Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate an effect of additional firing process after sintering of monolithic zirconia crown on marginal and internal fit through three-dimensional analysis.
Materials and methods
Ten monolithic zirconia crowns were fabricated using titanium abutment model. Monolithic zirconia crowns were designed, milled, and sintered as a control group, and additional firing with coloring was performed as a test group. Three dimensional analysis were performed by using triple-scan protocol, and cross-section analysis on mesio-distal and disto-lingual section was evaluated to measure marginal and internal fitness. Then, three-dimensional surface difference on between two groups was evaluated (α=.05).
Results
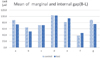
There was statistically significant difference between the control group (32.0 ± 24.3 µm) and the test group (17.0 ± 10.8 µm) in the mesial axial wall (P < .02) and the control group (60.2 ± 24.3 µm) and the test group (71.8 ± 21.5 µm) in the distal axial wall (P < .01). There was no statistically significant difference at the remaining point.
Figures and Tables
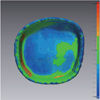
 | Fig. 3Scanned three-dimensional surface data. (A) Titanium master die, (B) Monolithic zirconia crown, (C) Superimposed crown on the master die. |
 | Fig. 4Measurement points for marginal gap (1, 6, a, g) and internal gap (2, 3, 4, 5, b, c, d, e, f). (A) Mesio-distal section, (B) Bucco-lingual section. |
 | Fig. 5Mean of marginal and internal gap of monolithic zirconia crown: Mesio-distal section (*Significant at P < .05). |
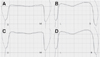 | Fig. 8Monolithic zirconia crown superimposed on the master die. (A, B) control group, (C, D) test group. |
Table 1
Marginal and internal gap discrepancy of monolithic zirconia crown: Mesio-distal section (Unit: µm)
References
1. Suárez MJ, Lozano JF, Paz Salido M, Martínez F. Three-year clinical evaluation of In-Ceram Zirconia posterior FPDs. Int J Prosthodont. 2004; 17:35–38.
2. Conrad HJ, Seong WJ, Pesun IJ. Current ceramic materials and systems with clinical recommendations: a systematic review. J Prosthet Dent. 2007; 98:389–404.

3. Lebon N, Tapie L, Duret F, Attal JP. Understanding dental CAD/CAM for restorations-dental milling machines from a mechanical engineering viewpoint. Part B: labside milling machines. Int J Comput Dent. 2016; 19:115–134.
4. Sturdevant JR, Bayne SC, Heymann HO. Margin gap size of ceramic inlays using second-generation CAD/CAM equipment. J Esthet Dent. 1999; 11:206–214.

6. Jacobs MS, Windeler AS. An investigation of dental luting cement solubility as a function of the marginal gap. J Prosthet Dent. 1991; 65:436–442.

7. Abduo J, Lyons K, Swain M. Fit of zirconia fixed partial denture: a systematic review. J Oral Rehabil. 2010; 37:866–876.

8. Vojdani M, Safari A, Mohaghegh M, Pardis S, Mahdavi F. The effect of porcelain firing and type of finish line on the marginal fit of zirconia copings. J Dent (Shiraz). 2015; 16:113–120.
9. Kim JH, Kim KB. Influence of high temperature of the porcelain firing process on the marginal fit of zirconia core. J Dent Hyg Sci. 2013; 13:135–141.
10. Balkaya MC, Cinar A, Pamuk S. Influence of firing cycles on the margin distortion of 3 all-ceramic crown systems. J Prosthet Dent. 2005; 93:346–355.

11. Holmes JR, Bayne SC, Holland GA, Sulik WD. Considerations in measurement of marginal fit. J Prosthet Dent. 1989; 62:405–408.

12. Moon BH, Yang JH, Lee SH, Chung HY. A study on the marginal fit of all ceramic using CCD camera. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 1998; 36:273–292.
13. McLean JW, von Fraunhofer JA. The estimation of cement film thickness by an in vivo technique. Br Dent J. 1971; 131:107–111.

14. Molin MK, Karlsson SL, Kristiansen MS. Influence of film thickness on joint bend strength of a ceramic/resin composite joint. Dent Mater. 1996; 12:245–249.

15. Holst S, Karl M, Wichmann M, Matta RE. A new triple-scan protocol for 3D fit assessment of dental restorations. Quintessence Int. 2011; 42:651–657.
16. Matta RE, Schmitt J, Wichmann M, Holst S. Circumferential fit assessment of CAD/CAM single crowns-a pilot investigation on a new virtual analytical protocol. Quintessence Int. 2012; 43:801–809.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download