Abstract
Objective
Methods
Results
Conclusions
Figures and Tables
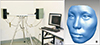 | Figure 1A, The three-dimensional structured light scanning system; B, initial three-dimensional facial image. |
 | Figure 2Six landmarks located on the midsagittal plane (Sn, Subnasale; Ls, labiale superius; Li, labiale inferius; stos, stomion superius; stoi, stomion inferius; B', soft B-point) and two bilateral landmarks (cphr, Right crista philtra; cphl, left crista philtra; chr, right chelion; chl, left chelion). |
 | Figure 3A, Nine vermilion angles (1, Right upper vermilion angle; 2, left upper vermilion angle; 3, right lower vermilion angle; 4, left lower vermilion angle; 5, upper vermilion base angle; 6, lower vermilion base angle; 7, right cupid's bow angle; 8, left cupid's bow angle; 9, central bow angle). B, Three straight-line distances (1, Mouth width; 2, cupid's bow width; 3, vermilion height). C, Four curve-length measurements (1, Upper vermilion fullness; 2, lower vermilion fullness; 3, upper lip curve length; 4, lower lip curve length). D, Surface area of the lip vermilion was measured in reverse engineering software (Rapidform 2009; Inus Technology, Seoul, Korea).See Figure 2 for definitions of each landmark.
|
 | Figure 4A–C, Pre-treatment three-dimensional lip vermilion images of one of the patients in the max-anchorage group (G1). D–F, Post-treatment three-dimensional lip vermilion image of one of the patients in the G1. |
 | Figure 5A–C, Pre-treatment three-dimensional lip vermilion image of one of the patients in the moderate-anchorage group (G2). D–F, Post-treatment three-dimensional lip vermilion image of one of the patients in the G2. |
 | Figure 6A–C, Pre-treatment three-dimensional lip vermilion image of one of the patients in the non-extraction group (G3). D–F, Post-treatment three-dimensional lip vermilion image of one of the patients in the G3. |
Table 6
Pearson correlation coefficients between incisor changes and vermilion changes

▴Incisor variable showed the strongest correlation (R-value) with the vermilion variable.
U1, Maxillary central incisor; NA, nasion-A point plane; SN, sella-nasion plane; FH, Frankfort horizontal plane; PP, palatal plane; AP, A point-pogonion plane; L1, mandibular central incisor; NB, nasion-B point plane; MP, mandibular plane.
**p < 0.01.
Table 7
Stepwise regression prediction for the changes in vermilion variables

Values are presented as number ± standard error.
Only regression models providing more than 45% of the vermilion variable changes are shown.
See Table 6 for abbreviation of each landmark.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print








 XML Download
XML Download