INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Literature search
• RQ1. What is the therapeutic gain from ICSs (vs. placebo) in adult patients with cough?
• RQ2. What is the magnitude of the placebo effects in ICS trials of adult patients with cough?
Data extraction
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Characteristics of the studies included
Table 1
Baseline characteristics of the 9 studies included

| Study (yr) | Design | Cough condition (duration) | No. of participants | Intervention | Control | Treatment duration (time point of outcome measurement) | Cough outcomes (score range) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Engel et al. (1989)30 | Randomized double-blind | Chronic bronchitis (cough and expectoration for at least 3 mon a year during at least the preceding 2 yr) | 18 | Medium-dose ICS (budesonide 400 mcg bid), MDI with spacer | Matching placebo | 4, 8, 12 wk | • Subjective outcomes: cough score (0–3) |
| Boulet et al. (1994)22 | Randomized double-blind (crossover design) | Non-asthmatic persistent cough (> 4 wk; all subjects had cough for longer than 8 wk); mean cough duration of 3 yr | 14 | High-dose ICS beclomethasone dipropionate 500 mcg qid), MDI with spacer | Matching placebo | 4 wk | • Subjective outcomes: cough score (0–10) |
| Pizzichini et al. (1999)23 | Randomized double-blind | Non-asthmatic chronic cough (> 1 yr); mean cough duration of 10.8 yr | 44 | Medium-dose ICS (budesonide 400 mcg bid), turbuhaler DPI | Matching placebo | 2 wk | • Subjective outcomes: cough severity VAS (0–100) |
| Ponsioen et al. (2005)26 | Randomized double-blind | Cough of ≥ 2 wk; 90% of subjects had acute or subacute cough | 133 | High-dose ICS (fluticasone propionate 500 mcg bid), MDI with spacer | Matching placebo | 2 wk | • Subjective outcomes: cough diary score (0–6) |
| Pornsuriyasak et al. (2005)25 | Randomized double-blind | Post-infectious cough (>3 wk); 95% of subjects had subacute cough; mean cough duration of 5.3 wk | 30 | Medium-dose ICS (budesonide 400 mcg bid), DPI | Matching placebo | 2, 4 wk | • Subjective outcomes: symptom score (1–20: the sum of 6 scores including cough frequency, cough bout frequency, cough associated symptom, nigh-time cough, frequency of cough medications, and number of cough medications) |
| Gillissen et al. (2007)29 | Randomized double-blind | Post-infectious cough (3–14 days following acute RTI) | 72 | High-dose ICS (HFA-budesonide dipropionate 400 mcg bid), MDI | Matching placebo | 11 days | • Subjective outcomes: cough intensity VAS (0–100) |
| • Objective outcomes: cough epochs objectively measured by Tussometry | |||||||
| Ribeiro et al. (2007)28 | Randomized double-blind | Chronic cough (> 8 wk); mean cough duration of 20 wk | 64 | High-dose ICS (CFC-beclomethasone 1500 mcg/day), MDI | Matching placebo | 2 wk | • Subjective outcomes: cough diary score (0–4) for 1) cough frequency, 2) cough severity, 3) duration of coughing, 4) sleep interruption and 5) Cough severity VAS (0–100) |
| Rytila et al. (2008)24 | Randomized double-blind | Cough with additional respiratory symptoms (> 2 mo); mean cough duration not reported | 140 | Medium-dose ICS (mometasone furoate 400 mcg), DPI | Matching placebo | 4, 8 wk | • Subjective outcomes: cough diary score (0–3) |
| Price et al. (2018)27 | Randomized double-blind | Chronic non-specific persistent respiratory symptoms (> 6 wk); a subgroup with cough | 235 | Medium-dose ICS (QVAR 80 mcg 2 puff bid), MDI | Matching placebo | 4 wk | • Subjective outcomes: cough severity VAS (0–100) |
Risk of bias assessment
RQ1. ICS therapeutic gain over a placebo effect in patients with cough
Table 2
Summary of cough severity and frequency outcome changes before and after placebo and ICS treatment in the 9 studies included

| Study | Outcome (scale) | Placebo treatment group | ICS treatment group | Therapeutic gain | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. (%) | Baseline score | Absolute change from baseline (mean ± SD) | Relative change from baseline (A, %) | No. (%) | Baseline score | Absolute change from baseline (mean ± SD) | Relative change from baseline (B, %) | (A-B) | |||
| Acute or subacute cough | |||||||||||
| Ponsioen et al. (2005)26 | Cough diary score (0–6) | 68 | 3.8 ± 1.0 | −1.9 ± 0.72 | −50.0% | 65 | 3.8 ± 1.0 | −2.4 ± 1.16 | −63.2% | +13.2% | |
| Pornsuriyasak et al. (2005)25 | Symptom score (1–20) (at 2 wk)†,‡ | 15 | 9.8 ± 2.4 | −5.53 ± 2.38 | −56.4% | 15 | 9.4 ± 5.0 | −5.47 ± 3.68 | −58.2% | +1.8% | |
| Symptom score (1–20) (at 4 wk)† | 15 | 9.8 ± 2.4 | −7.14 ± 2.12 | −72.9% | 15 | 9.4 ± 5.0 | −7.14 ± 3.73 | −76.0% | +3.1% | ||
| Gillissen et al. (2007)29 | Cough intensity VAS (0–100) | 38 | 66* | −45.1* | −68.3% | 32 | 68.6* | −43.4* | −63.3% | −5.0% | |
| Objective frequency of daytime cough epochs | 26.4 ± 15.8 | −13.1 ± 11.7 | −49.6% | 28.1 ± 16.2 | −15.4 ± 12.0 | −54.8% | +5.2% | ||||
| Chronic cough | |||||||||||
| Engel et al. (1989)30 | Cough score (0–3) (at 4 wk)‡ | 10 | 1.79 ± 0.76 | −0.16 ± 0.54 | −8.9% | 8 | 1.48 ± 0.41 | 0.15 ± 0.67 | 10.1% | −19.0% | |
| Cough score (0–3) (at 12 wk) | 10 | 1.79 ± 0.76 | −0.43 ± 0.55 | −24.0% | 8 | 1.48 ± 0.41 | −0.46 ± 0.37 | −31.1% | +7.1% | ||
| Boulet et al. (1994)22 | Daily cough score (0–10) | 7 | 1.91 ± 0.9 | −0.24 ± 0.88 | −12.6% | 7 | 3.35 ± 2.28 | −1.15 ± 1.56 | −34.3% | +21.7% | |
| Pizzichini et al. (1999)23 | Cough severity VAS (0–100) | 23 | 51 ± 24.6 | −3.7 ± 12.1 | −7.3% | 23 | 61.4 ± 24.0 | −7.7 ± 23.7 | −12.5% | +5.2% | |
| Ribeiro et al. (2007)28 | Cough severity diary score (0–4) | 20 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | −0.6 ± 0.5 | −40.0% | 44 | 1.39 ± 0.7 | −1.19 ± 0.52 | −85.6% | +45.6% | |
| Cough frequency diary score (0–4) | 2.1 ± 0.85 | −0.77 ± 0.74 | −36.7% | 1.98 ± 1.07 | −1.71 ± 0.79 | −86.4% | +49.7% | ||||
| Cough severity VAS (0–100) | 93* | −2* | −2.2% | 94* | −91* | −96.8% | +94.6% | ||||
| Rytila et al. (2008)24 | Cough diary score for morning and evening (combined; 0–3) (at 4 wk)‡ | 60 | 1.39 ± 0.46 | −0.29 ± 0.58 | −20.9% | 61 | 1.42 ± 0.47 | −0.46 ± 0.58 | −32.4% | +11.5% | |
| Cough diary score for morning and evening (combined; 0–3) (at 8 wk) | 60 | 1.39 ± 0.46 | −0.55 ± 0.77 | −39.5% | 61 | 1.42 ± 0.47 | −0.58 ± 0.70 | −40.8% | +1.3% | ||
| Price et al. (2018)27 | Cough severity VAS (0–100) | 112 | 42.52 ± 25.5 | −11.06 ± 21.05 | −26.0% | 123 | 45.09 ± 28.42 | −19.96 ± 20.89 | −44.3% | +18.3% | |
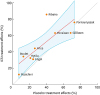 | Fig. 2Scatter plot of ICS and placebo treatment effects (relative change from baseline) in cough severity outcomes at final endpoints. Red solid line indicates linear prediction. Blue shadow represents a 95% confidence interval of the prediction.ICS, inhaled corticosteroids.
|
 | Fig. 3Forest plot of ICS treatment effects stratified by cough duration (subacute vs. chronic cough). Green squares indicate effect size and weight of each study for standard mean differences. Black diamonds represent the pooled effect size and 95% CI.SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval; ICS, inhaled corticosteroids.
|
RQ2. Placebo treatment effects in patients with cough
 | Fig. 4Forest plot of placebo treatment effects stratified by cough duration (subacute cough vs. chronic cough). Red squares indicate effect size and weight of each study for standard mean differences. Black diamonds represent the pooled effect size and 95% CIs.SE, standard error; CI, confidence interval.
|




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download