Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to determine the relation between quantitative magnetic resonance imaging biomarkers, and clinical performances in chronic phase of carbon monoxide intoxication.
Materials and Methods
Eighteen magnetic resonance scans and cognitive evaluations were performed, on patients with carbon monoxide intoxication in chronic phase. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) ratios of affected versus unaffected centrum semiovale, and corpus callosum were obtained. Signal intensity (SI) ratios between affected centrum semiovale, and normal pons in T2-FLAIR (fluid-attenuated inversion recovery) images were obtained. The Mini-Mental State Exam, and clinical outcome scores were assessed. Correlation coefficients were calculated, between MRI and clinical markers. Patients were further classified into poor-outcome and good-outcome groups based on clinical performance, and imaging parameters were compared. T2-SI ratio of centrum semiovale was compared, with that of 18 sex-matched and age-matched controls.
Results
T2-SI ratio of centrum semiovale was significantly higher in the poor-outcome group, than that in the good-outcome group and was strongly inversely correlated, with results from the Mini-Mental State Exam. ADC ratios of centrum semiovale were significantly lower in the poor outcome group than in the good outcome group, and were moderately correlated with the Mini-Mental State Exam score.
Conclusion
A higher T2-SI and a lower ratio of ADC values in the centrum semiovale, may indicate presence of more severe white matter injury and clinical impairment. T2-SI ratio and ADC values in the centrum semiovale, are useful quantitative imaging biomarkers for correlation with clinical performance in individuals with carbon monoxide intoxication.
References
21. Pracyk JB, Stolp BW, Fife CE, Gray L, Piantadosi CA. Brain computerized tomography after hyperbaric oxygen therapy for carbon monoxide poisoning. Undersea Hyperb Med. 1995; 22:1–7.
22. Sener RN. Acute carbon monoxide poisoning: diffusion MR imaging findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; 24:1475–1477.
23. Murata T, Kimura H, Kado H, et al. Neuronal damage in the interval form of CO poisoning determined by serial diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging plus 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001; 71:250–253.

24. Pierpaoli C, Righini A, Linfante I, Tao-Cheng JH, Alger JR, Di Chiro G. Histopathologic correlates of abnormal water diffusion in cerebral ischemia: diffusion-weighted MR imaging and light and electron microscopic study. Radiology. 1993; 189:439–448.

25. Beppu T, Fujiwara S, Nishimoto H, et al. Fractional anisotropy in the centrum semiovale as a quantitative indicator of cerebral white matter damage in the subacute phase in patients with carbon monoxide poisoning: correlation with the concentration of myelin basic protein in cerebrospinal fluid. J Neurol. 2012; 259:1698–1705.

Fig. 1.
Forty-eight-year-old male with CO intoxication. (a, b) Measurement of T2 signal intensity in CS (a) and normal appearing ventral pons (b). SI ratios between affected CS and normal pons on T2-FLAIR images are calculated.
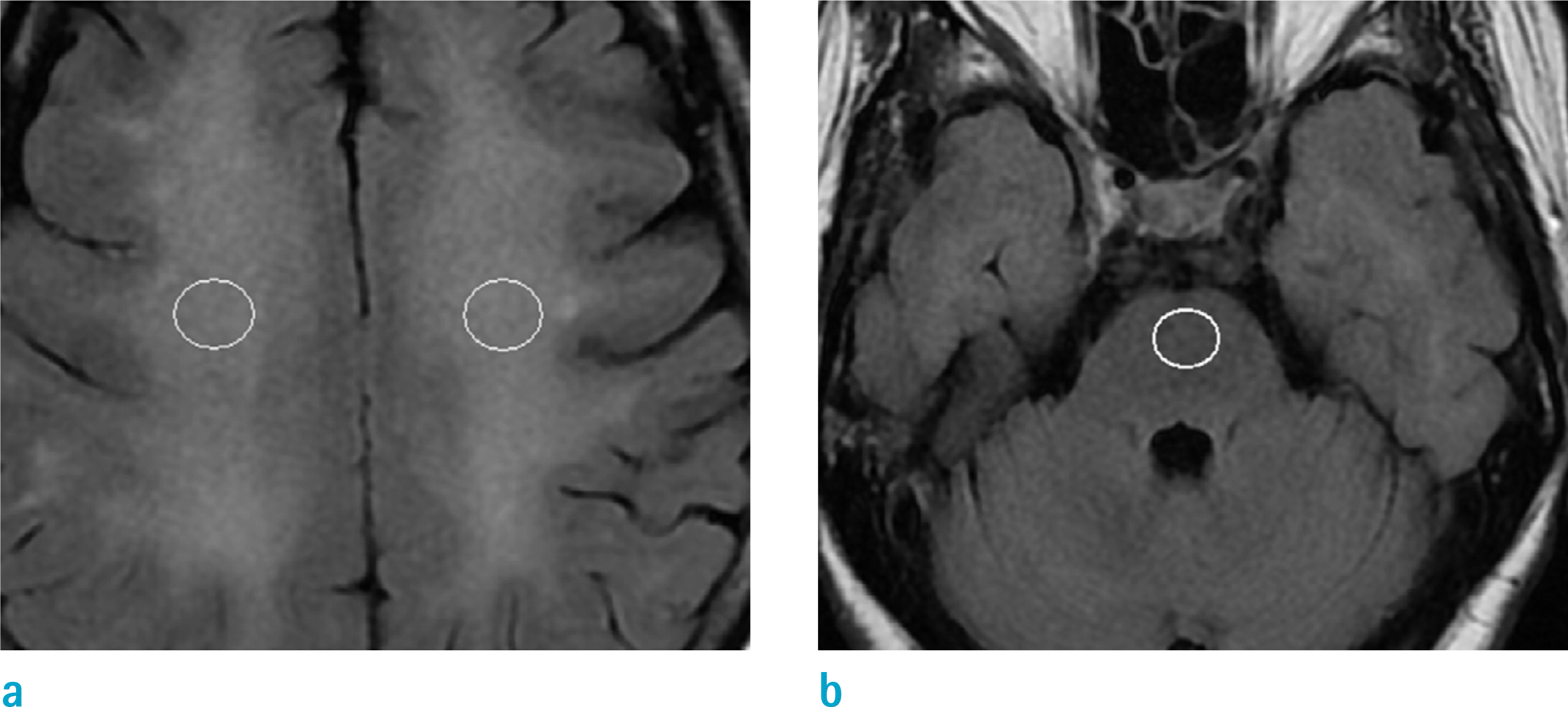
Fig. 2.
Forty-one-year-old female with CO intoxication. (a-f) ADC map (a), DWI (b), T2-FLAIR image (c) at the level of temporal lobe and ADC map (d), DWI (e), T2-FLAIR image (f) at the level of CS. T2-FLAIR image (c) shows normal-looking peripheral WM. T2-FLAIR image (f) shows bilateral symmetric confluent areas of high SI, in the CS. ROIs are placed on the involved CS (d) and normal-looking peripheral WM (a) on ADC maps. Bilateral involvement of basal ganglia, is also noted. There is no discernable SI change, in the corpus callosum.
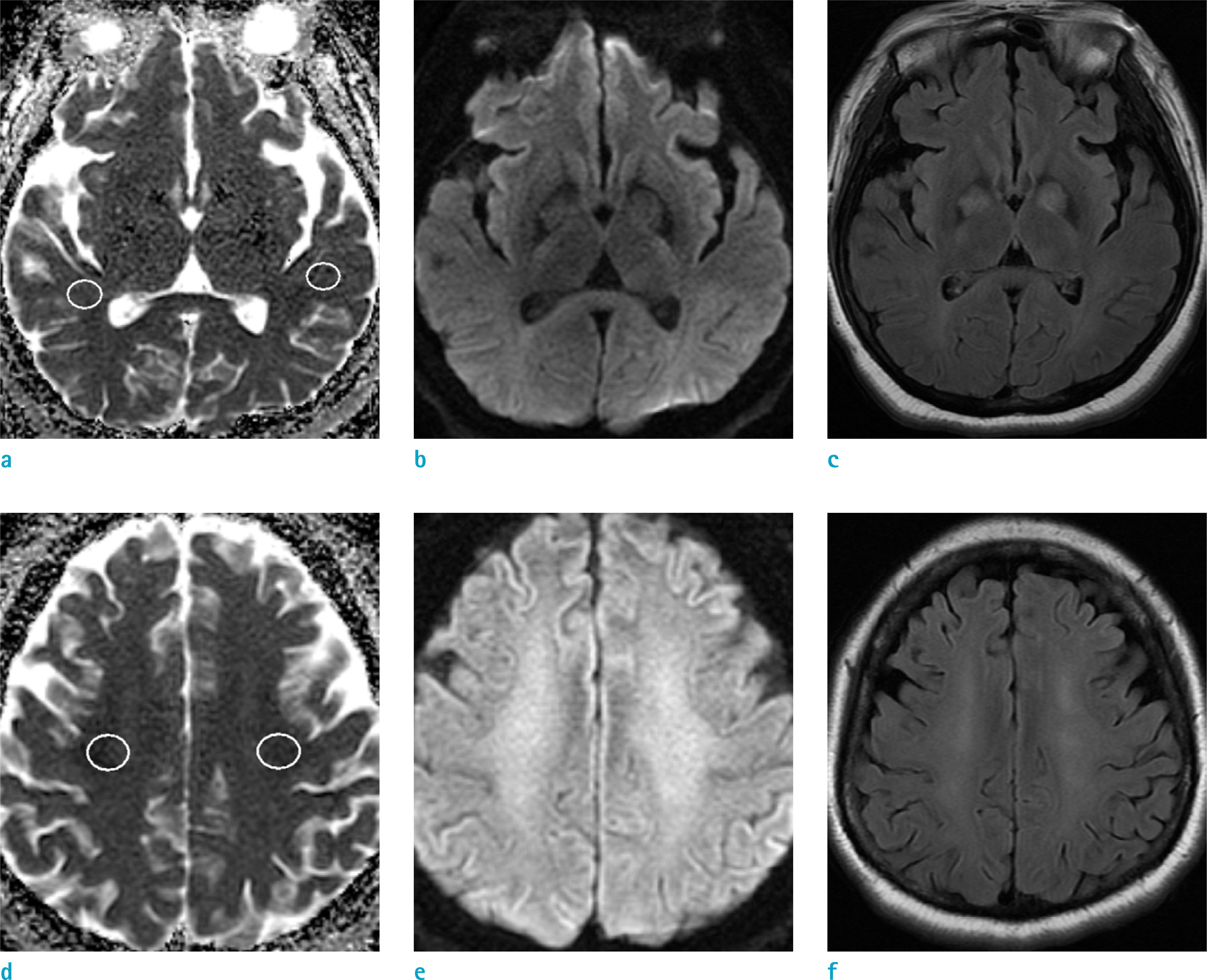
Fig. 3.
Thirty-six-year-old male with CO intoxication, in poor-outcome group (28 days after CO exposure). (a-c) T2-FLAIR image (c) show high SI in genu of corpus callosum. ADC map (a) and DWI (b) show restricted diffusion in genu. To obtain mean ADC values, ROIs are placed on the genu and normal-looking area of splenium on ADC map, using T2-FLAIR image as reference.
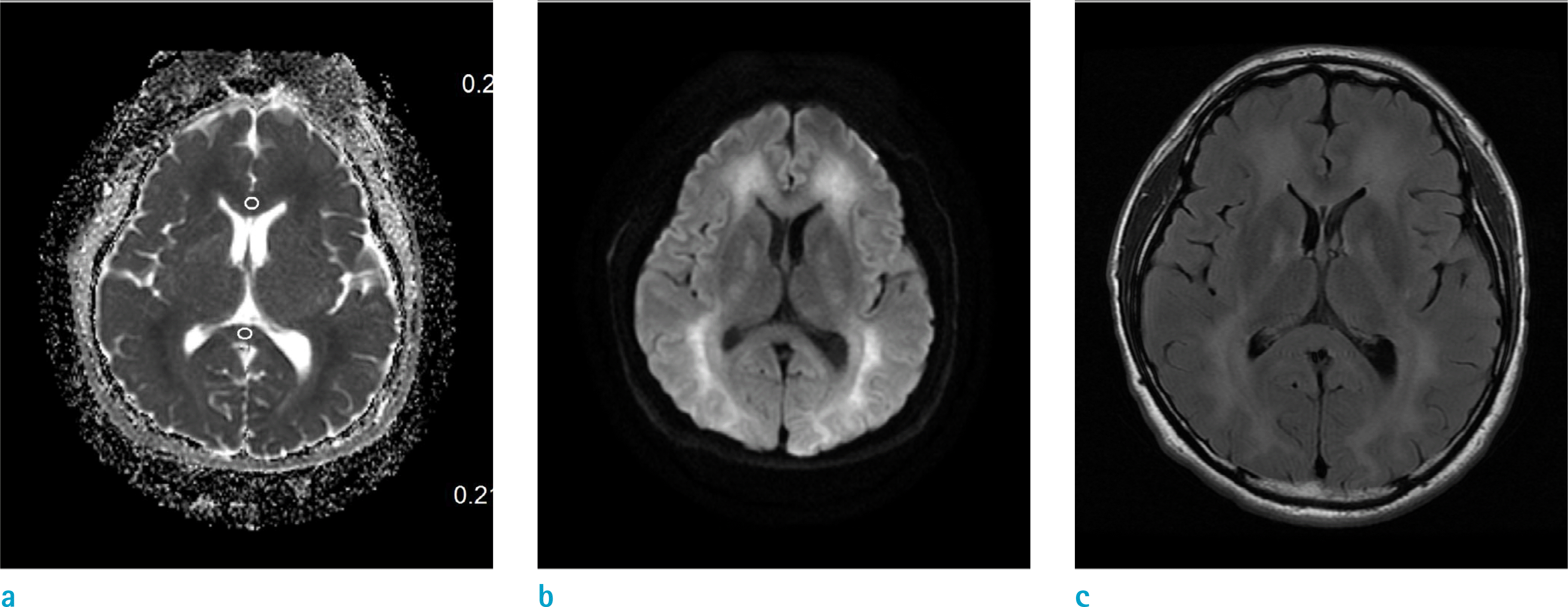
Fig. 4.
Thirty-four-year-old male with CO intoxication in good-outcome group (52 days after CO exposure). ADC map (a) shows iso to slight hyperintensity, and T2-FLAIR image (c) and DWI (b) show hyperintensity in the bilateral CS.
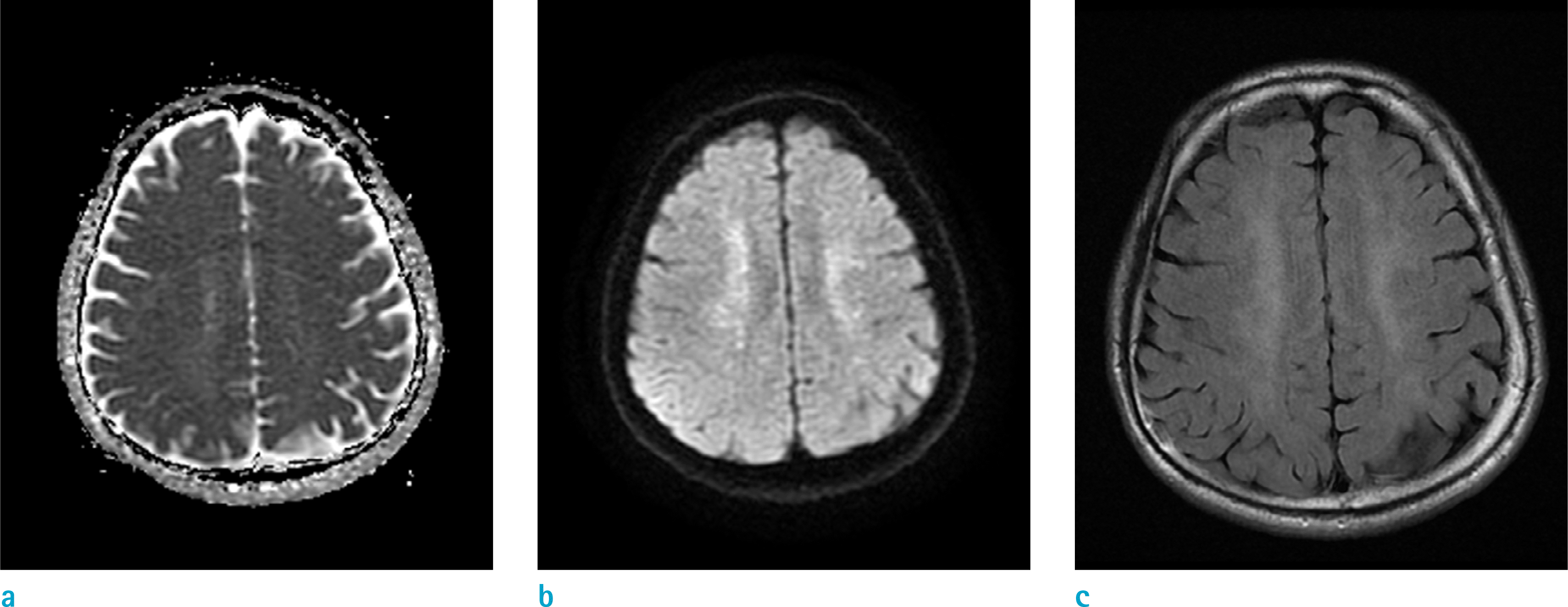
Fig. 5.
Differences of mean T2-SI ratios in CS between good-outcome and the poor-outcome groups based on clinical outcome scoring and Mini-Mental State Examination.
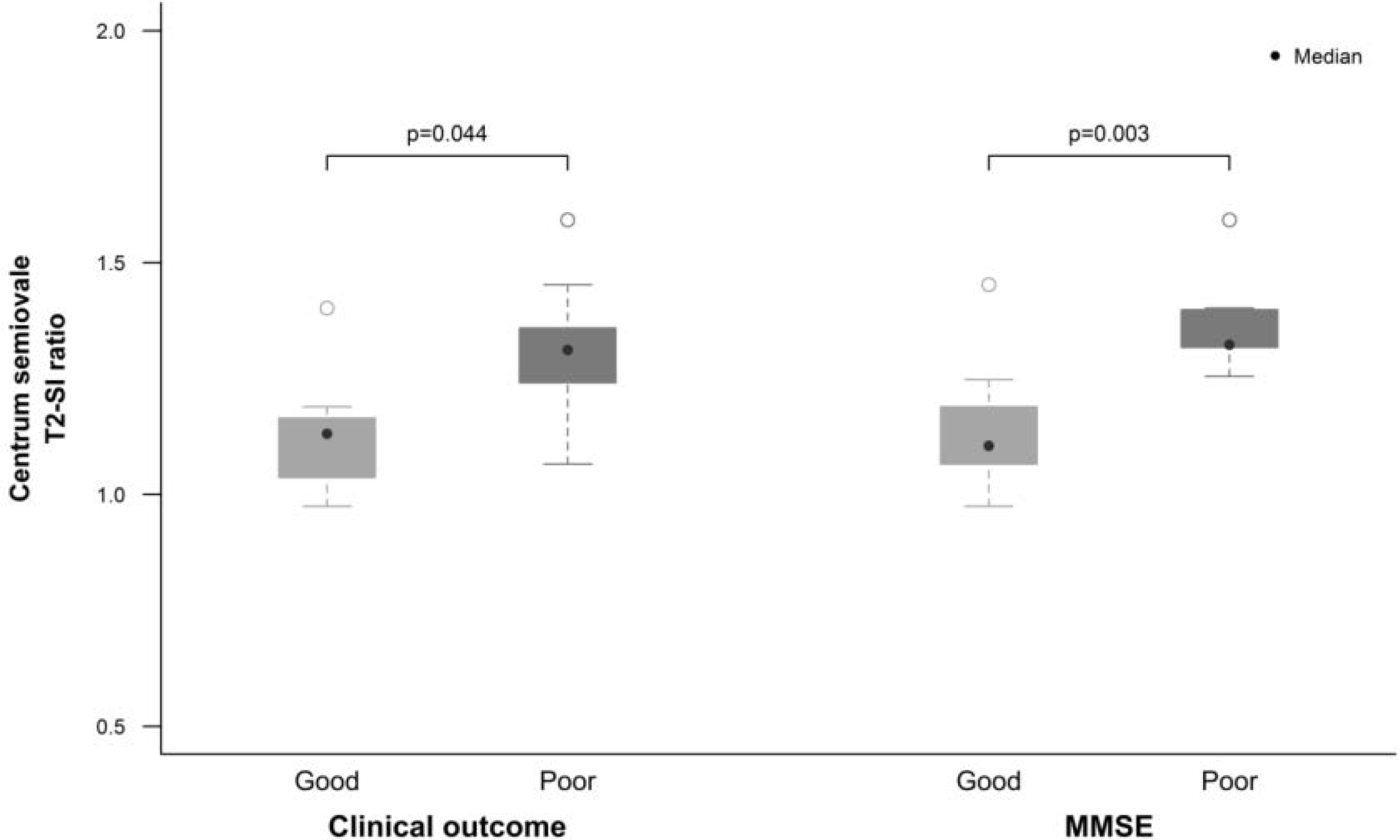
Table 1.
Demographic and Clinical Characteristic of All Subjects
| Variable | Total | |
|---|---|---|
| By patient | ||
| Age (year) | 56.4 ± 15.7* | |
| Sex, n (%) | Male | 9 (50) |
| Female | 9 (50) | |
| Status, n (%) | Chronic | 17 (94.4) |
| Subacute | 1 (5.6) | |
| Days to evaluation (day) | 46 ± 48* | |
| By lesion | ||
| CS T2 ratio, median (IQR) | 1.241 (1.092–1.323) | |
| CS ADC ratio, median (IQR) | 0.836 (0.740–1.091) | |
| CC ADC ratio, median (IQR) | 1.000 (0.859–1.000) | |
| By clinical result | ||
| MMSE score, median (IQR) | 14 (8–19) | |
| Clinical outcome score, median (IQR) | 3 (1.25–3) | |
Table 2.
Comparison of Characteristics Between Good and Poor Outcome Groups
| Variable | Good (n = 10) | Poor (n = 7) | Comparison (P-value) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRI measurements | |||
| A. MMSE scores | |||
| WM T2 ratio, median (IQR) | 1.105* (1.069–1.177) | 1.323* (1.317–1.398) | 0.003 |
| WM ADC ratio, median (IQR) | 0.957* (0.836–1.126) | 0.713* (0.692–0.778) | 0.036 |
| CC ADC ratio, median (IQR) | 1.000 (0.822–1.000) | 0.961 (0.902–1.000) | 0.855 |
| B. Clinical outcome scores | |||
| WM T2 ratio, median (IQR) | 1.131* (1.037–1.165) | 1.312* (1.241–1.359) | 0.044 |
| WM ADC ratio, median (IQR) | 1.007 (0.900–1.108) | 0.795 (0.715–0.836) | 0.224 |
| CC ADC ratio, median (IQR) | 1.000 (1.000–1.000) | 0.922 (0.822–1.000) | 0.361 |
Table 3.
Correlation Between MRI Measurements and Clinical Performances
Table 4.
Comparison of Characteristics Between Patient and Control Groups




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download