Abstract
Purpose
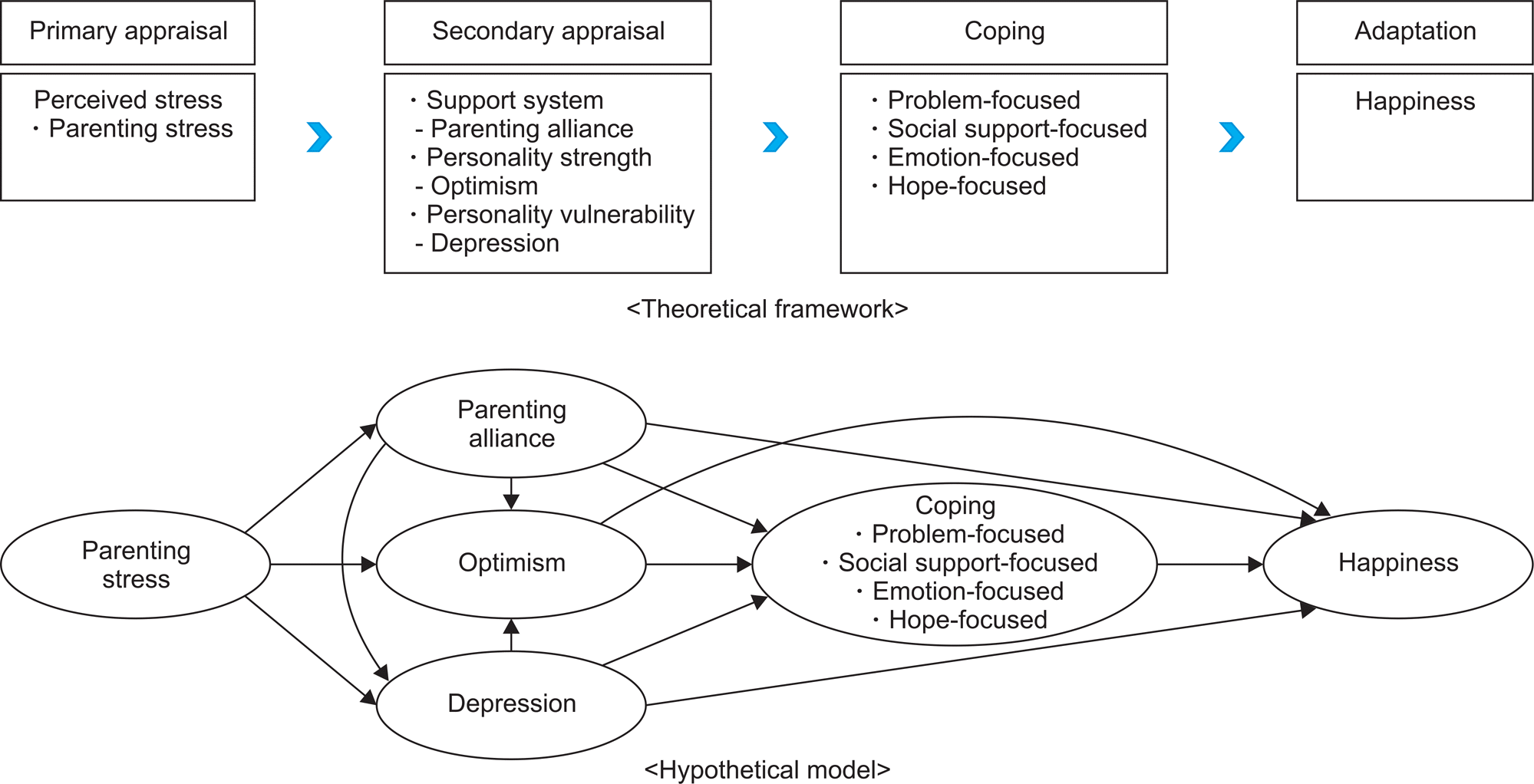
This study aimed to develop and test a model of the happiness of mothers with young children based on the stress-coping-adaptation model of Lazarus and Folkman.
Methods
The data collection period was from May to July 2016. A self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from 210 mothers with children under 5 years of age living in Seoul, Gyeonggi, and Gangwon provinces. The exogenous variable was parenting stress, and the endogenous variables were parenting alliance, depression, optimism, ways of coping, and happiness. Data from 201 questionnaires were analyzed using the SPSS 22.0 and AMOS 20.0 programs. Data analyses included descriptive statistics, factor analysis, and structural equation modeling.
Results
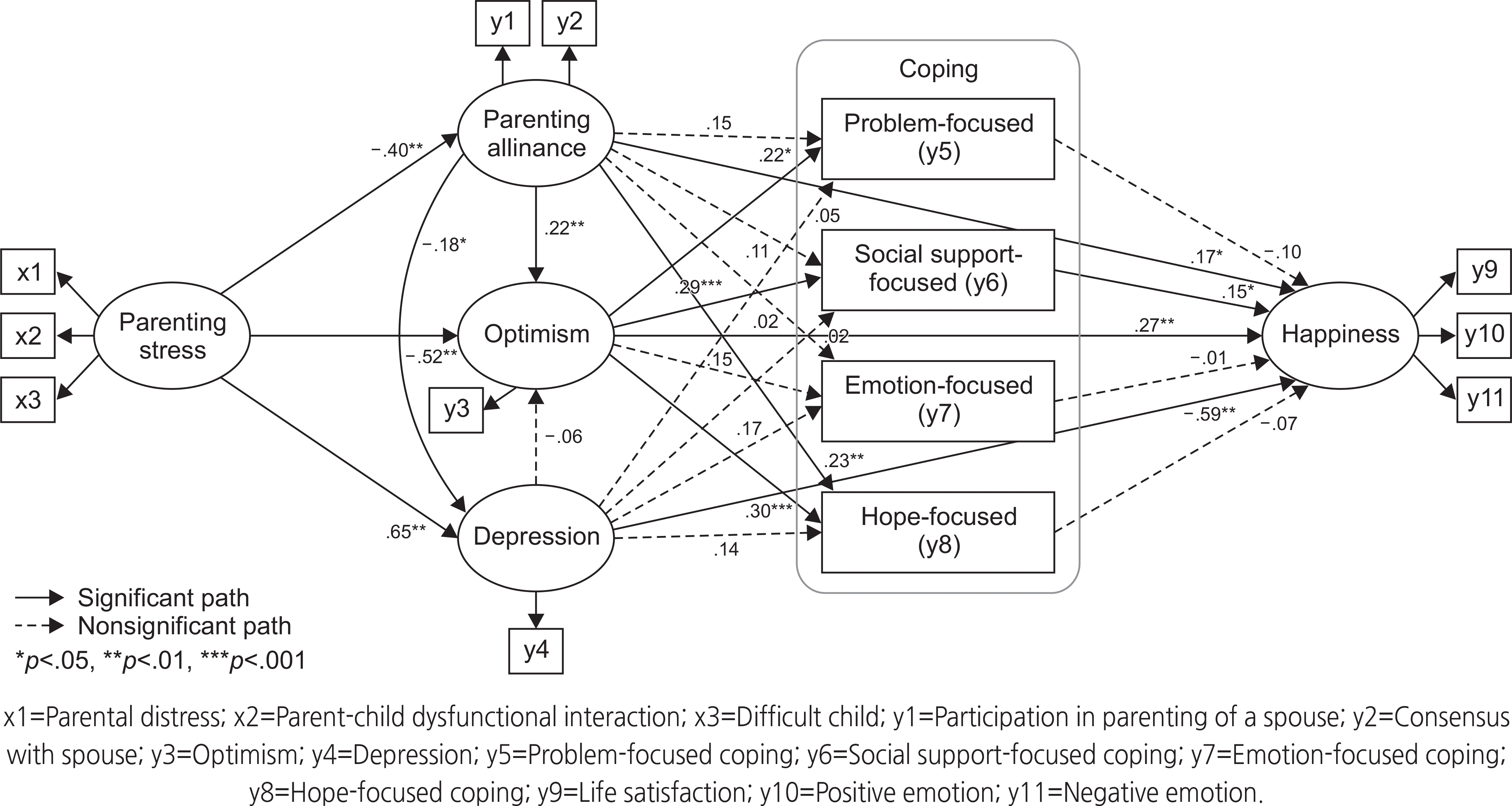
The final modified model showed a reasonable fit to the data, and out of 25 paths, 13 were statistically significant. This model explained 78.4% of the variance in the happiness of mothers with young children and confirmed that depression, optimism, parenting alliance, and social support-focused coping have a direct effect on the subject's happiness. Parenting stress also influenced happiness through parenting alliance, depression, and optimism.
Conclusion
In order to bolster the happiness of mothers with young children, positive psychological interventions that can minimize psychological vulnerabilities, such as depression, and that can enhance their strengths, such as optimism, may serve as effective ways of coping with and adapting to stress.
Go to : 
References
1. Park GJ, Kim YJ, Seo MW, Yoon MJ, Lee JS, Cho KO. Parent education (for parents of infants and toddlers). Paju: Yangse-owon;2012. p. 1–356.
2. Seginer R, Vermulst A, Gerris J. Bringing up adolescent children: A longitudinal study of parents’ child-rearing stress. International Journal of Behavioral Development. 2002; 26(5):410–422. https://doi.org/10.1080/01650250143000355.
3. Kim K. A study on work-family balance and happiness level of dual career families [dissertation]. Seoul: Sookmyung Women’s University;2018. p. 1–101.
4. Yeon EM, Choi H, Yoon HO. The longitudinal relationship among the emotional temperament of infant, father’s parenting engagement, and mother’s parenting stress using autoregressive cross-lagged model. Korean Journal of Early Childhood Education. 2015; 35(3):171–195. https://doi.org/10.18023/kjece.2015.35.3.008.
5. Crnic KA, Gaze C, Hoffman C. Cumulative parenting stress across the preschool period: Relations to maternal parenting and child behaviour at age 5. Infant and Child Development. 2005; 14(2):117–132. https://doi.org/10.1002/icd.384.

6. Lazarus RS, Folkman S. Stress, appraisal, and coping. New York (NY): Springer;1984. p. 1–436.
7. Folkman S, Moskowitz JT. Coping: Pitfalls and promise. Annual Review of Psychology. 2004; 55:745–774. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.psych.55.090902.141456.

8. Suh E, Koo J. A concise measure of subjective well-being(CO- MOSWB): Scale development and validation. Korean Journal of Social and Personality Psychology. 2011; 25(1):95–113. https://doi.org/10.21193/kjspp.2011.25.1.006.
9. Kim DR, Kim JW. Study of the correlation between the happiness of young children and that of their parents. The Journal of Korea Open Association for Early Childhood Education. 2008; 13(6):311–333.
10. Kim MJ, Kim J. The correlation between the mothers’ happiness and preschoolers’ attachment stability, and peer competence. Journal of Early Childhood Education & Educare Administration. 2010; 14(2):5–28.
11. Kim YM, Kim JW. The correlation between the mothers’ happiness and infants’ social-emotional behaviors. Journal of Children’s Literature and Education. 2011; 12(1):285–302.
12. Chung K, Kim MJ, Ha ES. The relationships between maternal happiness, parenting efficacy and ego-resiliency of young children. The Journal of Korea Open Association for Early Childhood Education. 2012; 17(1):73–97.
13. Chung K, Park S, Yoo M, Choi E. The variables related to maternal happiness for mothers of young children, school-aged children, and adolescents: A child’s age, the numbers of children, and maternal perceptions of the conditions of happiness. Korean Journal of Child Studies. 2013; 34(4):105–123. https://doi.org/10.5723/KJCS.2013.34.4.105.
14. Chung KS, Choi ES. The effects of mothers’ demographic, psychological, and relational factors on the happiness of mothers with young children. The Journal of Korea Open Association for Early Childhood Education. 2012; 17(5):143–163.
15. Han GH, Chang MN. A study of daily happiness of married women with young children using the day reconstruction method. Korean Journal of Family Welfare. 2011; 16(4):5–27.
16. Koo J, Suh E. Happiness in Korea: Who is happy and when? Korean Journal of Social and Personality Psychology. 2011; 25(2):143–166. https://doi.org/10.21193/kjspp.2011.25.2.008.
17. Park JY, Chang JY. The impact of optimism of parents of children with disabilities on life satisfaction: The mediating effects of positive perception of parenting children and coping behavior. Korean Journal of Special Education. 2014; 49(3):121–144. https://doi.org/10.15861/kjse.2014.49.3.121.

18. Kim SH, Hwang HI. A study on perceptions by mothers with young children about flourishing. Early Childhood Education Research & Review. 2015; 19(3):219–242.
19. Scheier MF, Carver CS, Bridges MW. Distinguishing optimism from neuroticism (and trait anxiety, self-mastery, and self-esteem): A reevaluation of the life orientation test. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1994; 67(6):1063–1078. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.67.6.1063.

20. Chang EC, Maydeu-Olivares A, D’Zurilla TJ. Optimism and pessimism as partially independent constructs: Relationship to positive and negative affectivity and psychological well-being. Personality and Individual Differences. 1997; 23(3):433–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0191-8869(97)00040-8.

21. Carver CS, Scheier MF, Segerstrom SC. Optimism. Clinical Psychology Review. 2010; 30(7):879–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpr.2010.01.006.

22. Ok KH, Chun HY. Maternal parenting stress of infants from different income groups: The relative importance of father involvement, the marital relationship, and meanings of parenthood. Korean Journal of Child Studies. 2012; 33(1):205–221. https://doi.org/10.5723/KJCS.2012.33.1.205.
23. Seo MJ, Choi ES. The effects of maternal depression on maternal parenting stress among mothers with young children: A focus on the moderating effects of mother’s and father’s perceived fatherly involvement in child rearing. Early Childhood Education Research & Review. 2016; 20(5):575–594.
24. Brissette I, Scheier MF, Carver CS. The role of optimism in social network development, coping, and psychological adjustment during a life transition. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2002; 82(1):102–111. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-3514.82.1.102.

25. Woo JP. The concept and understanding of structural equation modeling with AMOS 4.0-20.0. Seoul: Hannarae;2012. p. 160–176. 361-370.
26. Abidin R. Parenting stress index. 3rd ed. Odessa (FL): Psychological Assessment Resources;1995. p. 64–87.
27. Lee KS, Chung KM, Park JA, Kim HJ. Reliability and validity study for the Korean version of Parenting Stress Index Short Form (K-PSI-SF). The Korean Journal of Woman Psychology. 2008; 13(3):363–377. https://doi.org/10.18205/kpa.2008.13.3.007.
28. Abidin RR, Brunner JF. Development of a parenting alliance inventory. Journal of Clinical Child Psychology. 1995; 24(1):31–40. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15374424jccp2401_4.

29. Shin SJ, Chung MJ. Effects of stress, social support and efficacy on mothers’ parenting behaviors. Korean Journal of Child Studies. 1998; 19(1):27–42.
30. Kim JM, Lim HS, Heo SH. A validation study of the Korean version of the parenting sense of competence and the parenting alliance inventory. The Korean Journal of Developmental Psychology. 2014; 27(2):1–21.
31. Radloff LS. The CES-D scale: A self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement. 1977; 1(3):385–401. https://doi.org/10.1177/014662167700100306.
32. Chon KK, Choi SJ, Yang BC. Integrated adaptation of CES - D in Korea. Korean Journal of Health Psychology. 2001; 6(1):59–76.
33. Kim JH, Lee JH. Relations of perceived stress, cognitive set, and coping behaviors to depressidn: A focus on freshmen's stress experiences. Korean Journal of Counseling and Psychotherapy. 1988; 1(1):25–45.
34. Son YM. The relationship between perceived parental communication styles and perceived emotional competence and coping strategies [master’s thesis]. Seoul: Korea University;2009. p. 1–79.
35. Kim JI. Study of the relationship between the child’s feeling of happiness, mother’s feeling of happiness, parenting behaviors, and the elements of familial environment. Korea Journal of Child Care and Education. 2018; 109:53–77.

36. Lim N, Lee H, Suh E. Review of the Satisfaction with Life Scale (SWLS) findings in Korea. Korean Journal of Psychology. 2010; 29(1):21–47.
37. Clark DA, Beck AT, Alford BA. Scientific foundations of cognitive theory and therapy of depression. New York (NY): John Wiley & Sons;1999. p. 76–112.
38. Goodman SH, Brand SR. Infants of depressed mothers: Vulnerabilities, risk factors, and protective factors and protective factors for the later development of psychopathology. Zeanah CH, editor. Handbook of Infant Mental Health. 3rd ed. New York: The Guilford Press;2009. p. 153–170.
39. Murray L, Halligan S, Cooper PJ. Effects of postnatal depression on mother-infant interactions and child development. Bremner G, Wachs T, editors. The Wiley-Blackwell Handbook of Infant Development. 2nd ed. Oxford: Wiley-Blackwell;2010. p. 192–220.

40. Kim SY, Min JA, Chae JH. Relationship between life satisfaction and variables of demographic and psychological positive factors in patients with depression. Journal of Korean Society for Depressive and Bipolar Disorders. 2013; 11(3):161–169.
41. Bastian B, Kuppens P, De Roover K, Diener E. Is valuing positive emotion associated with life satisfaction? Emotion. 2014; 14(4):639–645. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0036466.

42. Choi H. Stress coping pattern and psychological adjustment in college student. Korean Journal of Psychology: General. 2013; 32(1):1–21.
43. Lim HJ, Choi HJ, Lee D. An examination of variables of birth’s psychological characteristics, couple’s characteristics, and mother’s psychological characteristics influencing on mother’s parenting style. Early Childhood Education Research & Review. 2012; 16(3):93–116.
44. Dehle C, Larsen D, Landers JE. Social support in marriage. The American Journal of Family Therapy. 2001; 29(4):307–324. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926180126500.

45. Seo SW, Lee DK. The effects of mother’s marital satisfaction, couple conflict and infants’ emotional temperament on mother’s parenting stress. Korean Journal of Early Childhood Education. 2013; 33(5):279–298. https://doi.org/10.18023/kjece.2013.33.5.012.
46. Raffaelli M, Andrade FCD, Wiley AR, Sanchez‐Armass O, Edwards LL, Aradillas‐Garcia C. Stress, social support, and depression: A test of the stress‐buffering hypothesis in a Mexican sample. Journal of Research on Adolescence. 2013; 23(2):283–289. https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.12006.

47. Yi JS, Choi YH. The effect of parenting stress and social support on the parenting efficacy of mothers. Korean Journal of Play Therapy. 2010; 13(1):19–32.
48. Kim SR, Choi HJ, Jeong KH, Lee YL. The effect of mothers’ parenting stress on children’s social and emotional behaviors according to fathers’ participation in child care: A structural equation modeling analysis. Early Childhood Education Re- search & Review. 2012; 16(1):551–575.
Go to : 
Table 1.
General Characteristics of the Subjects (N=201)
Table 2.
Descriptive Statistics of the Measured Va riables (N=201)
Table 3.
Standardized Direct, Indirect, and Total Effects for the Modified Model (N=201)




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download