Abstract
Unlike class I patients, skeletal class II patients have unstable occlusion thus leading to instability of mandibular complete denture. Therefore, mandibular implant overdenture has been the standard of care due to its advantages in stability and retention. The types of attachments can be divided into two categories: solitary and bar type. The indications vary between two categories. In this clinical report, digital technology was utilized from the implant planning to the choice of appropriate attachment. Implants were placed at the desired location as previously planned in terms of angle and depth. Maxillary removable partial denture and mandibular implant overdenture are expected to have fair prognosis. (J Korean Acad Prosthodont 2019;57:364-73)
Go to : 
REFERENCES
2.Schuyler CH. An evaluation of incisal guidance and its influence in restorative dentistry. J Prosthet Dent. 1959. 9:374–8.

3.Doundoulakis JH., Eckert SE., Lindquist CC., Jeffcoat MK. The implant-supported overdenture as an alternative to the complete mandibular denture. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003. 134:1455–8.

4.Sadowsky SJ. Mandibular implant-retained overdentures: a literature review. J Prosthet Dent. 2001. 86:468–73.

5.Batenburg RH., Meijer HJ., Raghoebar GM., Vissink A. Treatment concept for mandibular overdentures supported by endosseous implants: a literature review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1998. 13:539–45.
6.Preiskel HW. Precision attachments in prosthodontics: the application of intracoronal and extracoronal attachments. Quintessence Pub Co.;1984. p. 102–38.
7.Preiskel HW. Overdentures made easy: A guide to implantand root-supported prostheses. Quintessence Pub Co.;1996. p. 81–104.
8.Cakarer S., Can T., Yaltirik M., Keskin C. Complications associated with the ball, bar and Locator attachments for implant-supported overdentures. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2011. 16:e953–9.

9.Toolson LB., Smith DE. Clinical measurement and evaluation of vertical dimension. J Prosthet Dent. 1982. 47:236–41.

10.Klemetti E. Is there a certain number of implants needed to retain an overdenture? J Oral Rehabil. 2008. 35:80–4.

11.Hong HR., Pae A., Kim Y., Paek J., Kim HS., Kwon KR. Effect of implant position, angulation, and attachment height on peri-implant bone stress associated with mandibular two-implant overdentures: a finite element analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2012. 27:e69–76.
Go to : 
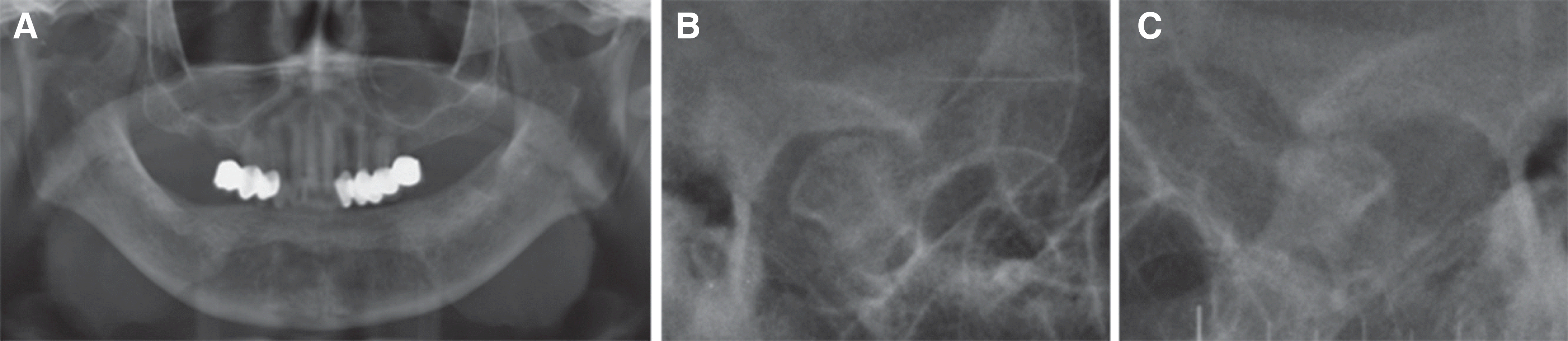 | Fig. 2.Radiographic view. (A) Panoramic view, (B) Right temporomandibular joint, (C) Left temporomandibular joint. |
 | Fig. 3.Intraoral photographs. (A) Maxilla, (B) Right lateral, (C) Frontal, (D) Left lateral, (E) Mandible. |
 | Fig. 4.Model analysis showing existing conventional complete denture. (A) Frontal view, (B) Right lateral view, (C) Anterior teeth. |
 | Fig. 5.Esthetics and function were verified with interim prostheses. (A) Maxilla, (B) Right lateral, (C) Frontal, (D) Left lateral, (E) Mandible. |
 | Fig. 9.Application of surgical stent using (A) Superposition of CT data and analysis model, (B) Intra oral photograph surgical stent fixed with pins, (C) Post operative panoramic view. |
 | Fig. 10.(A) Face-bow transfer, (B) Mounting with mandibular temporary denture and maxillary occlusal rim to make maxillary fixed prostheses. |
 | Fig. 11.Preparing for impression. (A) Definitive fixed prostheses on maxilla, CM LOC abutment (B) on mandible connected with CM LOC Female (C). |
 | Fig. 12.Final impression taking (B, E) with individual tray (A, D) and definitive cast fabrication (C, F). |
 | Fig. 13.(A) Centric relation record, Evaluation of occlusal vertical dimension with (B) interim prostheses (C), occlusal rim. |
 | Fig. 14.Bilaterally balanced occlusion. (A) Left Lateral movement, (B) Centric occlusion, (C) Right Lateral movement. |




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print









 XML Download
XML Download