Abstract
Purpose
Teleradiology has been widely used nationwide in various ways. In order to prepare a guideline, it was recognized that a survey on the actual condition of teleradiology in Korea was necessary.
Materials and Methods
The questionnaires were administered to training hospitals. Interviews were also conducted with teleradiology centers and teleradiologists. The bid records of Government e-Procurement System (Narajangteo) was examined.
Results
The main reason for requesting teleradiology was manpower shortage. The contracts were made on a per-case basis and all were interpreted with the reading radiolgists' names on the report. The report seemed to be delivered timely and access to clinical information was possible in some cases. The teleradiology fees collected from the e-procurement system were lower than those from other subjects, which is thought to be the result of the lowest bid method.
Figures and Tables
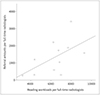
Fig. 1
Correlation between the number of referrals and reading workload per full-time radiologist in the training hospitals (p = 0.110).
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by the policy project of Korean Radiological Society in 2017: Survey on the Status of Teleradiology in Korea.
References
1. Kim GS, Han JG, Yoo HS, Do KH, Jung AY, Kang EJ, et al. 70 Years of the Korean Society of Radiology. Seoul: Seongmungak;2015.
2. Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. Portal for medical institutions. Accessed May 12, 2019. Available at. http://biz.hira.or.kr/.
3. Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. Health insurance medical care benefit cost. 2017. 07. 28. Accessed May 12, 2019. Available at. https://www.hira.or.kr/sViewer/index.do?ebookSn=39.
4. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Notice No. 2017 - 118 of the Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2017. 06. 30. Accessed May 12, 2019. Available at. http://www.mohw.go.kr/react/modules/download.jsp?BOARD_ID=5900&CONT_SEQ=340374&FILE_SEQ=209333.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download