This article has been
cited by other articles in ScienceCentral.
Dear Editor:
Papuloerythroderma of Ofuji (PEO) has been reported to be associated with internal malignancy
1, although the pathogenesis remains unclear. Th2 cytokines are known to play important roles in the pathogenesis of PEO
2. Meanwhile, recent studies have shown that Th2 deviation is associated with cancer development
34. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) is known to play an important role in the maturation of T-cell populations into the Th2 lineage
5.
A 65-year-old Japanese male who had had no past history of atopic dermatitis, asthma and rhinitis developed pruritic, flat-topped, red papules that gradually increased and coalesced into an erythroderma-like lesion. Transverse abdominal folds were spared, representing deck-chair sign (DCS) (
Fig. 1A). Skin biopsy revealed moderate acanthosis, perivascular infiltrate of lymphocytes and a few eosinophils in the upper dermis, and mild dermal fibrosis (
Supplementary Fig. 1A). Based on those findings, PEO was diagnosed
1. General examination was performed, considering the association with internal malignancy1. Gastrointestinal endoscopy disclosed the entire circumference of the tumor in the rectosigmoidal colon (RC) (
Fig. 1B). Biopsy of the RC lesion revealed that the tumor was adenocarcinoma, stage IIIa. Endoscopic resection of the cancer was performed and continuous 6 months chemotherapy were administered. Tumor recurrence is not being deteced so far. Topical steroidal ointment had been applied for the skin eruption. DCS finally resolved after two years of endoscopic resection and never appeared since then (
Fig. 1C). Immunohistochemical examination revealed that almost all lymphocytes in skin lesion were positive for CD4 (
Supplementary Fig. 1B) and the infiltrating lymphocyte ratio of CD4/8 around some parts of the tumor cells was 3.8 (
Supplementary Fig. 1C, D). CCR4 was expressed on infiltrating lymphocytes both in the skin lesion (
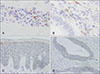
Fig. 2A) and around the tumor cells (
Fig. 2B), suggesting that Th2 cells were involved in the pathogenesis in the present case
2. Accordingly, Kanazawa et al.
4 showed the association of Th2 cells with gastric or colorectal patients. Of note, mild and moderate expressions of TSLP were observed in the lesional epidermal cells (
Fig. 2C,
Supplementary Fig. 2A) and in colorectal cancer cells (
Fig. 2D,
Supplementary Fig. 2B), respectively. Palucka and Banchereau
5 described that in a breast cancer model, TSLP, produced by tumor cells induces dendritic cells to express the OX40 ligand, which directs the generation of Th2 cells. In the present case, expression of TSLP seemed stronger in colorectal cancer cells than lesional epidermal cells (
Fig. 2C, D).
Finally, we speculate that TSLP produced by the tumors might primarily promote the Th2 deviation in the colorectal area, subsequently, contributing to the emergence of PEO.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to use immunohistochemical analyses of both skin lesions and internal malignant tumor from the same patient. More analyses should be accumulated to elucidate the pathomechanisms underlying any associations between internal malignancy and PEO.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
(A) Pruritic, flat-topped, red papules coalesced into an erythroderma-like lesion, representing deck-chair sign (DCS). (B) The entire circumference of the tumor in the rectosigmoidal colon. (C) DCS finally resolved after two years of endoscopic resection and never appeared since then. We received the patient's consent form about publishing all photographic materials.
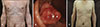
Fig. 2
(A) Some lymphocytes were CCR4 positive of the infiltrating lymphocytes in the upper dermis (CCR4, ×400). (B) CCR4 were partly positive in the infiltrating lymphocytes around the colorectal cancer cells (CCR4, ×400). (C) Epidermal cells from the lesional skin were mildly positive for anti-TSLP antibody (TSLP, ×400). (D) Colorectal cancer cells were moderately positive for anti-TSLP antibody (TSLP, ×400). TSLP: thymic stromal lymphopoietin.






 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download