INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
1. Search strategy and eligibility criteria
2. Data extraction and quality assessment
3. Kaplan-Meier analysis
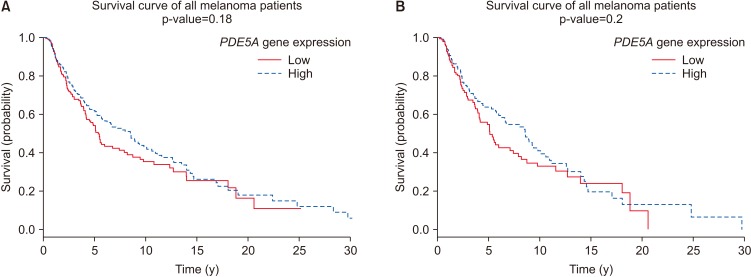 | Fig. 1Kaplan-Meier survival curve for differential expression levels of PDE5A gene in (A) 470 patients (180 females and 290 males) with a diagnosis of melanoma at any tumor stage (0–IV), ages 14–91 years; and (B) specifically male melanoma patients (n=287) with a diagnosis of melanoma at any tumor stage (0–IV), ages 18–91 years. Melanoma prognosis unaffected by high or low PDE5A expression in patients, regardless of gender, age, or tumor stage. |
RESULTS
1. Study selection and characteristics
Table 1
Study characteristics of observational studies
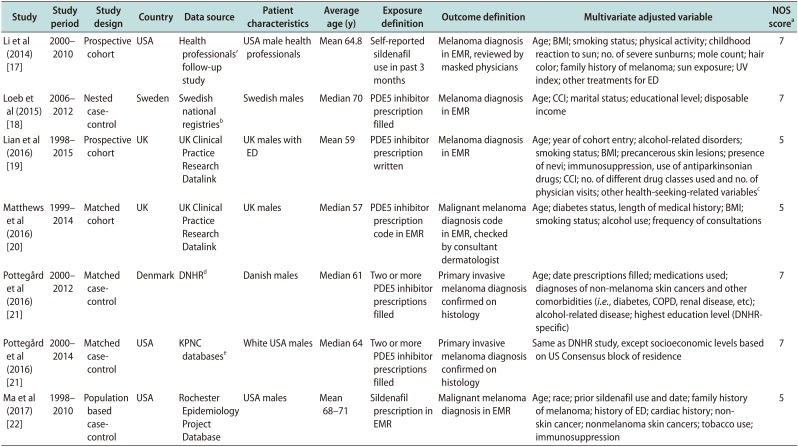
| Study | Study period | Study design | Country | Data source | Patient characteristics | Average age (y) | Exposure definition | Outcome definition | Multivariate adjusted variable | NOS scorea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al (2014) [17] | 2000–2010 | Prospective cohort | USA | Health professionals' follow-up study | USA male health professionals | Mean 64.8 | Self-reported sildenafil use in past 3 months | Melanoma diagnosis in EMR, reviewed by masked physicians | Age; BMI; smoking status; physical activity; childhood reaction to sun; no. of severe sunburns; mole count; hair color; family history of melanoma; sun exposure; UV index; other treatments for ED | 7 |
| Loeb et al (2015) [18] | 2006–2012 | Nested casecontrol | Sweden | Swedish national registriesb | Swedish males | Median 70 | PDE5 inhibitor prescription filled | Melanoma diagnosis in EMR | Age; CCI; marital status; educational level; disposable income | 7 |
| Lian et al (2016) [19] | 1998–2015 | Prospective cohort | UK | UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink | UK males with ED | Mean 59 | PDE5 inhibitor prescription written | Melanoma diagnosis in EMR | Age; year of cohort entry; alcohol-related disorders; smoking status; BMI; precancerous skin lesions; presence of nevi; immunosuppression, use of antiparkinsonian drugs; CCI; no. of different drug classes used and no. of physician visits; other health-seeking-related variablesc | 5 |
| Matthews et al (2016) [20] | 1999–2014 | Matched cohort | UK | UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink | UK males | Median 57 | PDE5 inhibitor prescription code in EMR | Malignant melanoma diagnosis code in EMR, checked by consultant dermatologist | Age; diabetes status, length of medical history; BMI; smoking status; alcohol use; frequency of consultations | 5 |
| Pottegård et al (2016) [21] | 2000–2012 | Matched casecontrol | Denmark | DNHRd | Danish males | Median 61 | Two or more PDE5 inhibitor prescriptions filled | Primary invasive melanoma diagnosis confirmed on histology | Age; date prescriptions filled; medications used; diagnoses of non-melanoma skin cancers and other comorbidities (i.e., diabetes, COPD, renal disease, etc); alcohol-related disease; highest education level (DNHRspecific) | 7 |
| Pottegård et al (2016) [21] | 2000–2014 | Matched casecontrol | USA | KPNC databasese | White USA males | Median 64 | Two or more PDE5 inhibitor prescriptions filled | Primary invasive melanoma diagnosis confirmed on histology | Same as DNHR study, except socioeconomic levels based on US Consensus block of residence | 7 |
| Ma et al (2017) [22] | 1998–2010 | Population based casecontrol | USA | Rochester Epidemiology Project Database | USA males | Mean 68–71 | Sildenafil prescription in EMR | Malignant melanoma diagnosis in EMR | Age; race; prior sildenafil use and date; family history of melanoma; history of ED; cardiac history; nonskin cancer; nonmelanoma skin cancers; tobacco use; immunosuppression | 5 |
NOS: Newcastle-Ottawa Scale, EMR: electronic medical record, BMI: body mass index, UV: ultraviolet, ED: erectile dysfunction, PDE5: phosphodiesterase 5, CCI: Charlson Comorbidity Index, DNHR: Danish Nationwide Health Registries, COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, KPNC: Kaiser Permanente Northern California.
aThe NOS is assessed on a 9-point scale based on the following criterion: selection, comparability, and outcome. bSwedish national registries include the Swedish Prescribed Drug Register, Swedish Melanoma Register, Prostate Cancer Data Base Sweden, and Swedish Cancer Registry. cOther health-seeking-related variables include influenza vaccination, referral to colonoscopy, and prostatespecific antigen testing. dDNHR include the Danish Cancer Registry, National Prescription Registry, National Registry of Patients, Danish Education Registries, and Danish Civil Registration System. eKPNC databases include the KPNC Registry, KPNC pharmacy database, and other KPNC electronic medical record databases.
2. No causal relationship between phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor use and melanoma
Table 2
Risk assessment between phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor exposure and melanoma
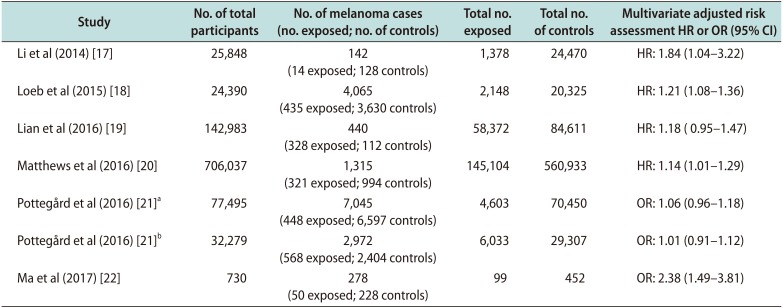
| Study | No. of total participants | No. of melanoma cases (no. exposed; no. of controls) | Total no. exposed | Total no. of controls | Multivariate adjusted risk assessment HR or OR (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li et al (2014) [17] | 25,848 | 142 (14 exposed; 128 controls) | 1,378 | 24,470 | HR: 1.84 (1.04–3.22) |
| Loeb et al (2015) [18] | 24,390 | 4,065 (435 exposed; 3,630 controls) | 2,148 | 20,325 | HR: 1.21 (1.08–1.36) |
| Lian et al (2016) [19] | 142,983 | 440 (328 exposed; 112 controls) | 58,372 | 84,611 | HR: 1.18 ( 0.95–1.47) |
| Matthews et al (2016) [20] | 706,037 | 1,315 (321 exposed; 994 controls) | 145,104 | 560,933 | HR: 1.14 (1.01–1.29) |
| Pottegård et al (2016) [21]a | 77,495 | 7,045 (448 exposed; 6,597 controls) | 4,603 | 70,450 | OR: 1.06 (0.96–1.18) |
| Pottegård et al (2016) [21]b | 32,279 | 2,972 (568 exposed; 2,404 controls) | 6,033 | 29,307 | OR: 1.01 (0.91–1.12) |
| Ma et al (2017) [22] | 730 | 278 (50 exposed; 228 controls) | 99 | 452 | OR: 2.38 (1.49–3.81) |
HR: hazard ratio, OR: odds ratio, CI: confidence interval.
aDanish Nationwide Health Registries (DNHR) include the Danish Cancer Registry, National Prescription Registry, National Registry of Patients, Danish Education Registries, and Danish Civil Registration System. bKaiser Permanente Northern California (KPNC) databases include the Kaiser Permanente Northern California Cancer Registry, KPNC pharmacy database, and other KPNC electronic medical record databases.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download