INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Patients
 | Fig. 1Patient enrollment diagram. Clinical data of 1,025 cirrhotic patients with HVPG measurements were collected retrospectively between January 2008 and June 2013. After excluding 453 patients, 572 non-critically-ill cirrhotic patients were analyzed. The severity of HVPG was divided into the following five HS groups according to previously reported cutoffs: group 1, 6–9 mmHg; group 2, 10–12 mmHg; group 3, 13–16 mmHg; group 4, 17–20 mmHg; and group 5, > 20 mmHg. Clinical stages were defined according to the classification by D'Amico et al.1417HVPG = hepatic venous pressure gradient, HS = hemodynamic stage, UNL = upper normal limit.
|
HVPG measurement
HVPG subgroup, clinical stage, and MELD score
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Baseline characteristics of patients
Table 1
Clinical characteristics of enrolled patients
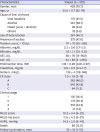
Patient characteristics according to the severity of PHT
Table 2
Patient characteristics and prognostic stages according to HS-1 groups

Cumulative survival according to CP class, clinical stage, and HVPG grade
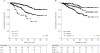 | Fig. 3Cumulative survival according to CP class and clinical stage. (A) The mortality rate differed significantly between CP classes A, B, and C (all P < 0.001, log-rank test). (B) The cumulative survival rate was significantly higher for both clinical stages 1 and 2 than for the decompensated stage (both P < 0.001, log-rank test).CP = Child-Pugh.
|
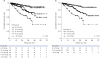 | Fig. 4Cumulative survival according to HVPG groups with hemodynamic stage-1 (HS-1) and HS-2. (A) The cumulative survival differed between following HS-1 groups: group 1 vs. 3, group 1 vs. 5, group 2 vs. 5, and group 4 vs. 5 (all P < 0.001, log-rank test). (B) However, the use of the traditional HVPG cutoffs of 10 and 16 mmHg did not improve the discrimination of mortality. Dividing HS into three groups for HS-2 (6–12, 13–20, and > 20 mmHg) resulted in significant differences in the 1- and 3-year cumulative survival rates: 96.6%, 94.0%, and 84.1% for the 1-year cumulative survival, respectively, and 91.4%, 75.3%, and 57.1% for the 3-year cumulative survival (P < 0.001, log-rank test).HVPG = hepatic venous pressure gradient, HS = hemodynamic stage.
|
Predictors of long-term mortality
Table 3
Cox regression analysis of variable factors and HVPG grades for mortality

Survival analysis in the presence of hypoalbuminemia and MELD groups
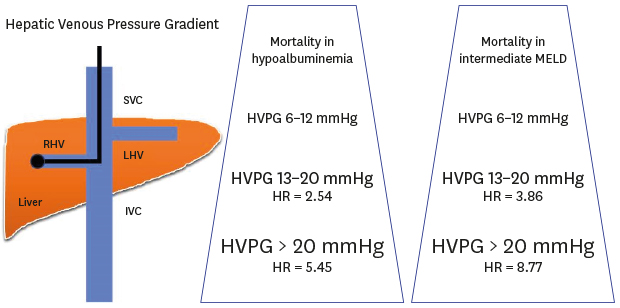
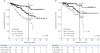 | Fig. 5Cumulative survival according to patients with hypoalbuminemia and an intermediate MELD score. (A) The mortality rates was significantly higher for HVPG 13–20 mmHg (HR, 2.54; 95% CI, 1.28–5.06; P = 0.008) and HVPG > 20 mmHg (HR, 5.45; 95% CI, 2.55–11.62; P < 0.001) than for HVPG 6–12 mmHg in patients with hypoalbuminemia. (B) When we divided the MELD scores into three groups (6–9, 10–15, and ≥ 16), in the intermediate-MELD-score group (score of 10–15), the mortality rates was significantly higher for HVPG 13–20 mmHg (HR,3.86; 95% CI, 1.16–12.91; P = 0.028) and HVPG > 20 mmHg (HR, 8.77; 95% CI, 2.41–31.94; P = 0.001) than for HVPG 6–12 mmHg.CI = confidence interval, HR = hazard ratio, HVPG = hepatic venous pressure gradient, MELD = model for end-stage liver disease.
|




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download