Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to determine the clinical outcomes after a less invasive locking plating technique in intra-articular fractures of the distal femur.
Materials and Methods
This was a retrospective 19 case series of patients with distal femoral intra-articular fractures treated with a less invasive locking plating technique in a single center (Dankook University Hospital) from June 2010 to April 2016. Nineteen patients (11 males and 8 females) with a mean age of 55.9 years were enrolled. The functional outcomes were evaluated using the visual analogue scale (VAS), range of knee joint motion (flexion & extension), and Knee Society score. The radiology outcomes were evaluated with parameters measured in a plain radiograph (deviation angle of alignment axis on coronal and sagittal plane, mechanical lateral distal femur angle).
Results
The mean follow-up period was 26.4 months (range, 12–72 months) and the mean duration to union was 15.94 weeks (range, 11–28 weeks). The mean VAS was 1.36 (range, 0–8) and the range of motion of the knee joint was extension 4.73° (range, 0°-30°) and flexion 107.36° (range, 60°-135°). The mean Knee Society score was 85.47 (range, 47–100). The mean deviation angle of the coronal alignment axis was 4.07° (range, 1.3°-8.8°), the mean deviation angle of the sagittal alignment axis was 3.23° (range, 0.7°-7.0°), and the mechanical lateral femoral angle was 87.75° (range, 82.8°-95.5°). Six patients had traumatic osteoarthritis at the final follow-up.
Conclusion
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical and radiologic outcomes of intraar-ticular fractures of the distal femur in patients who underwent an anatomical reduction through an open reduction, and converted to an extra-articular fracture with rigid internal fixation. The results were relatively satisfactory.
Go to : 
References
1. Hutson JJ Jr, Zych GA. Treatment of comminuted intraarticular distal femur fractures with limited internal and external tensioned wire fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 14:405–413. 2000.

2. Ramesh LJ, Rajkumar SA, Rajendra R, Rajagopal HP, Phanee-sha MS, Gaurav S. Ilizarov ring fixation and fibular strut grafting for C3 distal femoral fractures. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 12:91–95. 2004.

3. Lin D, Chen C, Lian K, Zhai W. Treatment of type C3.3 distal femoral fractures with double-plating fixation via U-shaped incision. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 24:683–686. 2010.
4. Zhang ZM, Liu J, Huang CX, Zhao ZF, Wang G, Qin CC. Treatment of type C3 distal femoral fractures with double-plating fixation via anteriormiddle approach. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 25:1049–1052. 2012.
5. Khalil AE, Ayoub MA. Highly unstable complex C3-type distal femur fracture: can double plating via a modified Olerud extensile approach be a standby solution? J Orthop Traumatol. 13:179–188. 2012.

6. Sîrbu PD, Asaftei R, Petreuş T, Lupaşcu C, Puha B, Luncă S. Transarticular approach and retrograde plate osteosynthesis (TARPO) using implants with angular stability: a series of 17 cases of complex distal femoral fractures type C3/AO. Chirurgia (Bucur). 109:233–237. 2014.
7. Krettek C, Schandelmaier P, Miclau T, Bertram R, Holmes W, Tscherne H. Transarticular joint reconstruction and indirect plate osteosynthesis for complex distal supracondylar femoral fractures. Injury. 28(Suppl 1):A31–41. 1997.

8. Kregor PJ. Distal femur fractures with complex articular involvement: management by articular exposure and submuscular fixation. Orthop Clin North Am. 33:153–175. ix,. 2002.
9. Egund N, Kolmert L. Deformities, gonarthrosis and function after distal femoral fractures. Acta Orthop Scand. 53:963–974. 1982.

10. Rademakers MV, Kerkhoffs GM, Sierevelt IN, Raaymakers EL, Marti RK. Intra-articular fractures of the distal femur: a longterm follow-up study of surgically treated patients. J Orthop Trauma. 18:213–219. 2004.
11. Zehntner MK, Marchesi DG, Burch H, Ganz R. Alignment of supracondylar/intercondylar fractures of the femur after internal fixation by AO/ASIF technique. J Orthop Trauma. 6:318–326. 1992.

12. Krettek C, Müller M, Miclau T. Evolution of minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) in the femur. Injury. 32(Suppl 3):SC14–23. 2001.

13. Frigg R, Appenzeller A, Christensen R, Frenk A, Gilbert S, Schavan R. The development of the distal femur less invasive stabilization system (LISS). Injury. 32(Suppl 3):SC24–31. 2001.

14. Markmiller M, Konrad G, Südkamp N. Femur-LISS and distal femoral nail for fixation of distal femoral fractures: are there differences in outcome and complications? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 426:252–257. 2004.
15. Schandelmaier P, Blauth M, Krettek C. Osteosynthese distaler femurfrakturen mit dem less invasive stabilizing system (LISS). Oper Orthop Traumatol. 13:178–197. 2001.

16. Schütz M, Schäfer M, Bail H, Wenda K, Haas N. Neue osteo-syntheseverfahren bei distalen femurfrakturen. Zentralbl Chir. 130:307–313. 2005.

17. Goesling T, Frenk A, Appenzeller A, Garapati R, Marti A, Krettek C. LISS PLT: design, mechanical and biomechanical characteristics. Injury. 34(Suppl 1):A11–15. 2003.

18. Ehlinger M, Ducrot G, Adam P, Bonnomet F. Distal femur fractures. Surgical techniques and a review of the literature. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 99:353–360. 2013.

19. Farouk O, Krettek C, Miclau T, Schandelmaier P, Guy P, Tscherne H. Minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis: does percutaneous plating disrupt femoral blood supply less than the traditional technique? J Orthop Trauma. 13:401–406. 1999.

20. Colborn GL, Mattar SG, Taylor B, Skandalalkis JE, Lumsden AB. The surgical anatomy of the deep femoral artery. Am Surg. 61:336–346. 1995.
Go to : 
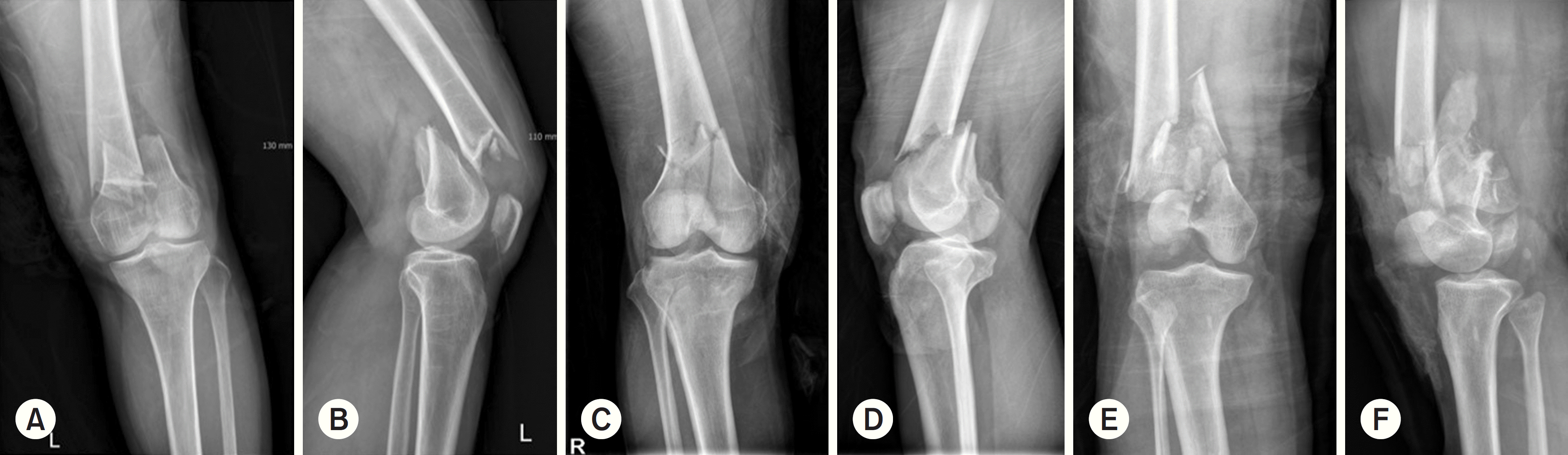 | Fig. 1.Simple radiographs show anterior-posterior and lateral view of distal femur fractures: AO/OTA classification. (A, B) type C1 fracture, (C, D) type C2 fracture, (E, F) type C3 fracture. |
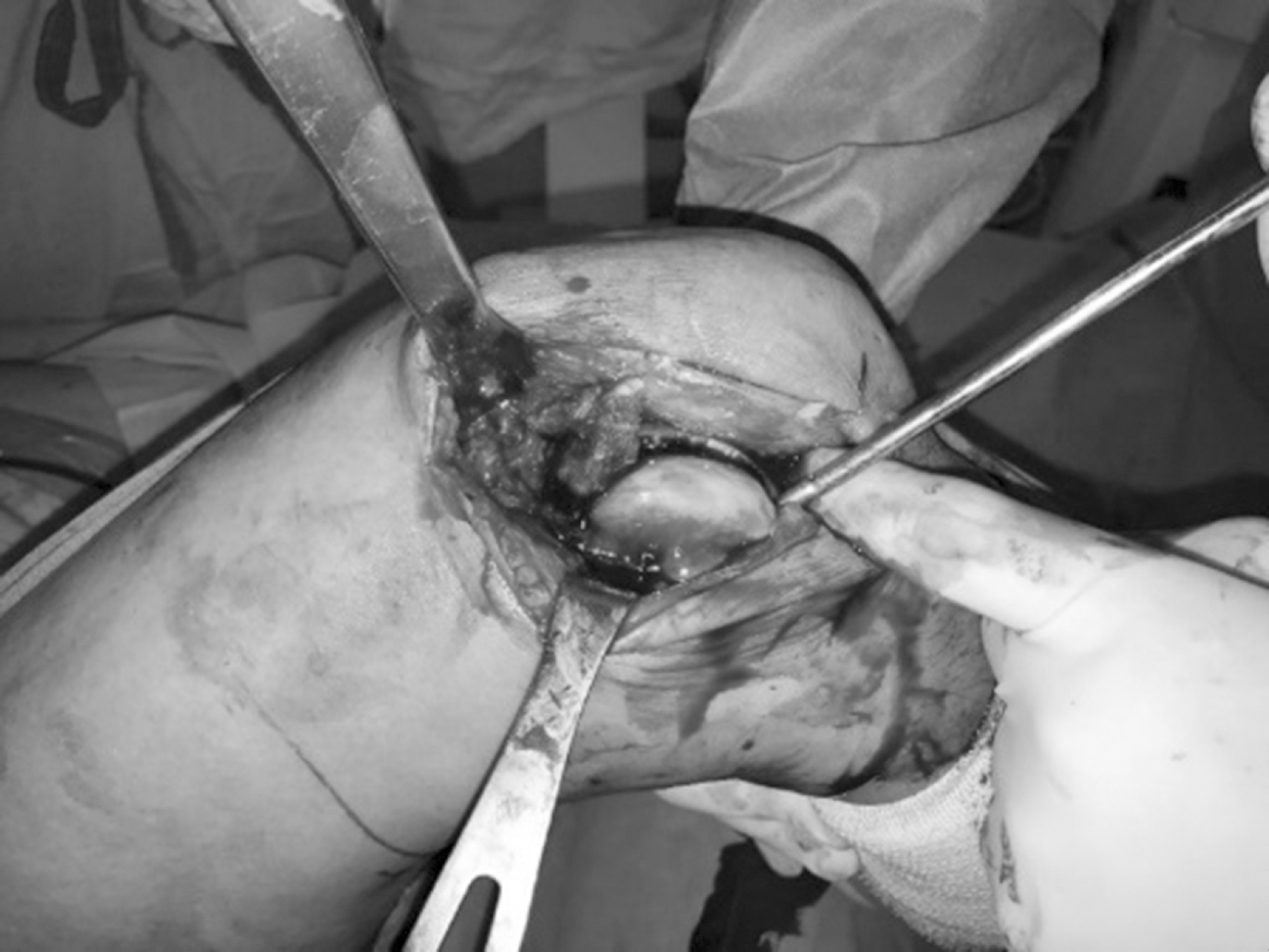 | Fig. 2.Intraoperative photograph showing the lateral parapatella approach for articular exposure and reconstruction. |
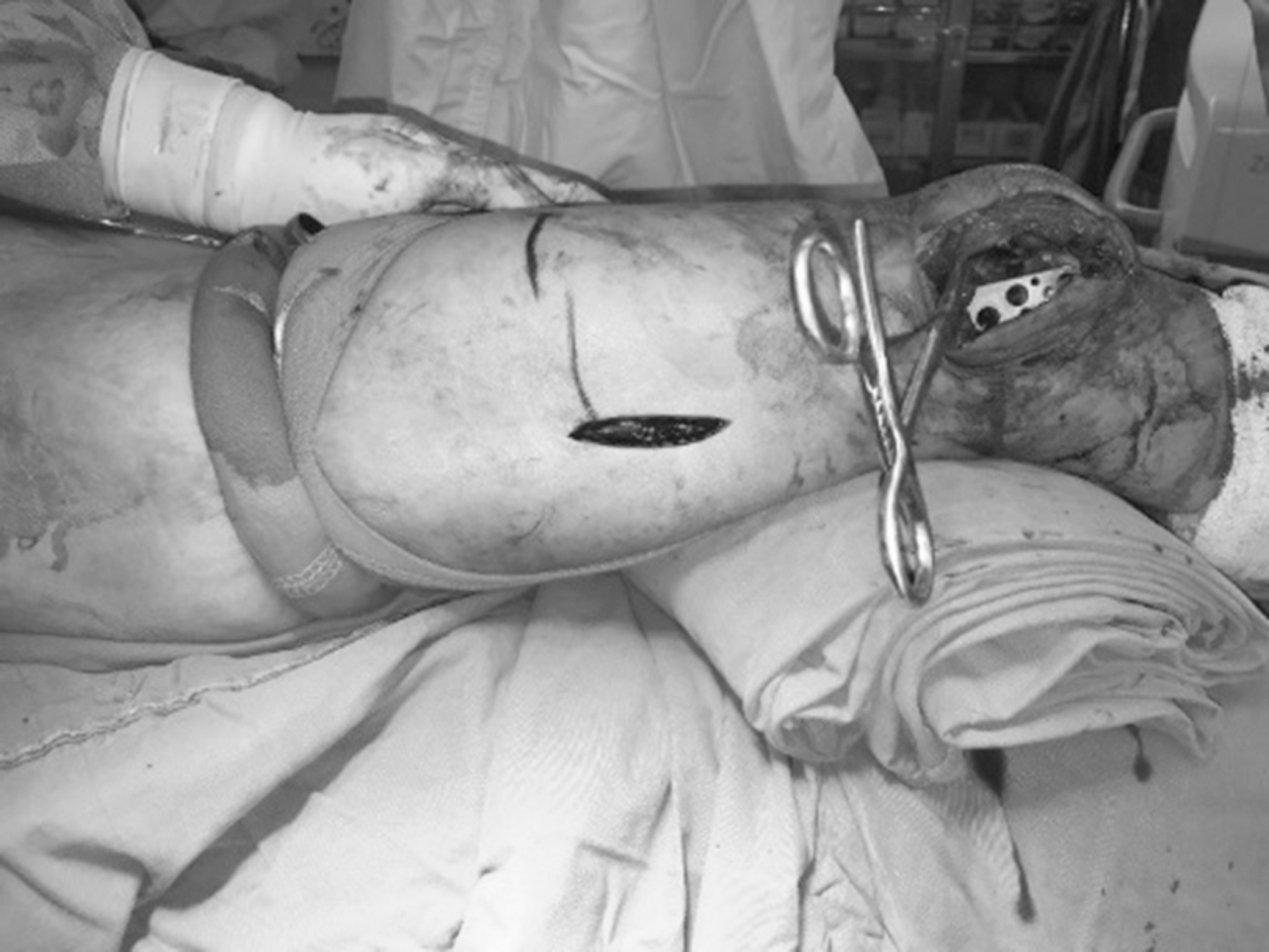 | Fig. 3.Following reduction, an appropriate-sized plate was slid in a distal-to-proximal direction over the periosteum at the lateral aspect of the distal femur. |
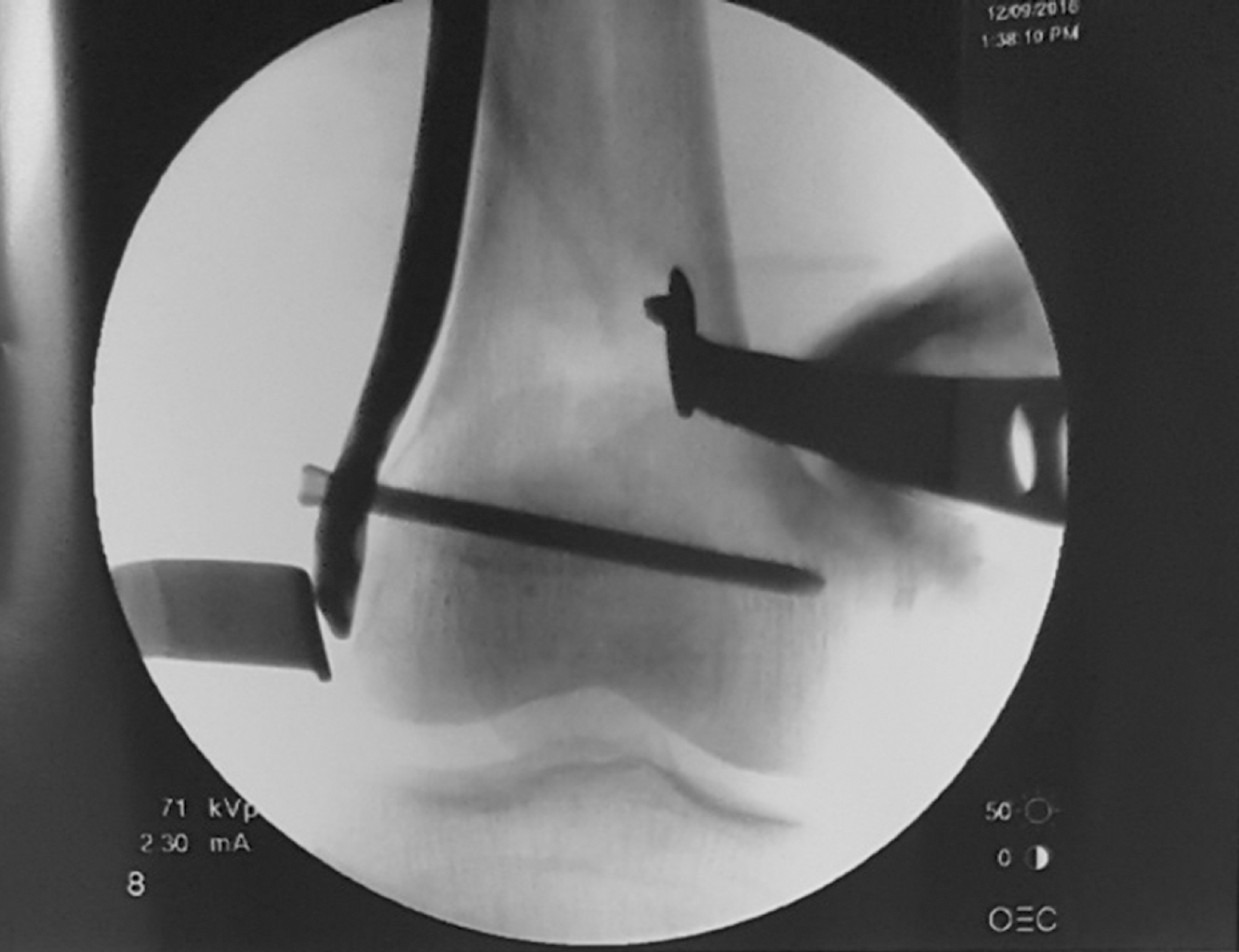 | Fig. 4.Intraoperative radiograph (using C-arm) for check the alignment of the distal femur and positioning of the plate. |
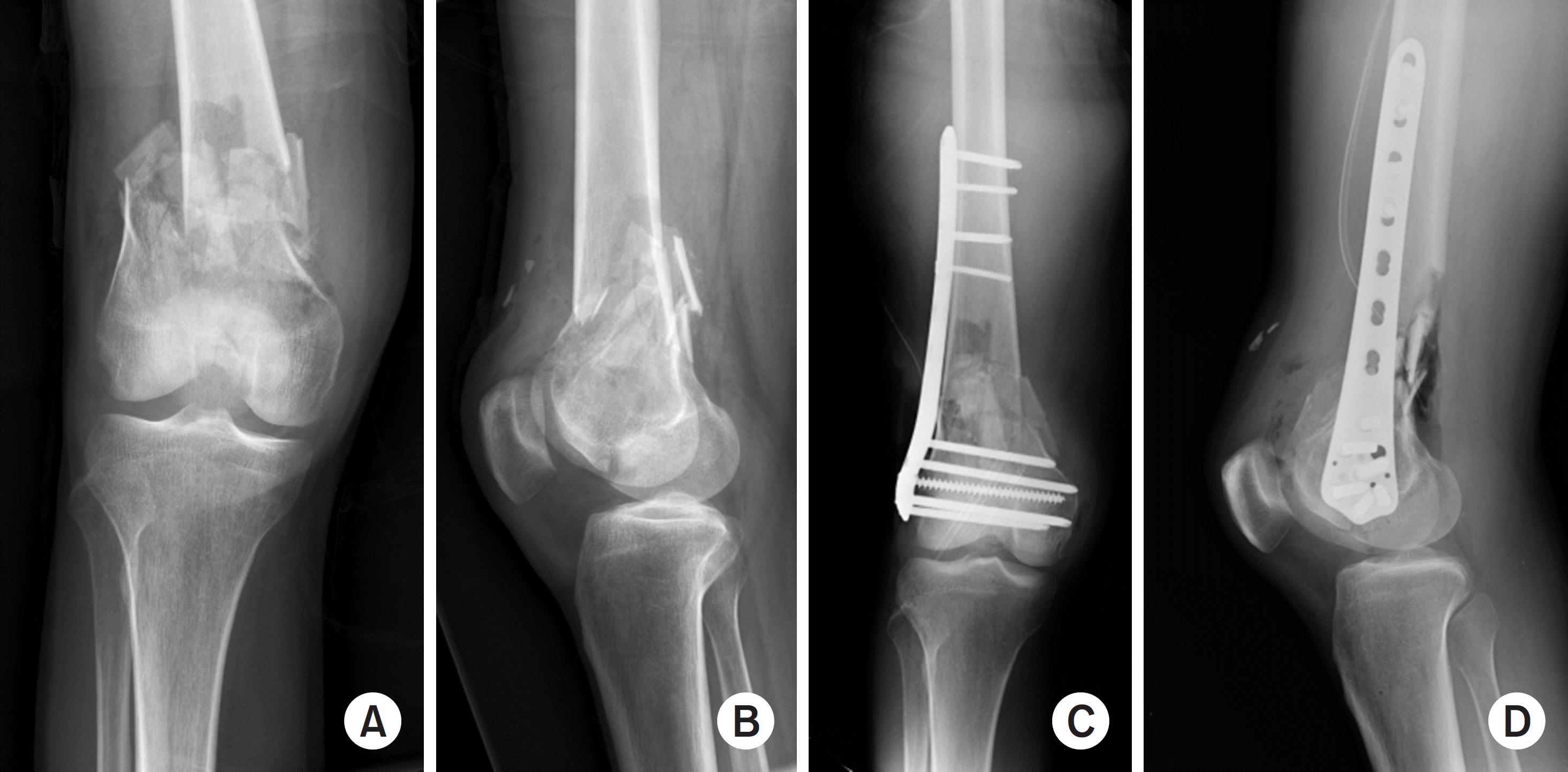 | Fig. 5.Preoperative and immediate postoperative X-rays: anteroposterior (A, C), lateral view (B, D). |
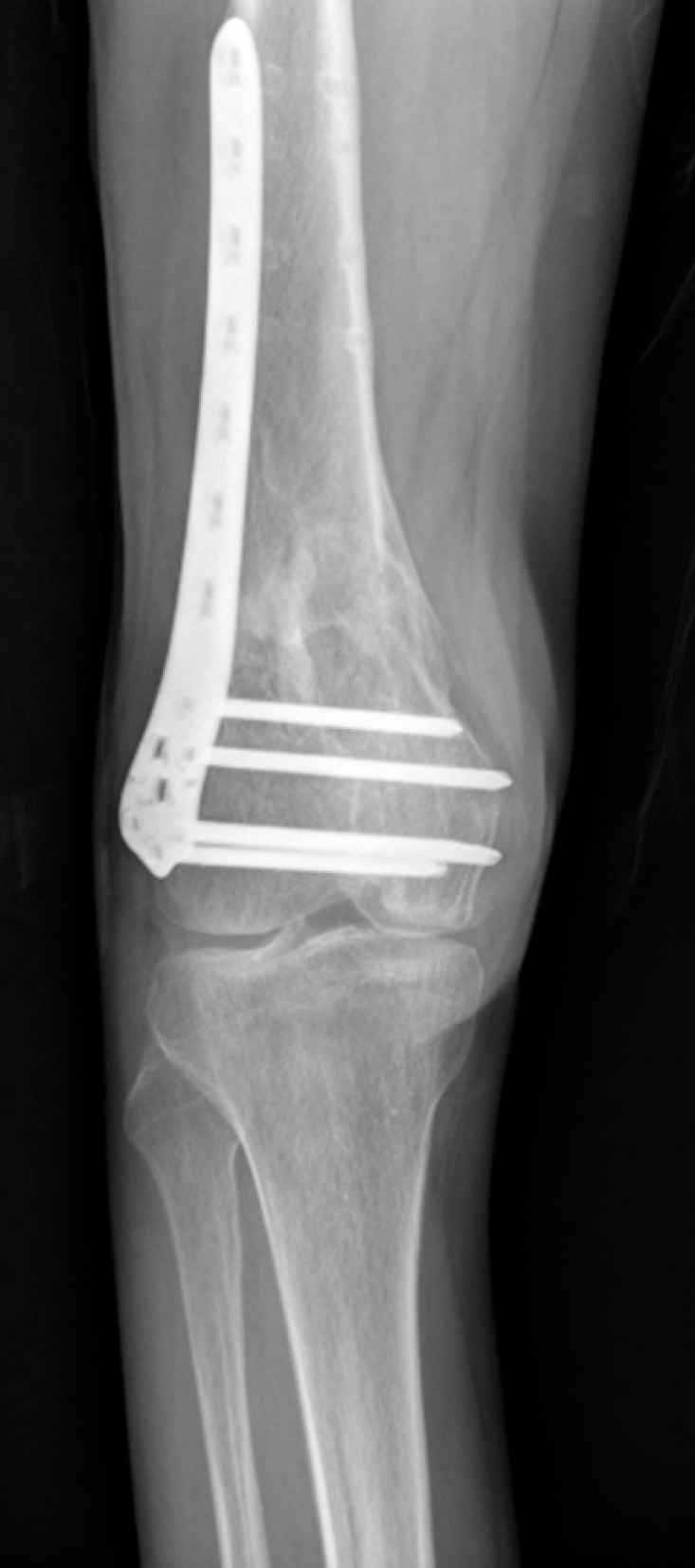 | Fig. 6.Radiological changes in osteoarthritis at the final follow-up after the minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis technique for a distal femur complete intra-articular fracture. |
Table 1.
Demographic Data
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (yr) | 55.9 (32–79) |
| Sex (male:female) | 11:8 |
| Injury mechanism (low:high energy) | 4:15 |
| Fracture type (AO/OTA classification) | |
| C1 | 2 |
| C2 | 4 |
| C3 | 13 |
Table 2.
Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes at the Final Follow-Up




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download