Abstract
Purpose
As the functional demands for activities in elderly patients are increasing according to their life extension, the need for surgical treatment is also increasing in elderly patients with displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. In addition to the extensile lateral approach (ELA), which is a surgical procedure that showed good results on intra-articular calcaneal fractures, the minimally invasive approach (MIA) also showed an outstanding result. This study compared the radiological and clinical results of intra-articular calcaneus fractures in elderly patients in two groups: ELA and MIA.
Materials and Methods
Thirty patients aged over 65 years with intra-articular calcaneus fractures, who could be followed-up more than 14 months, were included in this study. Thirteen patients of the MIA group and 17 patients of the ELA group were analyzed retrospectively using radiological and clinical assessments.
Results
No significant difference in union time, posterior facet reduction accuracy, subtalar osteoarthritis frequency, Bohler angle, calcaneal width, American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score, visual analogue scale score, 36–item short form survey, and foot function index was observed between the two groups. The p-value of the average height of the calcaneus correction, average length of calcaneal correction, and average loss of correction length were <0.001, 0.005, and 0.015, respectively. The incidence of complications, including soft tissue necrosis and bone infection, were 23.1% in the ELA group and none in the MIA group.
Go to : 
References
1. Järvholm U, Körner L, Thorén O, Wiklund LM. Fractures of the calcaneus. A comparison of open and closed treatment. Acta Orthop Scand. 55:652–656. 1984.

2. Su J, Cao X. Can operations achieve good outcomes in elderly patients with Sanders II-III calcaneal fractures? Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e7553. 2017.

3. Gaskill T, Schweitzer K, Nunley J. Comparison of surgical outcomes of intraarticular calcaneal fractures by age. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 92:2884–2889. 2010.

4. Sanders R. Displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 82:225–250. 2000.

5. Basile A. Operative versus nonoperative treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures in elderly patients. J Foot Ankle Surg. 49:25–32. 2010.

6. Herscovici D Jr, Widmaier J, Scaduto JM, Sanders RW, Walling A. Operative treatment of calcaneal fractures in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 87:1260–1264. 2005.

7. Hatzokos I, Karataglis D, Papadopoulos P, Dimitriou C, Christodoulou A, Pournaras J. Treatment of intraarticular comminuted os calcis fractures. Orthopedics. 29:25–29. 2006.

8. Khorbi A, Chebil M, Ben Maitigue M, et al. [Screw fixation without bone graft of calcaneal joint fractures: 35 cases]. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot. 92:45–51. 2006; French.
9. McGarvey WC, Burris MW, Clanton TO, Melissinos EG. Calcaneal fractures: indirect reduction and external fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 27:494–499. 2006.

10. Schepers T, Patka P. Treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures by ligamentotaxis: current concepts' review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 129:1677–1683. 2009.

11. Mittlmeier T, Morlock MM, Hertlein H, et al. Analysis of morphology and gait function after intraarticular calcaneal fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 7:303–310. 1993.

12. Benirschke SK, Sangeorzan BJ. Extensive intraarticular fractures of the foot. Surgical management of calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 292:128–134. 1993.
13. Boack DH, Wichelhaus A, Mittlmeier T, Hoffmann R, Haas NP. [Therapy of dislocated calcaneus joint fracture with the AO calcaneus plate]. Chirurg. 69:1214–1223. 1998; German.
14. Letournel E. Open treatment of acute calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 290:60–67. 1993.

15. Zwipp H, Tscherne H, Thermann H, Weber T. Osteosynthesis of displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus. Results in 123 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 290:76–86. 1993.
16. Dhillon MS, Bali K, Prabhakar S. Controversies in calcaneus fracture management: a systematic review of the literature. Musculoskelet Surg. 95:171–181. 2011.

17. Folk JW, Starr AJ, Early JS. Early wound complications of operative treatment of calcaneus fractures: analysis of 190 fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 13:369–372. 1999.

18. Burdeaux BD. Reduction of calcaneal fractures by the McReyn-olds medial approach technique and its experimental basis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 177:87–103. 1983.

19. Mann RA. Arthrodesis of the foot and ankle. Coughlin MJ, Mann RA, Saltzman CL, editors. Surgery of the foot and ankle. Vol 1. 8th ed.Philadelphia, Mosby: 1091–1123;2007.
20. Kline AJ, Anderson RB, Davis WH, Jones CP, Cohen BE. Minimally invasive technique versus an extensile lateral approach for intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 34:773–780. 2013.

21. Weber M, Lehmann O, Sägesser D, Krause F. Limited open reduction and internal fixation of displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 90:1608–1616. 2008.

22. Hospodar P, Guzman C, Johnson P, Uhl R. Treatment of displaced calcaneus fractures using a minimally invasive sinus tarsi approach. Orthopedics. 31:1112. 2008.

23. Johal HS, Buckley RE, Le IL, Leighton RK. A prospective randomized controlled trial of a bioresorbable calcium phosphate paste (alpha-BSM) in treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. J Trauma. 67:875–882. 2009.
24. Longino D, Buckley RE. Bone graft in the operative treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures: is it helpful? J Orthop Trauma. 15:280–286. 2001.

25. Su Y, Chen W, Zhang T, Wu X, Wu Z, Zhang Y. Bohler's angle's role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures: a retrospective study. BMC Surg. 13:40. 2013.

26. Gonzalez TA, Lucas RC, Miller TJ, Gitajn IL, Zurakowski D, Kwon JY. Posterior facet settling and changes in Bohler's angle in operatively and nonoperatively treated calcaneus fractures. Foot Ankle Int. 36:1297–1309. 2015.

27. Backes M, Dorr MC, Luitse JS, Goslings JC, Schepers T. Predicting loss of height in surgically treated displaced intraarticular fractures of the calcaneus. Int Orthop. 40:513–518. 2016.

28. Stulik J, Stehlik J, Rysavy M, Wozniak A. Minimally-invasive treatment of intraarticular fractures of the calcaneum. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 88:1634–1641. 2006.

29. Sanders R, Fortin P, DiPasquale T, Walling A. Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 290:87–95. 1993.
Go to : 
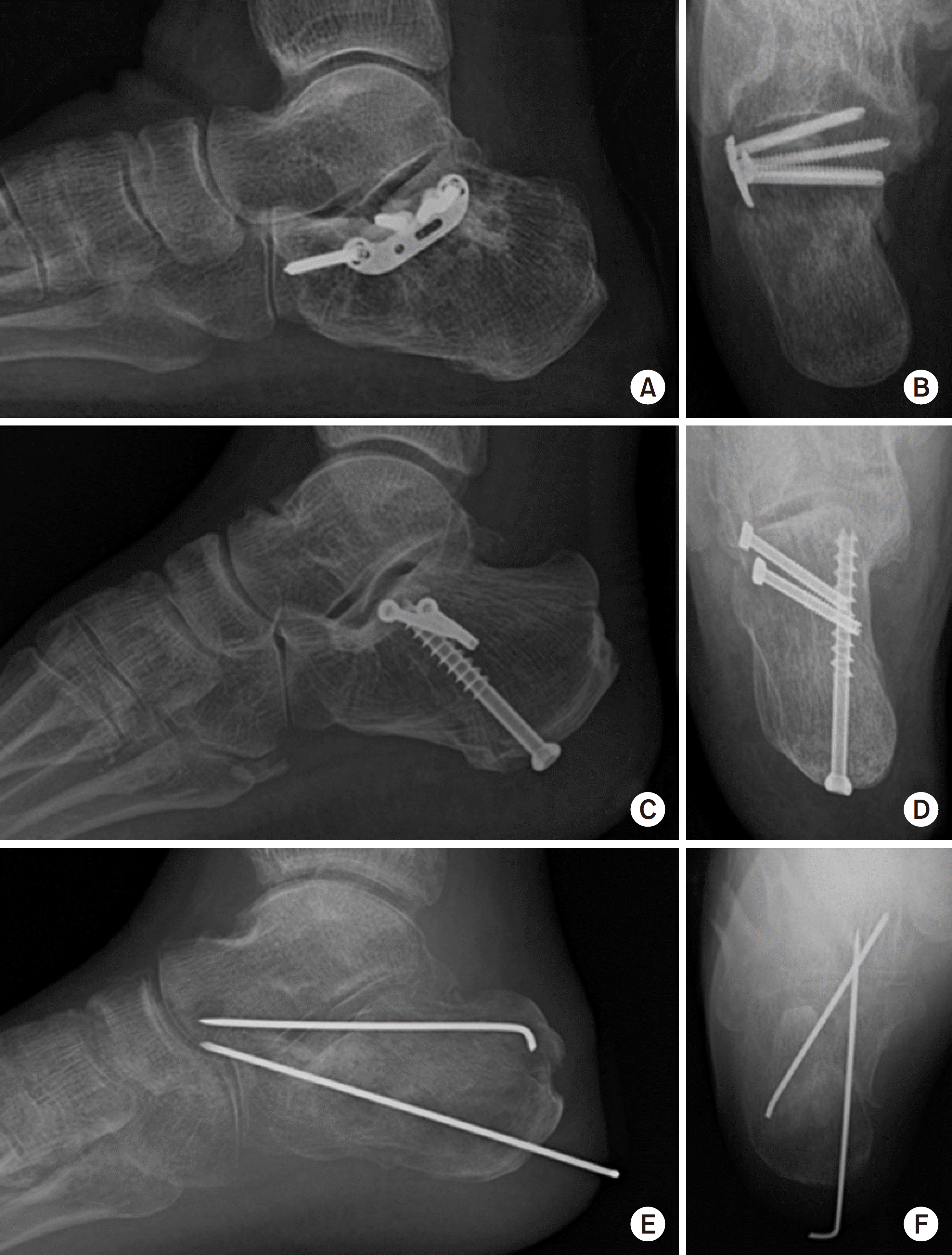 | Fig. 1.Minimally invasive approach. (A, C, E) Lateral radiographs of the calcaneus. (B, D, F) Axial radiographs of the calcaneus. |
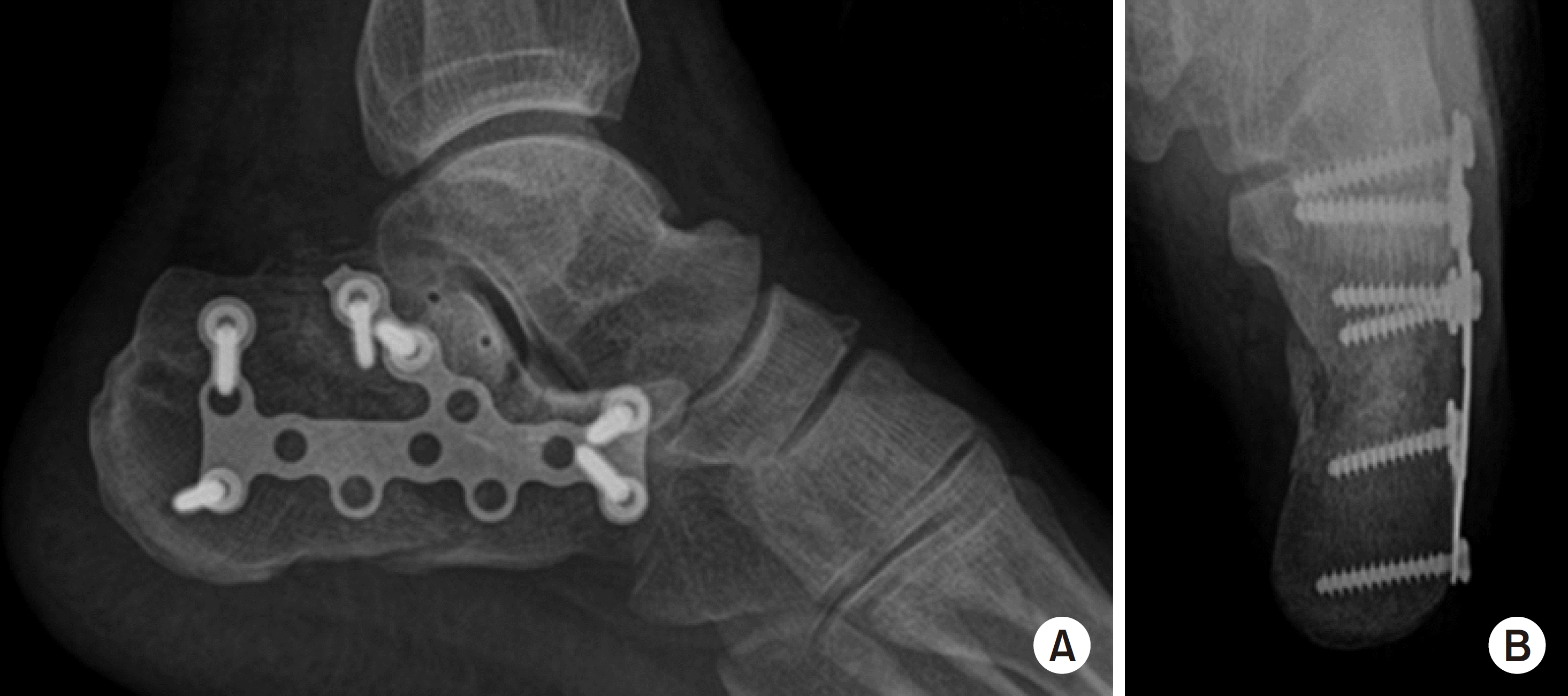 | Fig. 2.Extensile lateral approach. (A) Lateral radiograph of the calcaneus. (B) Axial radiograph of the calcaneus. |
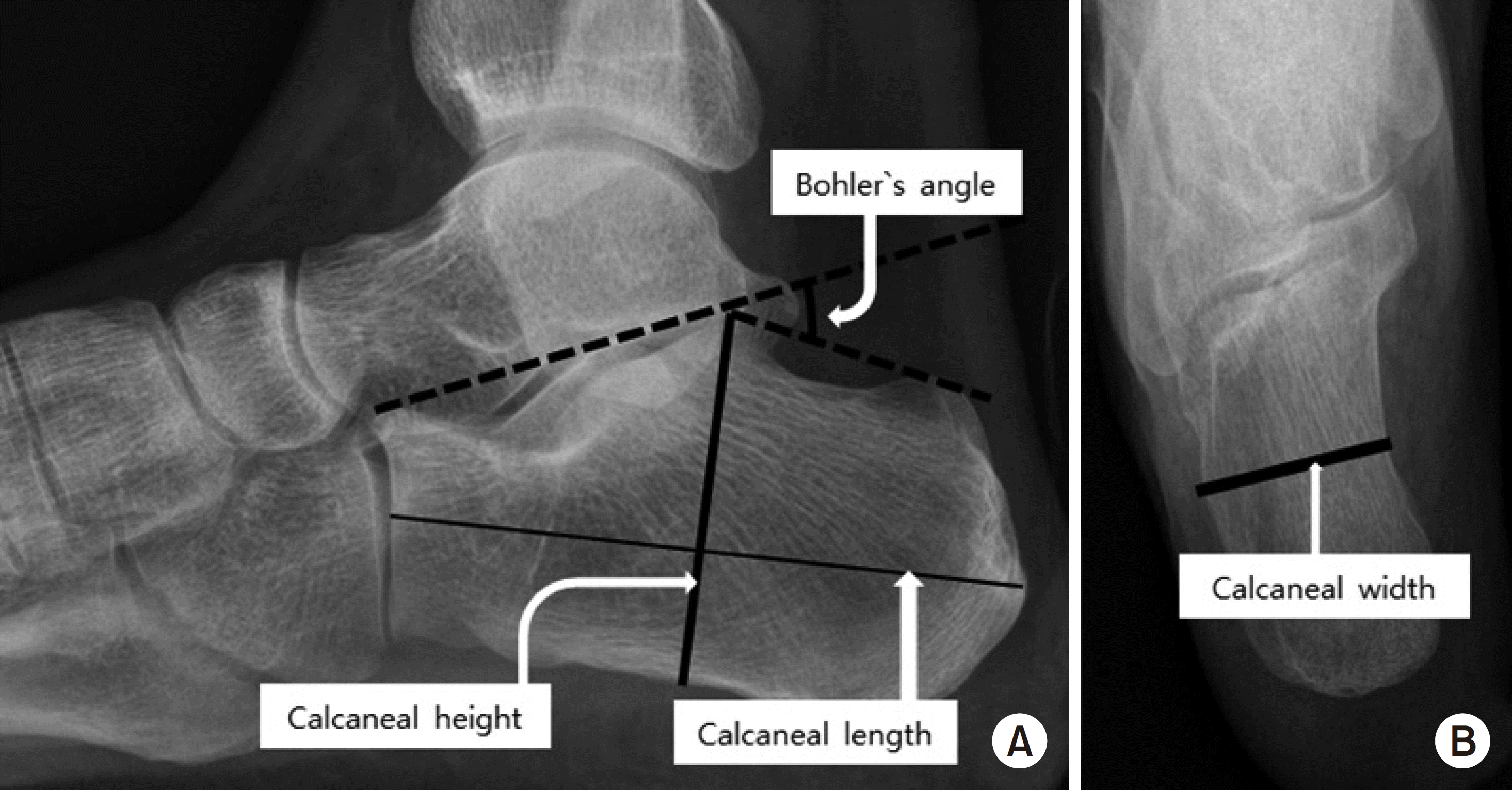 | Fig. 3.(A) Lateral radiograph of the calcaneus shows measurements of the Böhler angle, calcaneal height, calcaneal length. (B) Axial radiograph of the calcaneus shows measurements of the calcaneal width. |
Table 1.
Comparison of the Demographic Data and Clinical Outcome between the Treatment Groups
Table 2.
Comparison of the Radiologic Outcomes between the Treatment Groups




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download