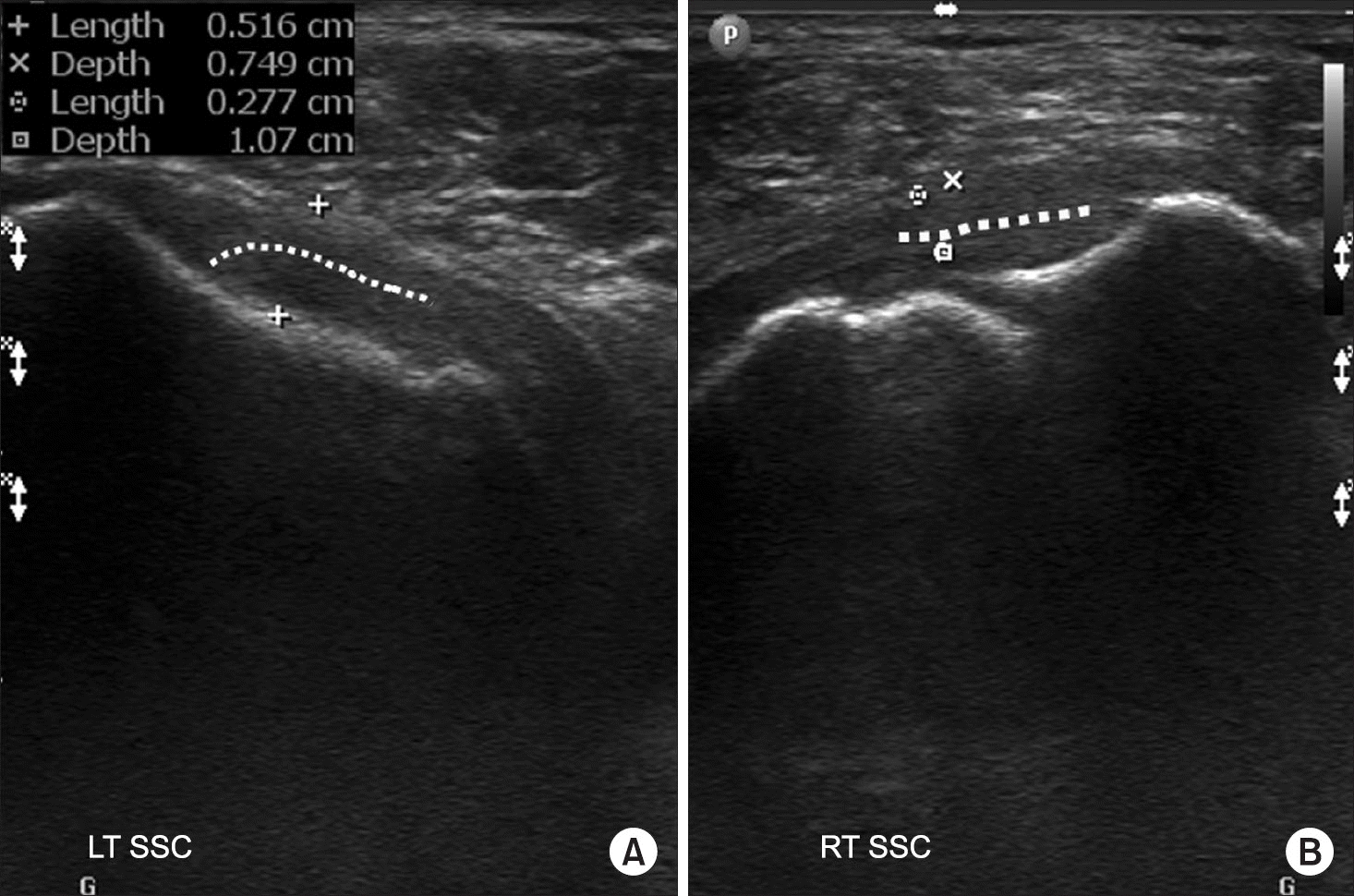
Figure 8.
Ultrasonography of the short axis of the long head of biceps tendon showing normal width (LT) (A) and narrow width (RT) (arrow) (B) of the bicipital groove. LT, left; RT, right.
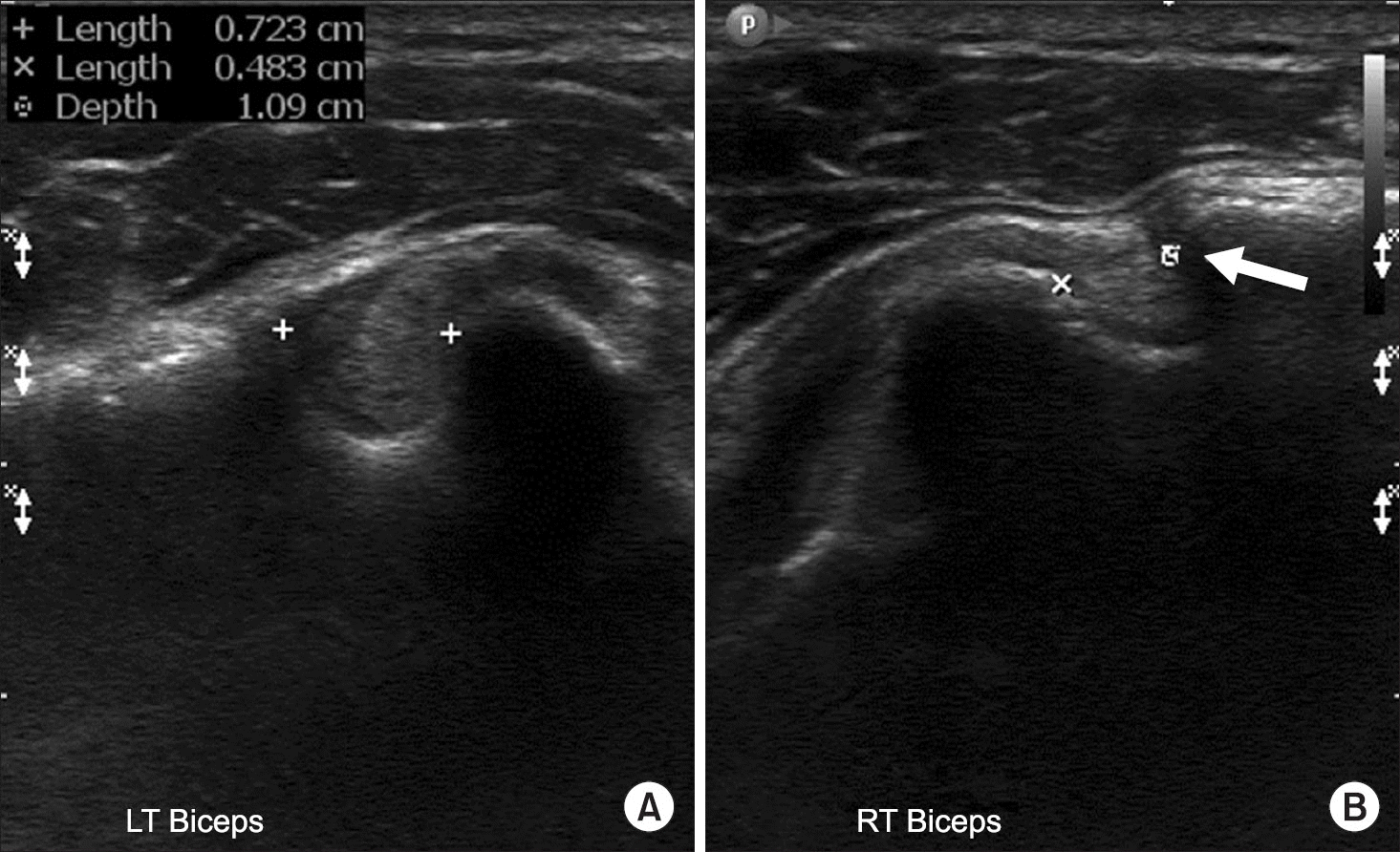
Figure 9.
Ultrasonography of the short axis of the long head of biceps tendon showing normal diameter (RT) (A) and the swollen tendon (LT) (arrows) (B). RT, right; LT, left.
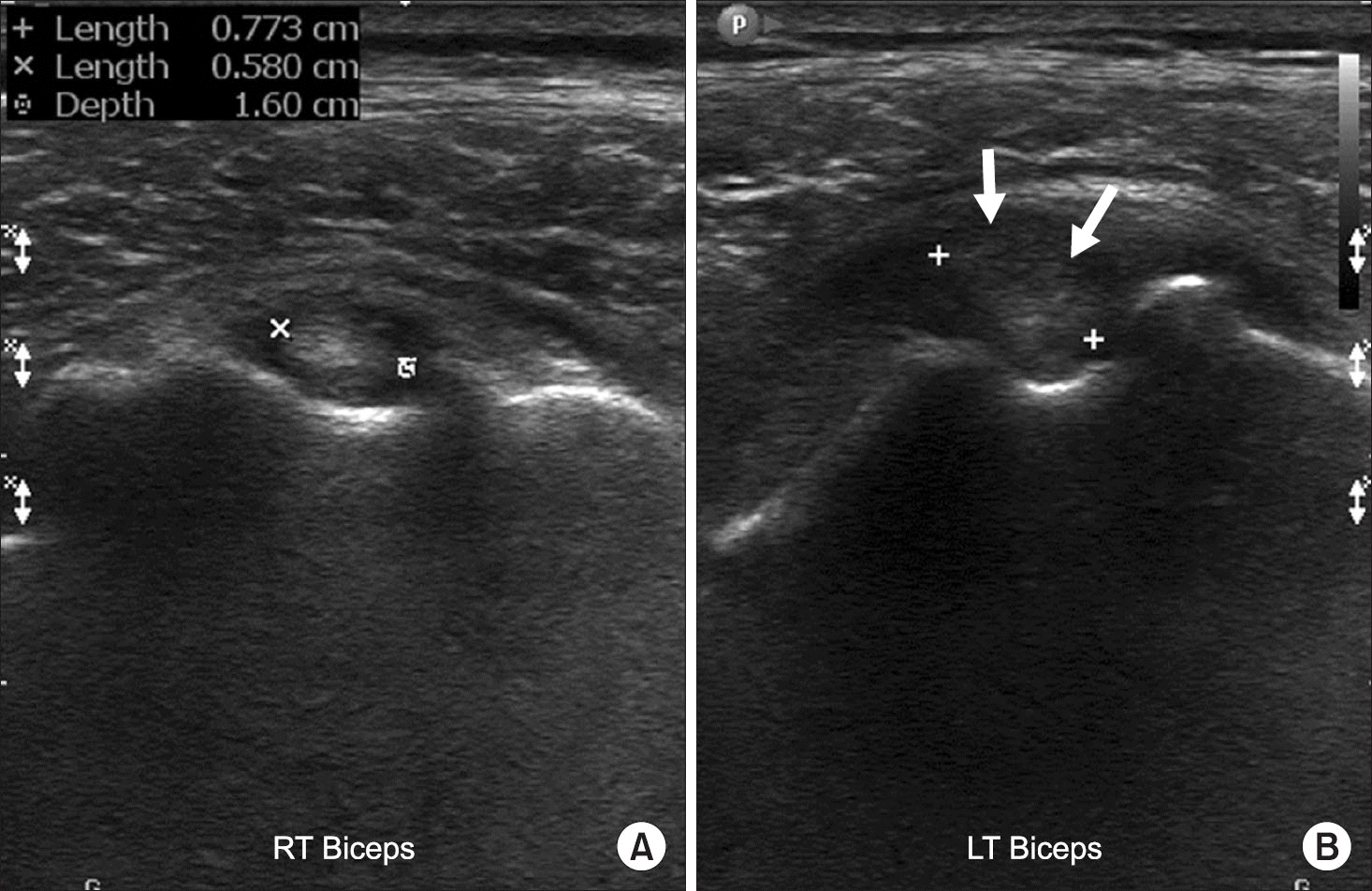
Figure 10.
Injury of the A-C JT. (A) Ultrasonography of the A-C JT showing a widened joint space (between two crosses) and fluid (arrow). (B) Intraoperative photo showing a torn acromio-clavicular ligament (arrow). RT, right; A-C JT, acromio-clavicular joint.
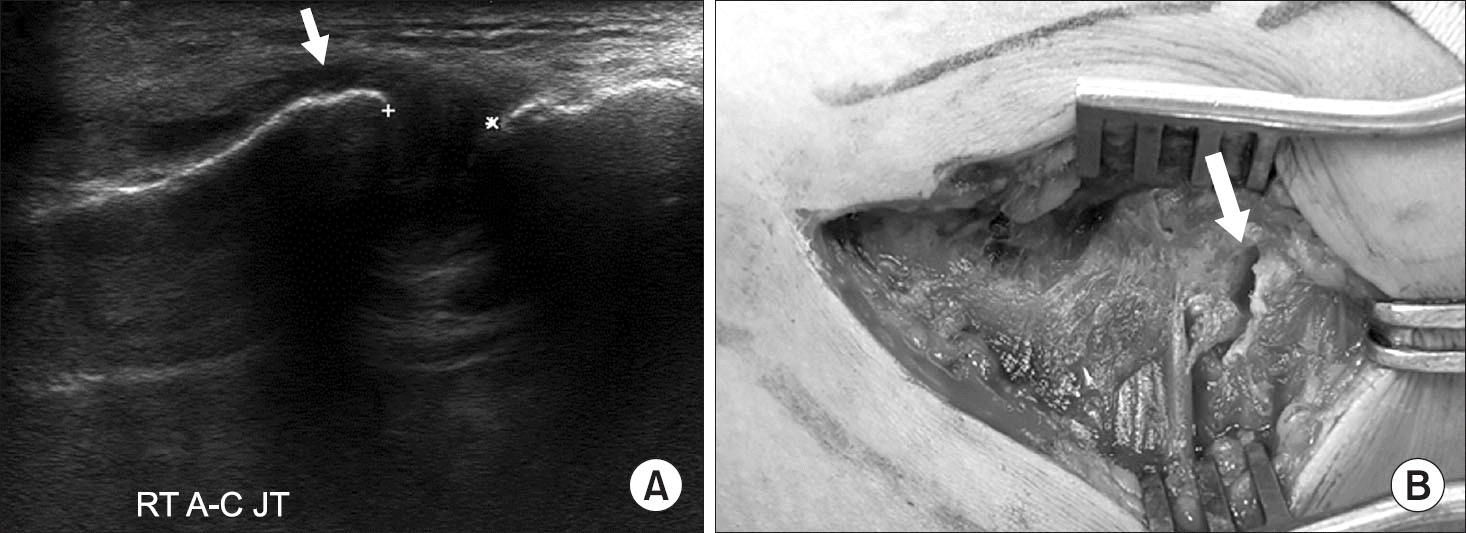
Figure 11.
Injury of the anterior labrum. (A) Position of the probe lying on the anterior shoulder (in the supine position). (B) Ultrasonography of the axial plane of the ANT shoulder showing a torn anteroinferior labrum (Bankart lesion) (arrow). H, humeral head; G, glenoid; LT, left; ANT, anterior.
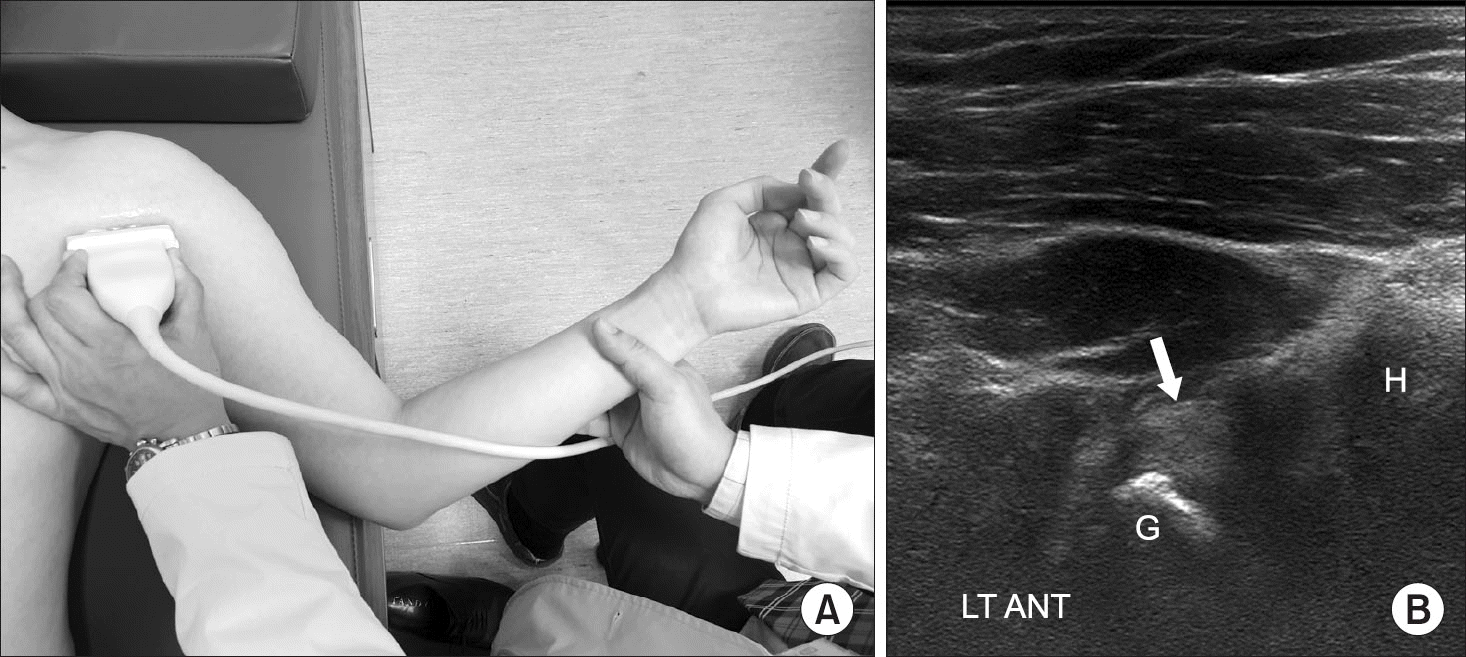
Table 1.
Reliability of Ultrasonography for the Cuff Tear




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download