A 64-year-old female without significant cardiovascular history other than hypertension presented to the emergency department due to a syncopal episode after sustained palpitations and escalating dyspnea. Comprehensive workup revealed a generalized left ventricular hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a sigmoid septum of 2.4 cm with a subsequent 82° angulation between the basal aspect of the septum and the ascending aorta (
Figure 1), and an aberrant accessory papillary muscle (AAPM) with severe calcification and fibrosis (
Figure 2 and
Figure 3). This unusual coalescence of anatomical variations triggered systolic anterior motion (SAM) of the mitral valve with severe mitral regurgitation and left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO, maximum pressure gradient at rest 41 mmHg, maximum pressure gradient during exercise 91 mmHg) (
Figure 4) under minimal stress. Patient was deemed as a surgical candidate due to poor response to maximal medical therapy and underwent septal myectomy and resection of the AAPM.
Sigmoid septum becomes severely symptomatic in only 1.9% of patients, particularly when focal hypertrophy surpasses 15 mm.
1) SAM and subsequent LVOTO may arise at rest in patients with very rare anatomical variations.
2) In the present case, the dynamic obstruction was exacerbated by a tethering effect of the AAPM as well further obstruction due to calcification and thickening secondary to severe fibrosis.
SAM is predictable,
3) especially in patients with very uncommon morphologic features like a basal interventricular septal thickness of > 15 mm, a distance from the mitral coaptation point to the septum of < 25 mm, an angle between the intersection of the mitral and aortic annulus of < 120°, and abnormal mitral leaflet length.
4) Although directed maximal medical therapy is preferred,
5) a surgical approach is required based on the combined severity of hemodynamic obstruction and clinical consequences.
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Mid-esophageal long axis view shows severe focal hypertrophy of the ventricular septum (arrow head) with an 82° angulation between the basal portion of the ventricular septum and the ascending aorta (line), as well as an accessory calcified papillary muscle.
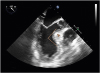
Figure 2
Transgastric long axis view shows an aberrant accessory papillary muscle (arrow head).
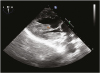
Figure 3
Three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography demonstrates an abnormal attachment of an aberrant papillary muscle (arrow head). AL: anterior leaflet of mitral valve, APM: aberrant papillary muscle, LVOT: left ventricular outflow tract, PL: posterior leaflet of mitral valve.
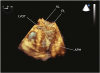
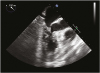
Figure 4
Mid-esophageal long axis view reveals severe systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve and obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download