Abstract
The Alternaria species are dematiaceous fungi. Human infection due to dematiaceous fungi is uncommon. Most reported cases of alternariosis have occurred in patients with immunodeficiency. The majority of cases were solid-organ transplantation recipients. Cutaneous alternariosis lesions are usually asymptomatic solitary nodules, plaques of ulcers or subcutaneous cysts. Here we report a case of a 77-year-old female who presented with hemorrhagic skin necrosis in right arm that had developed from hemorrhagic bullae. Her prior medical history included iatrogenic Cushing's syndrome, hypertension, interstitial lung disease and congestive heart failure. Following administration of itraconazole, her lesions improved.
The Alternaria species are dematiaceous fungi, whose distinguishing feature is the formation of grey to black colonies on culture media due to the presence of melanin pigment in their cell wall. These fungi commonly colonize human skin but are generally nonpathogenic in humans. The invasive disease caused by these organisms is called phaeohyphomycosis12. In Korea, Alternaria comprises 7.8% of deep cutaneous fungal infections and is the second most common pathogen among deep cutaneous fungal infections due to opportunistic infections3. Most reported cases of alternariosis have developed in immunocompromised hosts. The majority of these cases involved solid organ transplantation recipients; however, patients with Cushing's syndrome, autoimmune diseases, lymphoproliferative disorders, nephritic syndrome, congenital immunodeficiency or acquired immune deficiency syndrome have also been described45678. Cutaneous alternariosis is characterized with ulcerative papules, nodules, and plaques located on the face, knees, hands and forearms. Cysts and sinus tract may develop in severe disease. Systemic spread is considered to be rare9. Here we report a case of cutaneous alternariosis presenting with hemorrhagic skin necrosis in the right arm that had developed from hemorrhagic bullae.
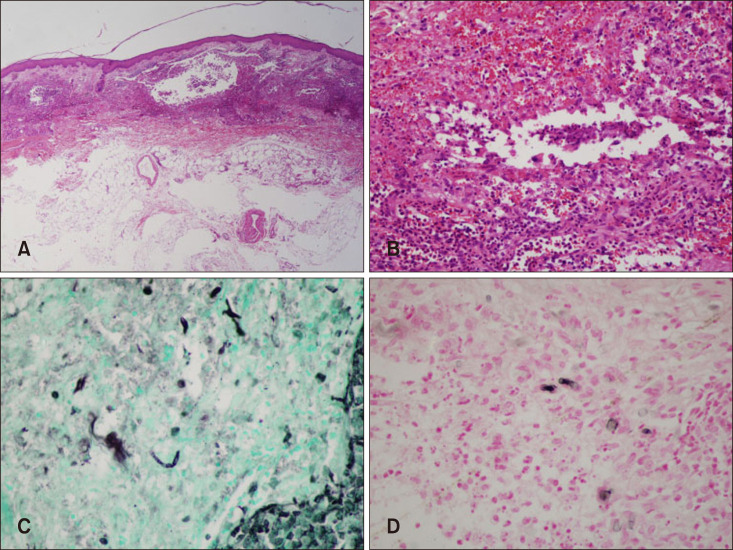
A 77-year-old female presented to the emergency room with right forearm pain. Seven days previously, erythema and swelling had developed on her right forearm and, three days later, bullae with bruising had developed. She had been taking prednisolone daily for 3 months for iatrogenic Cushing's syndrome. Her medical history also included hypertension, interstitial lung disease, and congestive heart failure, and she had undergone left total knee replacement due to osteoarthritis. Clinical examination revealed involvement of the right forearm with hemorrhagic bullae, swelling, and tenderness (Fig. 1A). There was no limitation in joint range of motion in the right wrist. Her body temperature was 37.5℃. Laboratory results indicated a white blood cell count of 11,760/mm3 (neutrophils, 86.4%), hemoglobin 13.6 g/dl, platelet 147,000/mm3, aspartate aminotransferase 41 IU/L, and alanine aminotransferase 73 IU/L. Magnetic resonance imaging of her wound revealed diffuse subcutaneous swelling with reticular enhancement. Fascia and muscle enhancement were not observed (Fig. 1B). Ampicillin/sulbactam was started as empirical antibiotic therapy (3 g every 6 hours) and a skin biopsy was performed. The biopsy showed suppurative dermal inflammation with granulomatous inflammation, and leukocytoclastic vasculitis was also noted. Using Fontana-Masson staining and the Gomori-methenamine silver stain revealed irregular septated fungal hyphae with budding and vesicles (Fig. 2). Aspiration of the bullae was performed, after which we administered itraconazole 200 mg twice daily and discontinued the ampicillin/sulbactam. A culture of the bullae aspiration confirmed the Alternaria species, noted as Alternaria alternata using the API 20C AUS system (BioMérieux, Marcy I'Etoile, France). Following this confirmation, we diagnosed subcutaneous alternariosis and, after administration of itraconazole for 6 weeks, her forearm lesion had improved. We received the patient's consent form about publishing all photographic materials.
Cutaneous alternariosis may occur following trauma or through colonization of a preexisting lesion or, more rarely, through hematologic spread, most commonly from pulmonary infection due to inhalation of the organism10. Here, the history of trauma was unclear, but there was no evidence of pulmonary infection and skin disease prior to the Alternaria infection. Therefore, we presumed that, in this patient, the cutaneous alternariosis was extrinsic and due to trauma. Additionally, the skin was thinning due to iatrogenic Cushing's syndrome, with high probability of pathogen invasion subsequent to skin trauma.
Clinical manifestations of Alternaria infections usually involve cutaneous or subcutaneous lesions, with ocular, sinusal or ungueal infetions being uncommon. Cutaneous alternariosis lesions are so variable as to be nonspecific and include crusted ulcers, verrucous or granulomatous and multilocular lesions. Subcutaneous nodules; usually involve asymptomatic solitary nodules, plaques of ulcers, or subcutaneous cysts. Lesions usually occur in exposed areas of the extremities and imply direct inoculation of the fungi from environmental sources11. However, hemorrhagic bullae in Alternaria infection have not yet been reported. Generally, hemorrhagic bullae are observed in case of infectious disease such as necrotizing fasciitis, bullous cellulitis, bullous impetigo, and ecthyma gangrenosum, and can develop due to a drug reaction, hypersensitivity, autoimmune bullous pemphigoid, pemphigoid vulgaris, pyoderma gangrenosum and vascular problems12. This case shows that cutaneous alternariosis can also present with hemorrhagic bullae and skin necrosis. Hsu et al.13 reported the mean duration from rash formation to diagnosis of alternariosis infection was 3.7 months. Most of cutaneous alternariosis showed subacute and chronic clinical course13. Most of cutaneous alternariosis showed subacute and chronic clinical course. But this case showed acute and aggressive course. It is different from the previous reported cases.
The diagnosis should be confirmed with a biopsy for histopathology and culture. A typical histologic lesion consists of a mixed granulomatous inflammatory infiltrate of the dermis intermingled with the presence of round or ovalshaped fungal cells and hyphae, that are identifiable with the Gomori-methenamine silver stain. A specific melanin stain such as Fontana-Masson can be used to identify the dark pigmented fungi accurately. Hyphae are mainly observed in immunocompromised hosts, and round spores appear mainly in immunocompetent hosts1. A. alternata has a distinctive form that is easy to identify, but it may be difficult to distinguish from other species of Alternaria, therefore molecular biologic tests may be helpful14. We performed a direct sequencing analysis of the internal transcribed spacer region of the ribosomal DNA to identify the causative fungus, and the species was noted as A. alternata.
Treatment of cutaneous alternariosis remains non-standardized. Small, well-defined lesions can be expected to resolve with excision alone. Otherwise, systemic antifungal therapy is needed as treatment of the underlying disease is essential. However, no consensus has been reached regarding the most appropriate antifungal agents or the duration of treatment. Itraconazole, amphotericin B, miconazole, terbinafine and ketoconazole efficacy has been reported. Of these, itraconazole has been used preferentially. Although spontaneous remission has sometimes been noted, the untreated disease usually follows a chronic course. Relapse occurs frequently even after months of long-term treatment. Therefore, long-term follow-up and prolongation of treatment are essential for at least one month after clinical resolution15. If possible, reduction of immunosuppressive agents can be helpful in the treatment16.
In conclusion, phaeohyphomycosis can be considered a potential etiologic agent when lesions present as hemorrhagic bullae with skin necrosis.
References
2. Ajello L, Georg LK, Steigbigel RT, Wang CJ. A case of phaeohyphomycosis caused by a new species of Phialophora. Mycologia. 1974; 66:490–498. PMID: 4601425.

3. Kim MS, Kim JK, Lee MW, Moon KC, Kim BJ, Son SW, et al. Epidemiology of deep cutaneous fungal infections in Korea (2006-2010). J Dermatol. 2015; 42:962–966. PMID: 26105506.

4. Romano C, Vanzi L, Massi D, Difonzo EM. Subcutaneous alternariosis. Mycoses. 2005; 48:408–412. PMID: 16262877.

5. Uenotsuchi T, Moroi Y, Urabe K, Fukagawa S, Tsuji G, Matsuda T, et al. Cutaneous alternariosis with chronic granulomatous disease. Eur J Dermatol. 2005; 15:406–408. PMID: 16172055.
6. Magina S, Lisboa C, Santos P, Oliveira G, Lopes J, Rocha M, et al. Cutaneous alternariosis by Alternaria chartarum in a renal transplanted patient. Br J Dermatol. 2000; 142:1261–1262. PMID: 10848774.

7. Laumaillé C, Le Gall F, Degeilh B, Guého E, Huerre M. [Cutaneous Alternaria infectoria infection after liver transplantation]. Ann Pathol. 1998; 18:192–194. French. PMID: 9706345.
8. Wiest PM, Wiese K, Jacobs MR, Morrissey AB, Abelson TI, Witt W, et al. Alternaria infection in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: case report and review of invasive alternaria infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1987; 9:799–803. PMID: 3326127.

9. Akman A, Sakalli Cakcak D, Ozhak Baysan B, Yazisiz V, Terzioglu E, Ciftcioglu MA, et al. Cutaneous alternariosis in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2007; 16:993–996. PMID: 18042595.

10. Elder DE. Lever's histopathology of the skin. 11th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins;2015. p. 739–740.
11. Lyke KE, Miller NS, Towne L, Merz WG. A case of cutaneous ulcerative alternariosis: rare association with diabetes mellitus and unusual failure of itraconazole treatment. Clin Infect Dis. 2001; 32:1178–1187. PMID: 11283807.

12. Hsiao CT, Lin LJ, Shiao CJ, Hsiao KY, Chen IC. Hemorrhagic bullae are not only skin deep. Am J Emerg Med. 2008; 26:316–319. PMID: 18358943.

13. Hsu CC, Chang SS, Lee PC, Chao SC. Cutaneous alternariosis in a renal transplant recipient: a case report and literature review. Asian J Surg. 2015; 38:47–57. PMID: 25554667.

14. Sohng SH, Choi JS, Kim YW, Kim BS, Choi JH, Shin DH. A case of cutaneous infection by Alternaria alternata. Korean J Med Mycol. 2014; 19:76–81.
15. Acland KM, Hay RJ, Groves R. Cutaneous infection with Alternaria alternata complicating immunosuppression: successful treatment with itraconazole. Br J Dermatol. 1998; 138:354–356. PMID: 9602891.
16. Gilaberte M, Bartralot R, Torres JM, Reus FS, Rodríguez V, Alomar A, et al. Cutaneous alternariosis in transplant recipients: clinicopathologic review of 9 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005; 52:653–659. PMID: 15793517.

Fig. 1
(A) Tender multiple ulceration and several hemorrhagic bullae with erythematous base on the right forearm area. (B) Diffuse subcutaneous swelling with reticular enhancement was noted. Swelling of dermis and the peripheral region is noted. These lesions show heterogenous signal intensity on both T1WI and T2WI without significant enhancement.
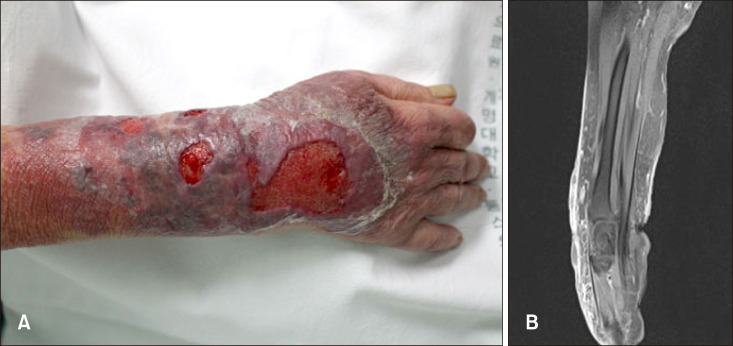
Fig. 2
Histological examination of a biopsy specimen from a right forearm. (A, B) Acute suppurative dermal inflammation with granulomatous inflammation (Hematoxylin & eosin stain, A: ×10, B: ×40). (C) Gomori-methenamine silver stain showed branched fungal hyphae (×400). (D) Fontana-Masson stain showed the presence of melanin pigment in the fungal wall (×400).




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download