Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Notes
References
Figure 1
Three-dimensional reconstruction and orientation of the cone-beam computed tomography image with three reference planes and three axes. The origin was set at the sella.
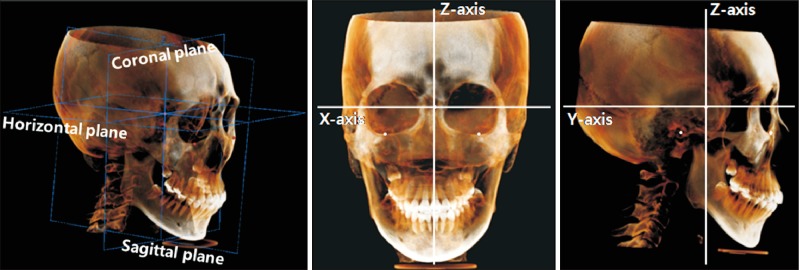
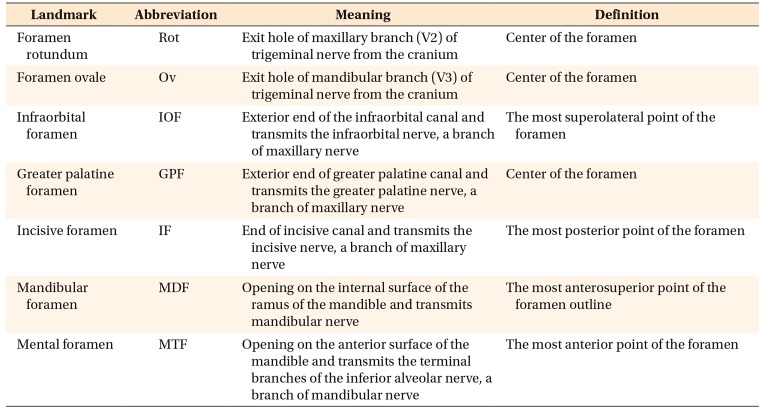
Figure 2
Description of landmarks in cone-beam computed tomography images. The images in each column have the same orientation as the corresponding images in the first row.
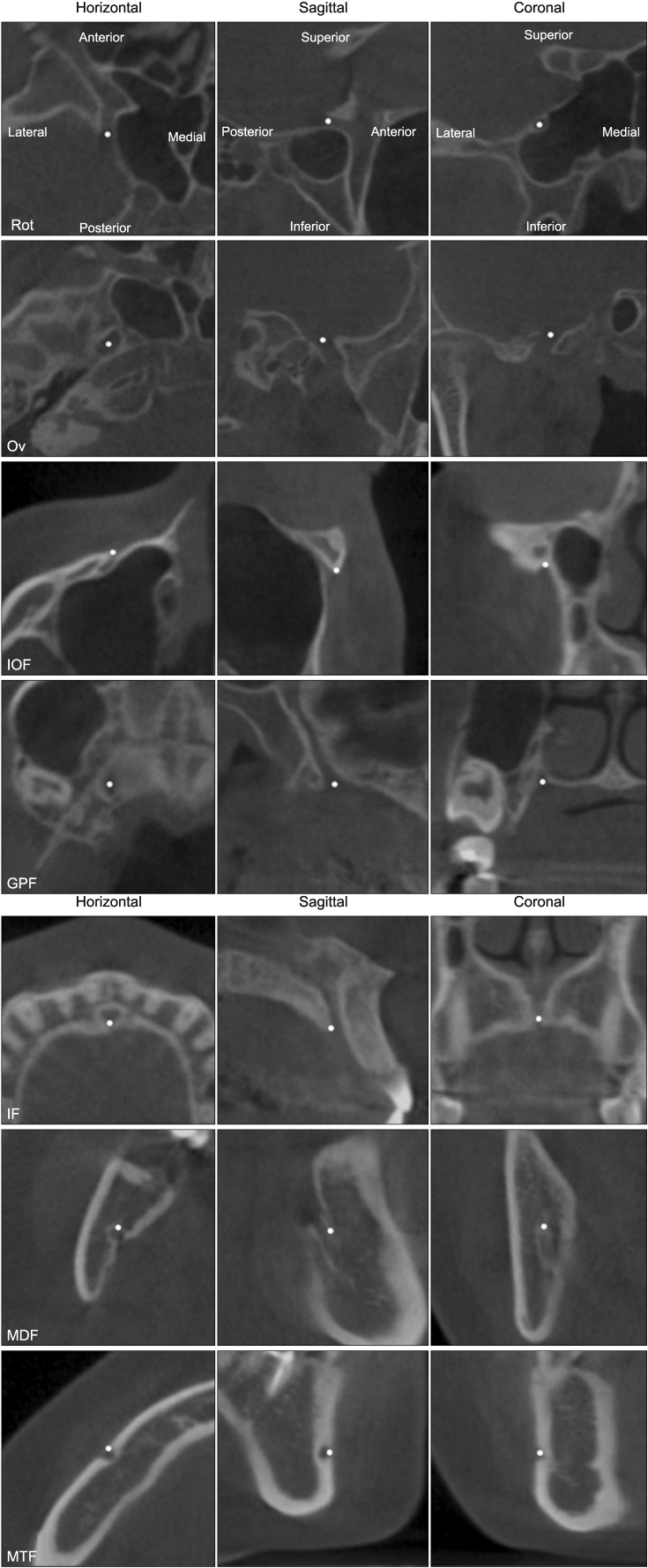
Figure 3
Linear (A) and angular (B) parameters in cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images. Identification of the landmark and measurements were performed three-dimensionally. To visualize the location of the landmarks and measurement parameters, they were simply drawn in the lateral maximum projection image of CBCT.
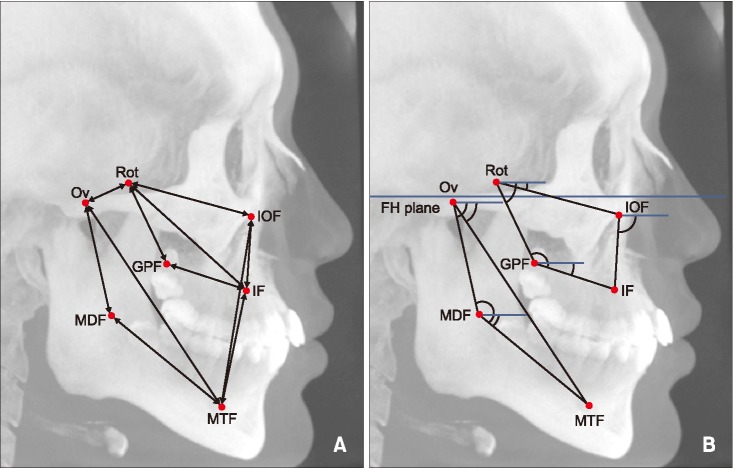
Figure 4
Spearman correlation analysis between conventional cephalometric parameters and the new cone-beam computed tomography parameters using foramina in maxillomandibular analysis.
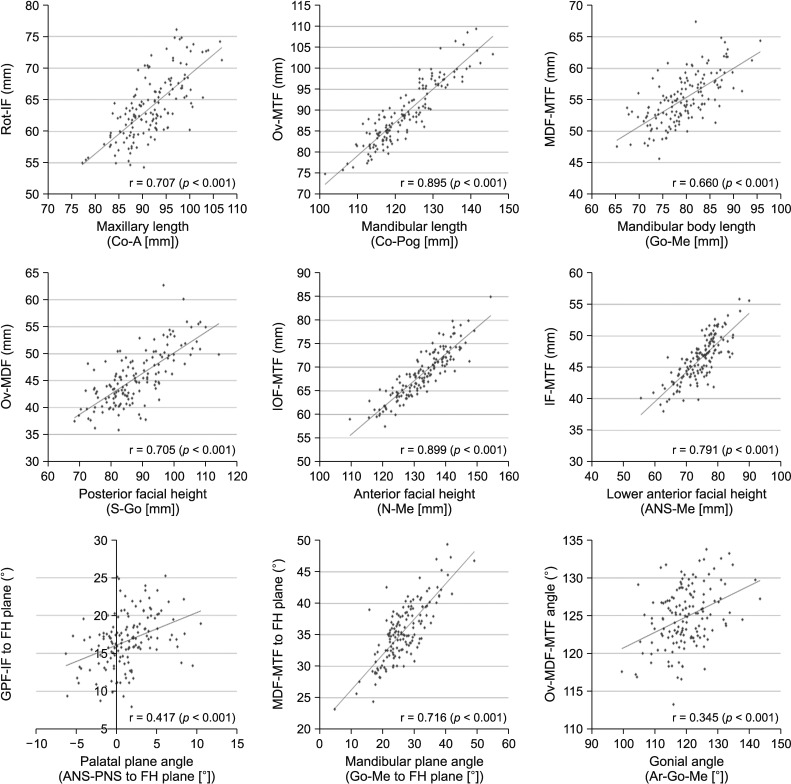
Figure 5
The locations of landmarks and measurements were visualized in the lateral maximum projection image of cone-beam computed tomography. Values of linear and angular parameters as measured in a 22-year-old male patient with skeletal Class II malocclusion (A), and a 23-year-old male patient with skeletal Class III malocclusion (B).
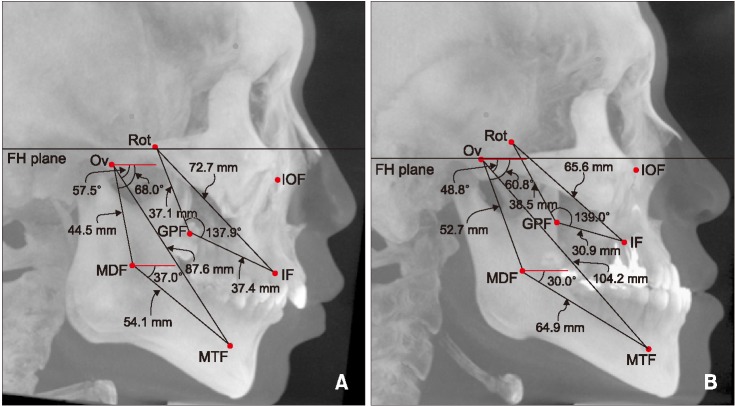
Table 3
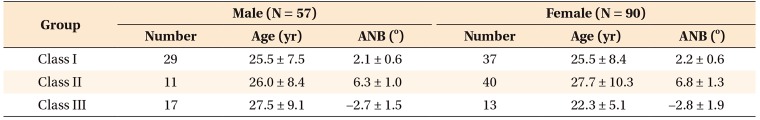
Comparison of cephalometric parameters between male patients in the three groups
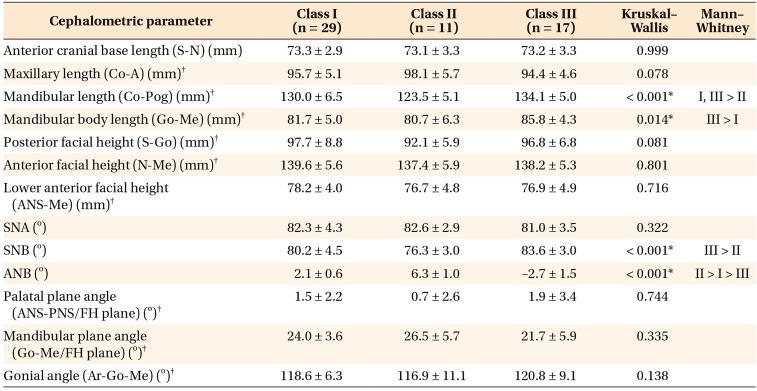
Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
S, Sella; N, nasion; Co, condylion; A, A point; Pog, pogonion; Go, gonion; Me, menton; ANS, anterior nasal spine; SNA, sellanasion-A point; SNB, sella-nasion-B point; ANB, A point-nasion-B point; PNS, posterior nasal spine; FH, Frankfort horizontal; Ar, articulare.
*p < 0.05.
†Parameters used for correlation analysis with cone-beam computed tomography parameters.
Table 4
Comparison of cephalometric parameters between female patients in the three groups
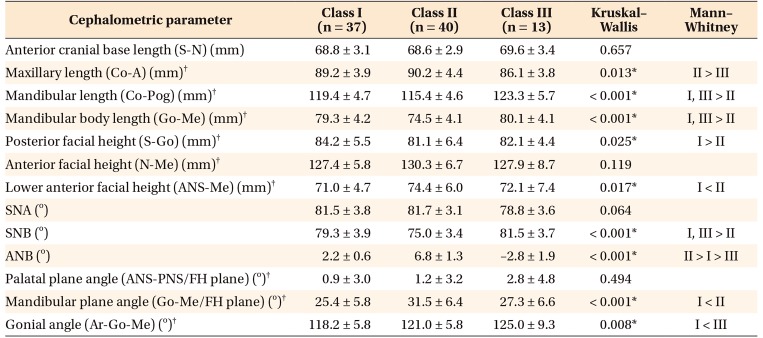
Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
See Table 3 for definition of each landmark or measurement.
*p < 0.05.
†Parameters used for correlation analysis with cone-beam computed tomography parameters.
Table 5
Comparison of foramina-based cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) parameters in male patients in the three groups
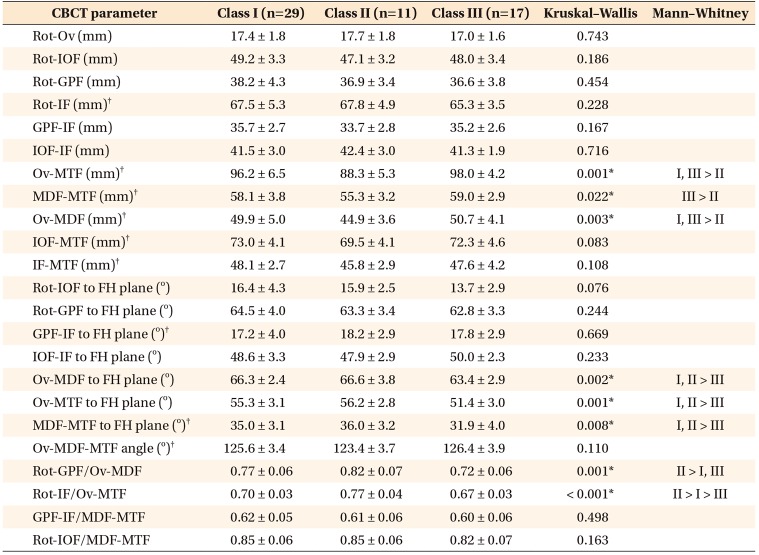
Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
FH, Frankfort horizontal plane.
See Table 2 for definition of each landmark.
*p < 0.05.
†Parameters used for correlation analysis with cephalometric parameters.
Table 6
Comparison of foramina-based cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) parameters in female patients in the three groups
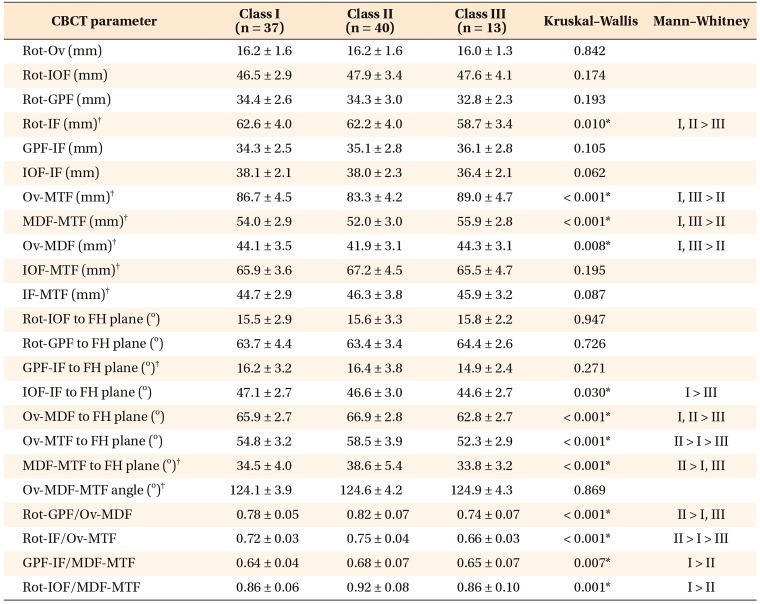
Values are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
FH, Frankfort horizontal plane.
See Table 2 for definition of each landmark.
*p < 0.05.
†Parameters used for correlation analysis with cephalometric parameters.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download