Abstract
Purpose
To report visual field changes after internal limiting membrane (ILM) peeling for macular epiretinal membrane (ERM) according to the severity of glaucoma.
Methods
A retrospective review of 37 eyes from 37 patients who underwent ILM peeling to treat ERM. Standard automated perimetry (Humphrey visual field 24-2 program) was performed preoperatively and postoperatively. Based on the Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (AGIS) scoring system of preoperative visual field, patients were classified into the early glaucoma (AGIS ≤ 1) group or the advanced glaucoma (AGIS ≥ 2) group. Postoperative visual field sensitivity at each point was compared with the preoperative value.
Results
Out of 37 eyes, 15 eyes had early glaucoma and 22 had advanced glaucoma. Eyes from both groups had poor postoperative visual field parameters. For eyes with advanced glaucoma, the visual field index was significantly reduced and the visual field damage was larger and wider compared to those with early glaucoma. In both groups, visual field impairment was greater on the nasal side than on the temporal side, and visual acuity was not significantly different. Postoperatively, the macular ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer thickness was decreased, especially on the temporal side of advanced glaucoma.
Figures and Tables
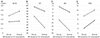 | Figure 1Comparison of postoperative changes in visual field parameters in early and advanced glaucoma. (A) Best-corrected visual acuity (logMAR). (B) Visual field index. (C) Mean deviation. (D) Pattern standard deviation. BCVA = best-corrected visual acuity; VFI = visual field index; MD = mean deviation; PSD = pattern standard deviation; logMAR = logarithm of the minimal angle of resolution. |
 | Figure 2Mean retinal sensitivity changes at each point of 24-2 Humphrey VF of each group. The 12 central boxes surrounded by bold lines are located within 10 eccentricity. The gray boxes indicated significantly deteriorated points postoperatively. (A) Early glaucoma. (B) Advanced glaucoma. Values are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (dB). *p < 0.05. |
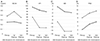 | Figure 3Longitudinal changes in visual field parameters in early and advanced glaucoma. (A) Best-corrected visual acuity (logMAR). (B) Visual field index. (C) Mean deviation. (D) Pattern standard deviation. BCVA = best-corrected visual acuity; VFI = visual field index; MD = mean deviation; PSD = pattern standard deviation; logMAR = logarithm of the minimal angle of resolution. |
Table 2
Postoperative changes in visual field parameters of each group

Continuous values are presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
BCVA = best corrected visual acuity; logMAR = logarithm of the minimal angle of resolution; VF = visual field; VFI = visual field index; MD = mean deviation; PSD = pattern standard deviation; AGIS = advanced glaucoma intervention study.
*Wilcoxon signed rank test.
Notes
References
1. Kim YC, Kim KS. The effect of internal limiting membrane peeling in treatment of idiopathic epiretinal membrane. J Korean Opthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:1067–1072.

2. de Bustros S, Thompson JT, Michels RG, et al. Vitrectomy for idiopathic epiretinal membranes causing macular pucker. Br J Ophthalmol. 1988; 72:692–695.

3. Poliner LS, Olk RJ, Grand MG, et al. Surgical management of premacular fibroplasia. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988; 106:761–764.

4. Kwok AK, Lai TY, Li WW, et al. Indocyanine green-assisted in ternal limiting membrane removal in epiretinal membrane surgery: a clinical and histologic study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004; 138:194–199.
5. Park DW, Dugel PU, Garda J, et al. Macular pucker removal with and without internal limiting membrane peeling: pilot study. Ophthalmology. 2003; 110:62–64.

6. Sorcinelli R. Surgical management of epiretinal membrane with indocyanine-green-assisted peeling. Ophthalmologica. 2003; 217:107–110.

7. Gandorfer A, Haritoglou C, Gass CA, et al. Indocyanine green-assisted peeling of the internal limiting membrane may cause retinal damage. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 132:431–433.

8. Haritoglou C, Ehrt O, Gass CA, et al. Paracentral scotomata: a new finding after vitrectomy for idiopathic macular hole. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001; 85:231–233.

9. Haritoglou C, Gass CA, Schaumberger M, et al. Macular changes after peeling of the internal limiting membrane in macular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001; 132:363–368.

10. Kim CY, Lee JH, Lee SJ, et al. Visual field defect caused by nerve fiber layer damage associated with an internal limiting lamina defect after uneventful epiretinal membrane surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002; 133:569–571.

11. Uemura A, Kanda S, Sakamoto Y, Kita H. Visual field defects after uneventful vitrectomy for epiretinal membrane with indocyanine green-assisted internal limiting membrane peeling. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 136:252–257.

12. Wolf S, Schnurbusch U, Wiedemann P, et al. Peeling of the basal membrane in the human retina: ultrastructural effects. Ophthalmology. 2004; 111:238–243.
13. Yamashita T, Uemura A, Kita H, Sakamoto T. Analysis of the retinal nerve fiber layer after indocyanine green-assisted vitrectomy for idiopathic macular holes. Ophthalmology. 2006; 113:280–284.

14. Tsuchiya S, Higashide T, Sugiyama K. Visual field changes after vitrectomy with internal limiting membrane peeling for epiretinal membrane or macular hole in glaucomatous eyes. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0177526.

15. Park K, Kim J, Lee J. Measurement of macular structure-function relationships using spectral domain-optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) and pattern electroretinograms (PERG). PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0178004.

16. Paques M, Massin P, Santiago PY, et al. Visual field loss after vitrectomy for full-thickness macular holes. Am J Ophthalmol. 1997; 124:88–94.

17. Pendergast SD, McCuen BW 2nd. Visual field loss after macular hole surgery. Ophthalmology. 1996; 103:1069–1077.

18. Hutton WL, Fuller DG, Snyder WB, et al. Visual field defects after macular hole surgery. A new finding. Ophthalmology. 1996; 103:2152–2158. discussion 8-9.
19. Boldt HC, Munden PM, Folk JC, Mehaffey MG. Visual field defects after macular hole surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 1996; 122:371–381.

20. Melberg NS, Thomas MA. Visual field loss after pars plana vitrectomy with air/fluid exchange. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995; 120:386–388.

21. Kim KH, Lee JW, Lee JE, et al. Visual field defect developed after internal limiting membrane peeling in a patient with epiretinal membrane. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011; 52:378–384.

22. Advanced glaucoma intervention study. 2. Visual field test scoring and reliability. Ophthalmology. 1994; 101:1445–1455.
23. Sivalingam A, Eagle RC Jr, Duker JS, et al. Visual prognosis correlated with the presence of internal-limiting membrane in histopathologic specimens obtained from epiretinal membrane surgery. Ophthalmology. 1990; 97:1549–1552.
24. Haritoglou C, Gandorfer A, Gass CA, et al. The effect of indocyanine-green on functional outcome of macular pucker surgery. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003; 135:328–337.

25. Imamura Y, Ishida M. Retinal thinning after internal limiting membrane peeling for idiopathic macular hole. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2018; 62:158–162.

26. Lee J, Park JM. Analysis of ganglion cell-inner plexiform layer thickness after internal limiting membrane peeling. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2016; 57:1369–1377.

27. Tadayoni R, Paques M, Massin P, et al. Dissociated optic nerve fiber layer appearance of the fundus after idiopathic epiretinal membrane removal. Ophthalmology. 2001; 108:2279–2283.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download