Abstract
Background and Purpose
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
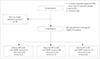 | Fig. 1Flow chart of the selection process to enroll eligible patients. The numbers of finally included patients with abnormal results either for QST (CDT) or QSART are in boldface. CDT: cold detection threshold, NCS: nerve conduction test, QSART: quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test, QST: quantitative sensory testing, SFN: small-fiber neuropathy. |
 | Fig. 2Small-Fiber Neuropathy Symptom Inventory Questionnaire plus ‘Sirim’ findings. The symptoms are listed in order from the most to the least frequent based on the sum of ‘often’ and ‘always’ frequencies. |
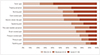 | Fig. 3Neuropathic Pain Symptom InventoryI plus ‘Sirim’ (cold) pain findings. A numerical rating scale ranging from 0 to 10 was used to score pain intensity. |
 | Fig. 4Correlations among SFN-SIQ plus ‘Sirim’ pain (A) and NPSI plus ‘Sirim’ pain (B). Correlations were considered to be significant (and are indicated by blue circles) for Spearman's rho (ρ)>0.3 and p<0.01. NPSI: Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory, SFN-SIQ: Small-Fiber Neuropathy Symptoms Inventory Questionnaire. |
 | Fig. 5Comparison of pain profiles among patients with different CDT and QSART results. The group with only abnormal CDT findings had more-severe stabbing pain compared to the group with both abnormal CDT and abnormal QSART findings in multiple logistic regression analysis after controlling for age, sex, and disease duration. A: burning pain, B: squeezing pain, C: pressure pain, CDT: cold detection threshold, D: stabbing pain (*), E: electric-shock-like pain, F: brush-evoked pain, G: pressure-evoked pain, H: cold-evoked pain, I: pins-and-needles sensation, J: tingling sensation, K: ‘Sirim’ pain, NRS: numerical rating scale, QSART: quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test. |
Table 1
Baseline characteristics of the 63 study subjects with clinically suspected small-fiber neuropathy (n=63)

Data are n (%), mean±SD (range), or median [interquartile range] values. *QST and QSART were performed in 57 (90%) and 56 (89%) patients, respectively, †Other includes two cases with positivity for rheumatoid factor, and one case each of positive anti-double stranded DNA IgM, Sjogren's syndrome, monoclonal gammopathy, and a side effect of isoniazid. BMI: body mass index, QSART: quantitative sudomotor axon reflex test, QST: quantitative sensory testing.
Acknowledgements
Notes
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Eun Bin Cho, Byoung Joon Kim.
Formal analysis: Eun Bin Cho.
Funding acquisition: Eun Bin Cho.
Investigation: Eun Bin Cho, Jin Myoung Seok, Ju-Hong Min, Bum Chun Suh, Ki-Jong Park, Byoung Joon Kim.
Methodology: Eun Bin Cho, Byoung Joon Kim.
Project administration: Eun Bin Cho, Jin Myoung Seok, Byoung Joon Kim.
Supervision: Eun Bin Cho, Byoung Joon Kim.
Validation: Eun Bin Cho, Jin Myoung Seok, Ju-Hong Min, Bum Chun Suh, Ki-Jong Park, Byoung Joon Kim.
Visualization: Eun Bin Cho.
Writing—original draft: Eun Bin Cho.
Writing—review & editing: Eun Bin Cho, Jin Myoung Seok, Ju-Hong Min, Bum Chun Suh, Ki-Jong Park, Byoung Joon Kim.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download