Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
초록
대상과 방법
결과
Figures and Tables
 | Fig. 1Left breast cancer in a 44-year-old woman.A. Ultrasound image shows a 10-mm sized and irregular shaped mass (arrows).
B. The vascularity is minimal at color Doppler ultrasound image. It was classified as BI-RADS category 4A and pathologically proved as invasive ductal carcinoma.
C. An ultrasonography image showing another 5-mm sized round mass in the same breast quadrant. This lesion was also classified as BI-RADS category 4A. This small lesion was pathologically determined to be an invasive ductal carcinoma using ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy. The patient underwent breast-conserving surgery and the final diagnosis was invasive ductal carcinoma (T1a) with a multifocal ductal carcinoma in situ.
BI-RADS = Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System
|
 | Fig. 2A 39-year-old woman with a screening-detected mass in the left breast. Ultrasound image showing a 4-mm sized mass (A) with a microlobulated margin. The vascularity is not evident (B). The mass was classified as Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System category 4A, and ductal carcinoma in situ was pathologically confirmed using core needle biopsy. After breast-conserving surgery, the T1aN0 lesion was diagnosed to include an invasive ductal carcinoma with a pathologic size of 5 mm. |
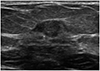 | Fig. 3A 64-year-old woman with a palpable lesion in the left breast. Ultrasound image showing a 9-mm sized mass with a complex cystic and solid pattern and microlobulated margin. The mass was classified as Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System category 4A, and ductal carcinoma in invasive ductal carcinoma was pathologically confirmed using core needle biopsy. After a modified radical mastectomy, T1aN0 cancer, including an invasive ductal carcinoma with a pathologic size of 2 mm, was diagnosed. |
Table 3
Comparisons of Immunohistopathological Characteristics between Large and Small Breast Cancers
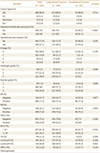
*Papillary carcinoma (n = 4), tubular carcinoma (n = 6) metaplastic carcinoma (n = 2), neuroendocrine carcinoma (n = 1), apocrine carcinoma (n = 1), medullary carcinoma (n = 1).
ER = estrogen receptor, HER-2 = human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, IDC = invasive ductal carcinoma, ILC = invasive lobar carcinoma, PR = progesterone receptor, TN = triple-negative cancer




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download