INTRODUCTION
DEFINITIONS AND MEASUREMENT OF BODY COMPOSITION
Table 1
Definitions of Body Composition Compartments

METHODS
RESULTS
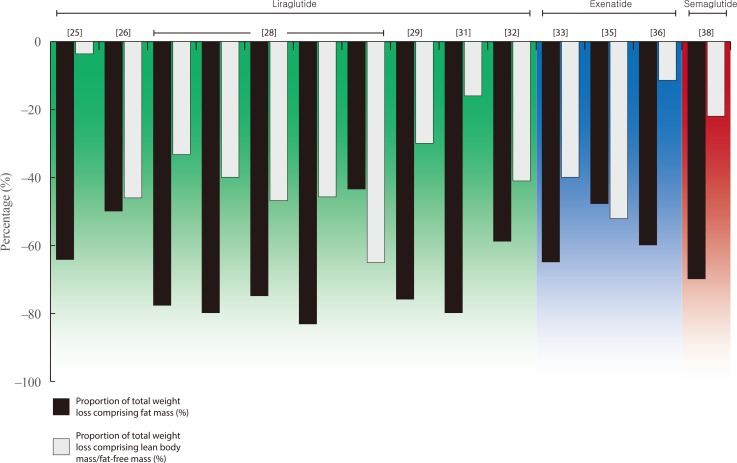 | Fig. 1 |
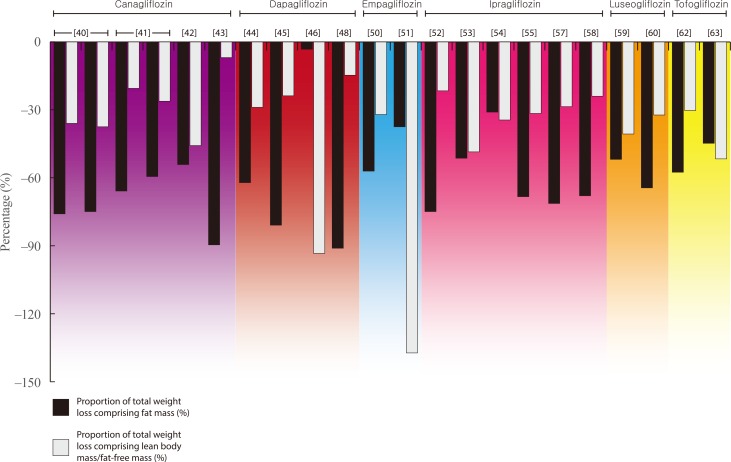 | Fig. 2 |
Table 2
Studies Reporting Changes in Body Composition with GLP-1RA Therapy
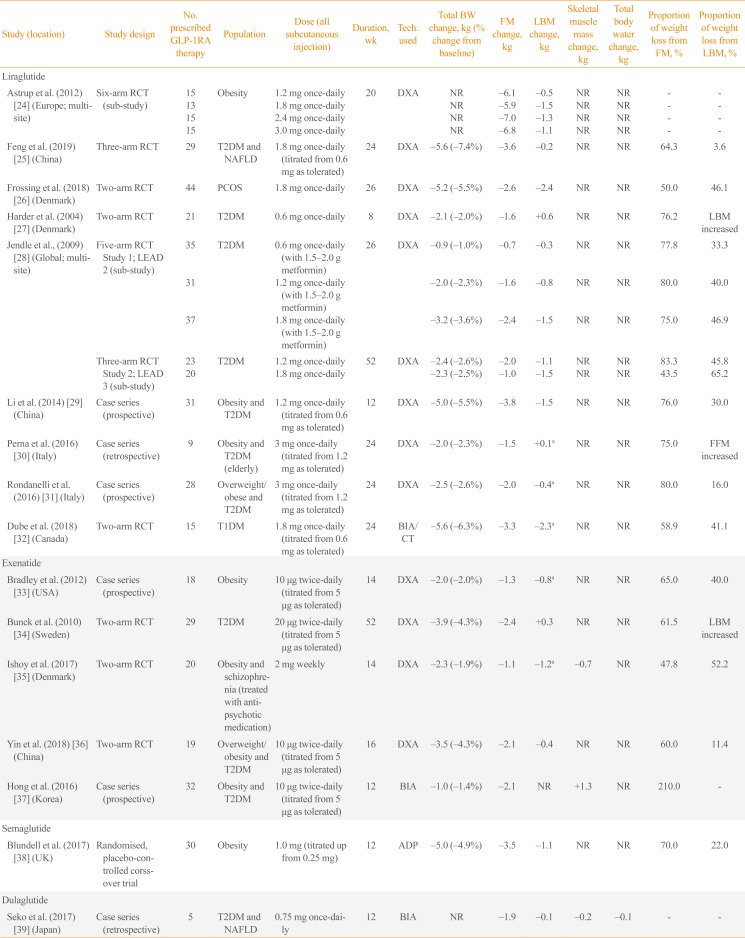
| Study (location) | Study design | No. prescribed GLP-1RA therapy | Population | Dose (all subcutaneous injection) | Duration, wk | Tech. used | Total BW change, kg (% change from baseline) | FM change, kg | LBM change, kg | Skeletal muscle mass change, kg | Total body water change, kg | Proportion of weight loss from FM, % | Proportion of weight loss from LBM, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liraglutide | |||||||||||||
| Astrup et al. (2012) [24] (Europe; multi-site) | Six-arm RCT (sub-study) | 15 | Obesity | 1.2 mg once-daily | 20 | DXA | NR | −6.1 | −0.5 | NR | NR | - | - |
| 13 | 1.8 mg once-daily | NR | −5.9 | −1.5 | NR | NR | - | - | |||||
| 15 | 2.4 mg once-daily | NR | −7.0 | −1.3 | NR | NR | - | - | |||||
| 15 | 3.0 mg once-daily | NR | −6.8 | −1.1 | NR | NR | - | - | |||||
| Feng et al. (2019) [25] (China) | Three-arm RCT | 29 | T2DM and NAFLD | 1.8 mg once-daily (titrated from 0.6 mg as tolerated) | 24 | DXA | −5.6 (−7.4%) | −3.6 | −0.2 | NR | NR | 64.3 | 3.6 |
| Frossing et al. (2018) [26] (Denmark) | Two-arm RCT | 44 | PCOS | 1.8 mg once-daily | 26 | DXA | −5.2 (−5.5%) | −2.6 | −2.4 | NR | NR | 50 | 46.1 |
| Harder et al. (2004) [27] (Denmark) | Two-arm RCT | 21 | T2DM | 0.6 mg once-daily | 8 | DXA | −2.1 (−2.0%) | −1.6 | +0.6 | NR | NR | 76.2 | LBM increased |
| Jendle et al., (2009) [28] (Global; multi-site) | Five-arm RCT Study 1; LEAD 2 (sub-study) | 35 | T2DM | 0.6 mg once-daily (with 1.5–2.0 g metformin) | 26 | DXA | −0.9 (−1.0%) | −0.7 | −0.3 | NR | NR | 77.8 | 33.3 |
| 31 | 1.2 mg once-daily (with 1.5–2.0 g metformin) | −2.0 (−2.3%) | −1.6 | −0.8 | NR | NR | 80 | 40 | |||||
| 37 | 1.8 mg once-daily (with 1.5–2.0 g metformin) | −3.2 (−3.6%) | −2.4 | −1.5 | NR | NR | 75.0 | 46.9 | |||||
| Three-arm RCT Study 2; LEAD 3 (sub-study) | 23 | T2DM | 1.2 mg once-daily | 52 | DXA | −2.4 (−2.6%) | −2.0 | −1.1 | NR | NR | 83.3 | 45.8 | |
| 20 | 1.8 mg once-daily | −2.3 (−2.5%) | −1.0 | −1.5 | NR | NR | 43.5 | 65.2 | |||||
| Li et al. (2014) [29] (China) | Case series (prospective) | 31 | Obesity and T2DM | 1.2 mg once-daily (titrated from 0.6 mg as tolerated) | 12 | DXA | −5.0 (−5.5%) | −3.8 | −1.5 | NR | NR | 76.0 | 30.0 |
| Perna et al. (2016) [30] (Italy) | Case series (retrospective) | 9 | Obesity and T2DM (elderly) | 3 mg once-daily (titrated from 1.2 mg as tolerated) | 24 | DXA | −2.0 (−2.3%) | −1.5 | +0.1a | NR | NR | 75.0 | FFM increased |
| Rondanelli et al. (2016) [31] (Italy) | Case series (prospective) | 28 | Overweight/ obese and T2DM | 3 mg once-daily (titrated from 1.2 mg as tolerated) | 24 | DXA | −2.5 (−2.6%) | −2.0 | −0.4a | NR | NR | 80.0 | 16.0 |
| Dube et al. (2018) [32] (Canada) | Two-arm RCT | 15 | T1DM | 1.8 mg once-daily (titrated from 0.6 mg as tolerated) | 24 | BIA/ CT | −5.6 (−6.3%) | −3.3 | −2.3a | NR | NR | 58.9 | 41.1 |
| Exenatide | |||||||||||||
| Bradley et al. (2012) [33] (USA) | Case series (prospective) | 18 | Obesity | 10 μg twice-daily (titrated from 5 μg as tolerated) | 14 | DXA | −2.0 (−2.0%) | −1.3 | −0.8a | NR | NR | 65 | 40 |
| Bunck et al. (2010) [34] (Sweden) | Two-arm RCT | 29 | T2DM | 20 μg twice-daily (titrated from 5 μg as tolerated) | 52 | DXA | −3.9 (−4.3%) | −2.4 | +0.3 | NR | NR | 61.5 | LBM increased |
| Ishoy et al. (2017) [35] (Denmark) | Two-arm RCT | 20 | Obesity and schizophrenia (treated with anti-psychotic medication) | 2 mg weekly | 14 | DXA | −2.3 (−1.9%) | −1.1 | −1.2a | −0.7 | NR | 47.8 | 52.2 |
| Yin et al. (2018) [36] (China) | Two-arm RCT | 19 | Overweight/ obesity and T2DM | 10 μg twice-daily (titrated from 5 μg as tolerated) | 16 | DXA | −3.5 (−4.3%) | −2.1 | −0.4 | NR | NR | 60 | 11.4 |
| Hong et al. (2016) [37] (Korea) | Case series (prospective) | 32 | Obesity and T2DM | 10 μg twice-daily (titrated from 5 μg as tolerated) | 12 | BIA | −1.0 (−1.4%) | −2.1 | NR | +1.3 | NR | 210 | - |
| Semaglutide | |||||||||||||
| Blundell et al. (2017) [38] (UK) | Randomised, placebo-controlled corss-over trial | 30 | Obesity | 1.0 mg (titrated up from 0.25 mg) | 12 | ADP | −5.0 (−4.9%) | −3.5 | −1.1 | NR | NR | 70.0 | 22.0 |
| Dulaglutide | |||||||||||||
| Seko et al. (2017) [39] (Japan) | Case series (retrospective) | 5 | T2DM and NAFLD | 0.75 mg once-daily | 12 | BIA | NR | −1.9 | −0.1 | −0.2 | −0.1 | - | - |
GLP-1RA, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; BW, body weight; FM, fat mass; LBM, lean body mass; RCT, randomised controlled trial; DXA, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; NR, not reported; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; PCOS, polycystic ovarian syndrome; LEAD, Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes phase 3 programme for liraglutide; FFM, fat-free mass; T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; BIA, bioelectrical impedance analysis; CT, computed tomography; ADP, air displacement plethysmography.
aFFM.
Table 3
Studies Reporting Changes in Body Composition with SGLT2i Therapy
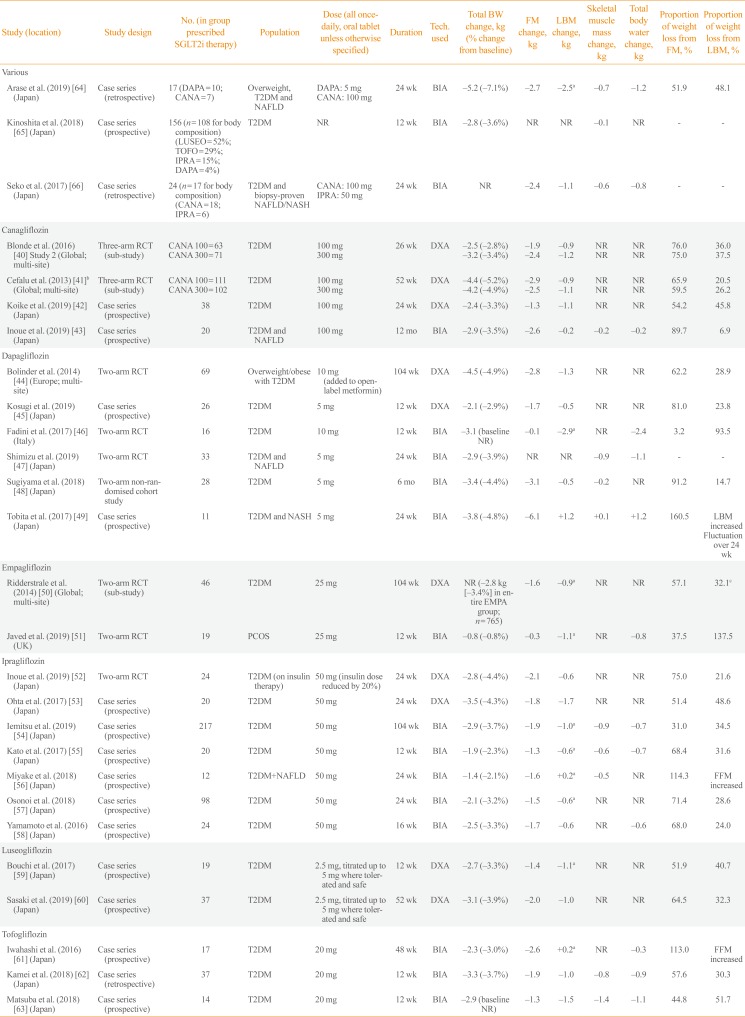
| Study (location) | Study design | No. (in group prescribed SGLT2i therapy) | Population | Dose (all once-daily, oral tablet unless otherwise specified) | Duration | Tech. used | Total BW change, kg (% change from baseline) | FM change, kg | LBM change, kg | Skeletal muscle mass change, kg | Total body water change, kg | Proportion of weight loss from FM, % | Proportion of weight loss from LBM, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Various | |||||||||||||
| Arase et al. (2019) [64] (Japan) | Case series (retrospective) | 17 (DAPA=10; CANA=7) | Overweight, T2DM and NAFLD | DAPA: 5 mg | 24 wk | BIA | −5.2 (−7.1%) | −2.7 | −2.5a | −0.7 | −1.2 | 51.9 | 48.1 |
| CANA: 100 mg | |||||||||||||
| Kinoshita et al. (2018) [65] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 156 (n=108 for body composition) (LUSEO=52%; TOFO=29%; IPRA=15%; DAPA=4%) | T2DM | NR | 12 wk | BIA | −2.8 (−3.6%) | NR | NR | −0.1 | NR | - | - |
| Seko et al. (2017) [66] (Japan) | Case series (retrospective) | 24 (n=17 for body composition) (CANA=18; IPRA=6) | T2DM and biopsy-proven NAFLD/NASH | CANA: 100 mg | 24 wk | BIA | NR | −2.4 | −1.1 | −0.6 | −0.8 | - | - |
| IPRA: 50 mg | |||||||||||||
| Canagliflozin | |||||||||||||
| Blonde et al. (2016) [40] Study 2 (Global; multi-site) | Three-arm RCT (sub-study) | CANA 100=63 | T2DM | 100 mg | 26 wk | DXA | −2.5 (−2.8%) | −1.9 | −0.9 | NR | NR | 76 | 36.0 |
| CANA 300=71 | 300 mg | −3.2 (−3.4%) | −2.4 | −1.2 | NR | NR | 75 | 37.5 | |||||
| Cefalu et al. (2013) [41]b (Global; multi-site) | Three-arm RCT (sub-study) | CANA 100=111 | T2DM | 100 mg | 52 wk | DXA | −4.4 (−5.2%) | −2.9 | −0.9 | NR | NR | 65.9 | 20.5 |
| CANA 300=102 | 300 mg | −4.2 (−4.9%) | −2.5 | −1.1 | NR | NR | 59.5 | 26.2 | |||||
| Koike et al. (2019) [42] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 38 | T2DM | 100 mg | 24 wk | DXA | −2.4 (−3.3%) | −1.3 | −1.1 | NR | NR | 54.2 | 45.8 |
| Inoue et al. (2019) [43] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 20 | T2DM and NAFLD | 100 mg | 12 mo | BIA | −2.9 (−3.5%) | −2.6 | −0.2 | −0.2 | −0.2 | 89.7 | 6.9 |
| Dapagliflozin | |||||||||||||
| Bolinder et al. (2014) [44] (Europe; multi-site) | Two-arm RCT | 69 | Overweight/obese with T2DM | 10 mg (added to open-label metformin) | 104 wk | DXA | −4.5 (−4.9%) | −2.8 | −1.3 | NR | NR | 62.2 | 28.9 |
| Kosugi et al. (2019) [45] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 26 | T2DM | 5 mg | 12 wk | DXA | −2.1 (−2.9%) | −1.7 | −0.5 | NR | NR | 81 | 23.8 |
| Fadini et al. (2017) [46] (Italy) | Two-arm RCT | 16 | T2DM | 10 mg | 12 wk | BIA | −3.1 (baseline NR) | −0.1 | −2.9a | NR | −2.4 | 3.2 | 93.5 |
| Shimizu et al. (2019) [47] (Japan) | Two-arm RCT | 33 | T2DM and NAFLD | 5 mg | 24 wk | BIA | −2.9 (−3.9%) | NR | NR | −0.9 | −1.1 | - | - |
| Sugiyama et al. (2018) [48] (Japan) | Two-arm non-randomised cohort study | 28 | T2DM | 5 mg | 6 mo | BIA | −3.4 (−4.4%) | −3.1 | −0.5 | −0.2 | NR | 91.2 | 14.7 |
| Tobita et al. (2017) [49] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 11 | T2DM and NASH | 5 mg | 24 wk | BIA | −3.8 (−4.8%) | −6.1 | 1.2 | 0.1 | 1.2 | 160.5 | LBM increased Fluctuation over 24 wk |
| Empagliflozin | |||||||||||||
| Ridderstrale et al. (2014) [50] (Global; multi-site) | Two-arm RCT (sub-study) | 46 | T2DM | 25 mg | 104 wk | DXA | NR (−2.8 kg [–3.4%] in entire EMPA group; n=765) | −1.6 | −0.9a | NR | NR | 57.1 | 32.1c |
| Javed et al. (2019) [51] (UK) | Two-arm RCT | 19 | PCOS | 25 mg | 12 wk | BIA | −0.8 (−0.8%) | −0.3 | −1.1a | NR | −0.8 | 37.5 | 137.5 |
| Ipragliflozin | |||||||||||||
| Inoue et al. (2019) [52] (Japan) | Two-arm RCT | 24 | T2DM (on insulin therapy) | 50 mg (insulin dose reduced by 20%) | 24 wk | DXA | −2.8 (−4.4%) | −2.1 | −0.6 | NR | NR | 75 | 21.6 |
| Ohta et al. (2017) [53] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 20 | T2DM | 50 mg | 24 wk | DXA | −3.5 (−4.3%) | −1.8 | −1.7 | NR | NR | 51.4 | 48.6 |
| Iemitsu et al. (2019) [54] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 217 | T2DM | 50 mg | 104 wk | BIA | −2.9 (−3.7%) | −1.9 | −1.0a | −0.9 | −0.7 | 31 | 34.0 |
| Kato et al. (2017) [55] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 20 | T2DM | 50 mg | 12 wk | BIA | −1.9 (−2.3%) | −1.3 | −0.6a | −0.6 | −0.7 | 68.4 | 31.6 |
| Miyake et al. (2018) [56] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 12 | T2DM+NAFLD | 50 mg | 24 wk | BIA | −1.4 (−2.1%) | −1.6 | +0.2a | −0.5 | NR | 114.3 | FFM increased |
| Osonoi et al. (2018) [57] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 98 | T2DM | 50 mg | 24 wk | BIA | −2.1 (−3.2%) | −1.5 | −0.6a | NR | NR | 71.4 | 28.6 |
| Yamamoto et al. (2016) [58] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 24 | T2DM | 50 mg | 16 wk | BIA | −2.5 (−3.3%) | −1.7 | −0.6 | NR | −0.6 | 68 | 24.0 |
| Luseogliflozin | |||||||||||||
| Bouchi et al. (2017) [59] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 19 | T2DM | 2.5 mg, titrated up to 5 mg where tolerated and safe | 12 wk | DXA | −2.7 (−3.3%) | −1.4 | −1.1a | NR | NR | 51.9 | 40.7 |
| Sasaki et al. (2019) [60] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 37 | T2DM | 2.5 mg, titrated up to 5 mg where tolerated and safe | 52 wk | DXA | −3.1 (−3.9%) | −2.0 | −1.0 | NR | NR | 64.5 | 32.3 |
| Tofogliflozin | |||||||||||||
| Iwahashi et al. (2016) [61] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 17 | T2DM | 20 mg | 48 wk | BIA | −2.3 (−3.0%) | −2.6 | +0.2a | NR | −0.3 | 113 | FFM increased |
| Kamei et al. (2018) [62] (Japan) | Case series (retrospective) | 37 | T2DM | 20 mg | 12 wk | BIA | −3.3 (−3.7%) | −1.9 | −1.0 | −0.8 | −0.9 | 57.6 | 30.3 |
| Matsuba et al. (2018) [63] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) | 14 | T2DM | 20 mg | 12 wk | BIA | −2.9 (baseline NR) | −1.3 | −1.5 | −1.4 | −1.1 | 44.8 | 51.7 |
SGLT2i, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor; BW, body weight; FM, fat mass; LBM, lean body mass; DAPA, dapagliflozin; CANA, canagliflozin; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; BIA, bioelectrical impedance analysis; LUSEO, luseogliflozin; TOFO, tofogliflozin; IPRA, ipragliflozin; NR, not reported; NASH, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; RCT, randomised controlled trial; DXA, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; EMPA, empagliflozin; PCOS, polycystic ovarian syndrome; FFM, fat-free mass.
aFFM; bSame as “Study 1” in Blonde et al. (2016) [41]; cCalculated using mean weight loss in entire cohort.
Table 4
Studies Reporting Changes in Body Composition with GLP-1RA and SGLT2i Combination Therapy
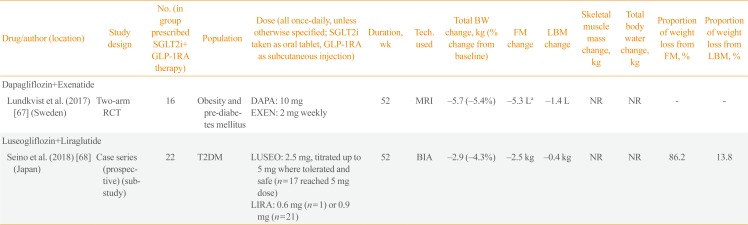
| Drug/author (location) | Study design | No. (in group prescribed SGLT2i+ GLP-1RA therapy) | Population | Dose (all once-daily, unless otherwise specified; SGLT2i taken as oral tablet, GLP-1RA as subcutaneous injection) | Duration, wk | Tech. used | Total BW change, kg (% change from baseline) | FM change | LBM change | Skeletal muscle mass change, kg | Total body water change, kg | Proportion of weight loss from FM, % | Proportion of weight loss from LBM, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dapagliflozin+Exenatide | |||||||||||||
| Lundkvist et al. (2017) [67] (Sweden) | Two-arm RCT | 16 | Obesity and pre-diabetes mellitus | DAPA: 10 mg | 52 | MRI | −5.7 (−5.4%) | −5.3 La | −1.4 L | NR | NR | - | - |
| EXEN: 2 mg weekly | |||||||||||||
| Luseogliflozin+Liraglutide | |||||||||||||
| Seino et al. (2018) [68] (Japan) | Case series (prospective) (sub-study) | 22 | T2DM | LUSEO: 2.5 mg, titrated up to 5 mg where tolerated and safe (n=17 reached 5 mg dose) | 52 | BIA | −2.9 (−4.3%) | −2.5 kg | −0.4 kg | NR | NR | 86.2 | 13.8 |
| LIRA: 0.6 mg (n=1) or 0.9 mg (n=21) |
GLP-1RA, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist; SGLT2i, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor; BW, body weight; FM, fat mass; LBM, lean body mass; RCT, randomised controlled trial; DAPA, dapagliflozin; EXEN, exenatide; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NR, not reported; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; LUSEO, luseogliflozin; LIRA, liraglutide; BIA, bioelectrical impedance analysis.
aTotal adipose tissue.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download