Figures and Tables
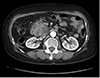 | Fig. 1Abdominal computed tomography (CT). CT image shows about 6 cm sized multilobulated cystic lesion and low-density lesion at center in the head of pancreas. |
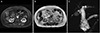 | Fig. 2Pancreatic magnetic resonance images (MRI). (A) MRI shows multilocular cystic lesion with low-signal intensity lesion at center in head of pancreas on T1-weighted axial image (B), multilobular cystic lesion in head of pancreas on T2-weighted axial image. (C) Multilobular cystic lesion in head of pancreas with dilatation of bile and pancreatic duct on T2-weighted magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. |
References
1. Correa-Gallego C, Ferrone CR, Thayer SP, Wargo JA, Warshaw AL, Fernández-Del Castillo C. Incidental pancreatic cysts: do we really know what we are watching. Pancreatology. 2010; 10:144–150.

2. Farrell JJ, Fernández-del Castillo C. Pancreatic cystic neoplasms: management and unanswered questions. Gastroenterology. 2013; 144:1303–1315.

3. Chu LC, Singhi AD, Haroun RR, Hruban RH, Fishman EK. The many faces of pancreatic serous cystadenoma: radiologic and pathologic correlation. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2017; 98:191–202.

4. Federle MP, McGrath KM. Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2007; 36:365–376.

5. Choi JY, Kim MJ, Lee JY, et al. Typical and atypical manifestations of serous cystadenoma of the pancreas: imaging findings with pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:136–142.

6. Woo YS, Lee KT. Clinical approach to incidental pancreatic cystic neoplasm in outpatient clinics. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2017; 70:13–20.

7. Lombardo C, Iacopi S, Menonna F, et al. Incidence and reasons of pancreatic resection in patients with asymptomatic serous cystadenoma. Pancreatology. 2018; 18:577–584.

8. Khalpey Z, Rajab TK, Ashley SW. Serous cystadenoma causing the double duct sign. J Gastrointest Surg. 2012; 16:1282–1283.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download