Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
MALAT1 was upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by hypoxia. qRT-PCR assay was performed to measure the expression of MALAT1 in Huh7, SNU-423, PLC, and Hep3B cells cultured under normoxic or hypoxic condition. *p<0.05. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.
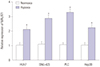
Fig. 2
Knockdown of MALAT1 suppressed growth and induced apoptosis of Hep3B cells after hypoxia challenge. Hep3B cells were transfected with si-NC or si-MALAT1. For N-control group, cells were cultured under normoxia condition for 72 hours; for H-control group, cells were first challenged with hypoxia (1% oxygen) for 24 hours, followed by culturing under normoxia condition for 48 hours. (A) MALAT1 expression level in each treatment group was measured by qRT-PCR. (B) Hep3B cell proliferation in each treatment group was evaluated by MTT assay. (C and D) Hep3B cell apoptotic rate in each treatment group was detected by flow cytometry. *p<0.05: when compared with N-control group, †p<0.05: when compared with H-si-NC group. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.

Fig. 3
Knockdown of MALAT1 suppressed migration and invasion of Hep3B cells promoted by hypoxia. Hep3B cells were transfected with si-NC or si-MALAT1, and normoxia and hypoxia treatment were performed as described in Fig. 2A. Cell migration (A) and invasion (B) were evaluated by Transwell assay. *p<0.05: when compared with N-control group, †p<0.05: when compared with H-si-NC group. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.

Fig. 4
MALAT1 interacted with miR-200a in hypoxic Hep3B cells. (A) The predicted binding sites between miR-200a and MALAT1 mRNA through Starbase v2.0. Luciferase reporter plasmids containing wild-type (WT) or mutated (MUT) MALAT1 binding sites of miR-200a were established. (B and C) Hep3B cells were co-transfected with MALAT1-WT or MALAT1-MUT luciferase reporter and miR-200a, miR-NC, anti-NC, or anti-miR-200a, followed by the determination of luciferase activity at 48 h after transfection. (D) Hep3B cells were transfected with si-NC, si-MALAT1, pcDNA3.1 empty vector, and pcDNA-MALAT1 overexpression plasmid, and miR-200a expression level was measured by qRT-PCR. *p<0.05: when compared with N-control group, †p<0.05: when compared with H-miR-NC group. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.

Fig. 5
Upregulation of miR-200a inhibited the proliferation, invasion, migration, and induced apoptosis in Hep3B cells under hypoxia. Hep3B cells in (B–F) were treated as described in Fig. 2. (A) qRT-PCR analysis of the expression of miR-200a in Huh7, SNU-423, PLC, and Hep3B cells with or without hypoxia challenge. (B) miR-200a expression level in Hep3B cells was measured by qRT-PCR assay. (C) Cell proliferation was evaluated by MTT assay. (D) Cell apoptotic rate was detected by flow cytometry. (E and F) Cell migration and invasion were evaluated by Transwell assay. *p<0.05: when compared with N-control group, †p<0.05: when compared with H-miR-NC group. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.

Fig. 6
Downregulation of miR-200a partially reversed the effect of MALAT1 knockdown on hypoxia-challenged Hep3B cells. Hep3B cells were transfected with si-MALAT1 or si-MALAT1+anti-miR-200a and were challenged with normoxia or hypoxia as described in Fig. 2. (A) miR-200a expression in each group was evaluated by qRT-PCR. (B) Cell proliferation was detected by MTT assay. (C) Cell apoptotic rate was detected by flow cytometry. (D and E) Cell migration and invasion were measured by Transwell assay. *p<0.05: when compared with H-control group, †p<0.05: when compared with H-si-MALAT1 group. MALAT1, metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1.

Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: Zheng-Bin Zhao, Fei Chen.
Data curation: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai.
Formal analysis: Xiao-Fang Bai, Zheng-Bin Zhao.
Funding acquisition: Zheng-Bin Zhao, Xiao-Fang Bai.
Investigation: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai.
Methodology: Zheng-Bin Zhao, Xiao-Fang Bai.
Project administration: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai.
Resources: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai.
Software: Xiao-Fang Bai, Fei Chen.
Supervision: Xiao-Fang Bai, Zheng-Bin Zhao.
Validation: Fei Chen, Zheng-Bin Zhao.
Visualization: Xiao-Fang Bai, Zheng-Bin Zhao.
Writing—original draft: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai, Zheng-Bin Zhao.
Writing—review & editing: Fei Chen, Xiao-Fang Bai.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download