INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Subjects
Measurement of blood pressures in both arms and IABDs
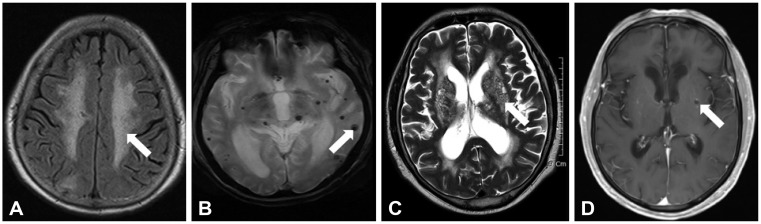
Protocol of brain MRI and definition of cerebral SVDs
Clinical and laboratory variables
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Demographics and comparisons between patients with IABD ≥10 mm Hg and <10 mm Hg
Table 1
Clinical characteristics and comparison of study patients according to different values of the IASBD and the IADBD
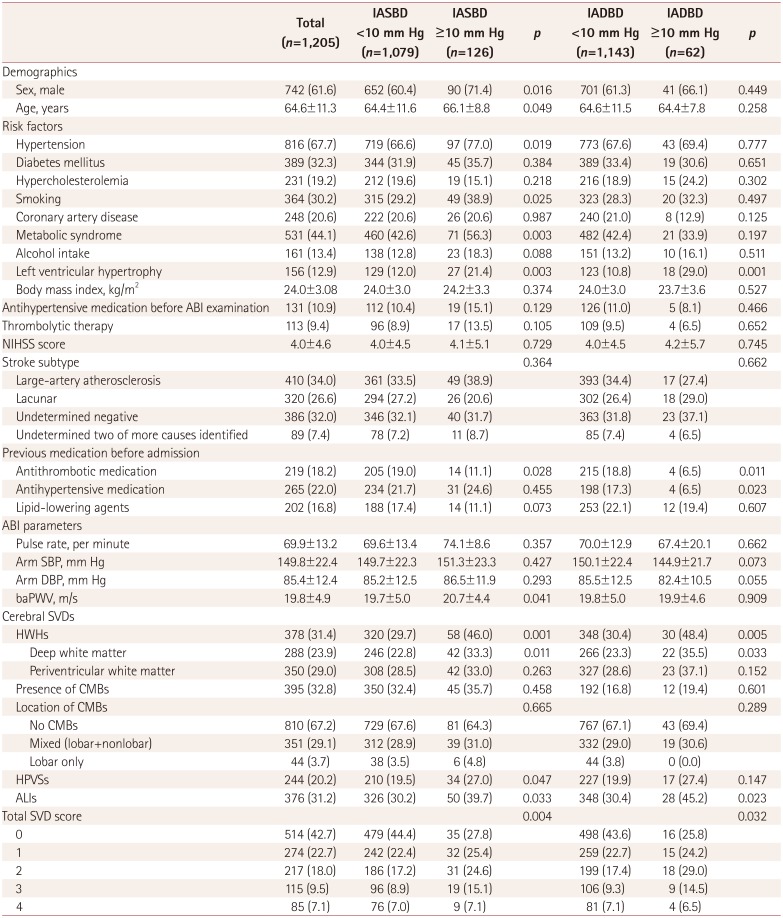
Data are n (%) or mean±SD values.
ABI: ankle-brachial index, ALIs: asymptomatic lacunar infarctions, baPWV: brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity, CMBs: cerebral microbleeds, DBP: diastolic blood pressure, HPVSs: high-grade perivascular spaces, HWHs: high-grade white-matter hyperintensities, IADBD: interarm diastolic blood pressure difference, IASBD: interarm systolic blood pressure difference, NIHSS: National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, SBP: systolic blood pressure, SVD: small-vessel disease.
Association between IABD and presence of cerebral SVDs
Table 2
Clinical characteristics and comparison of the study patients according to the presence of different types of cerebral SVDs
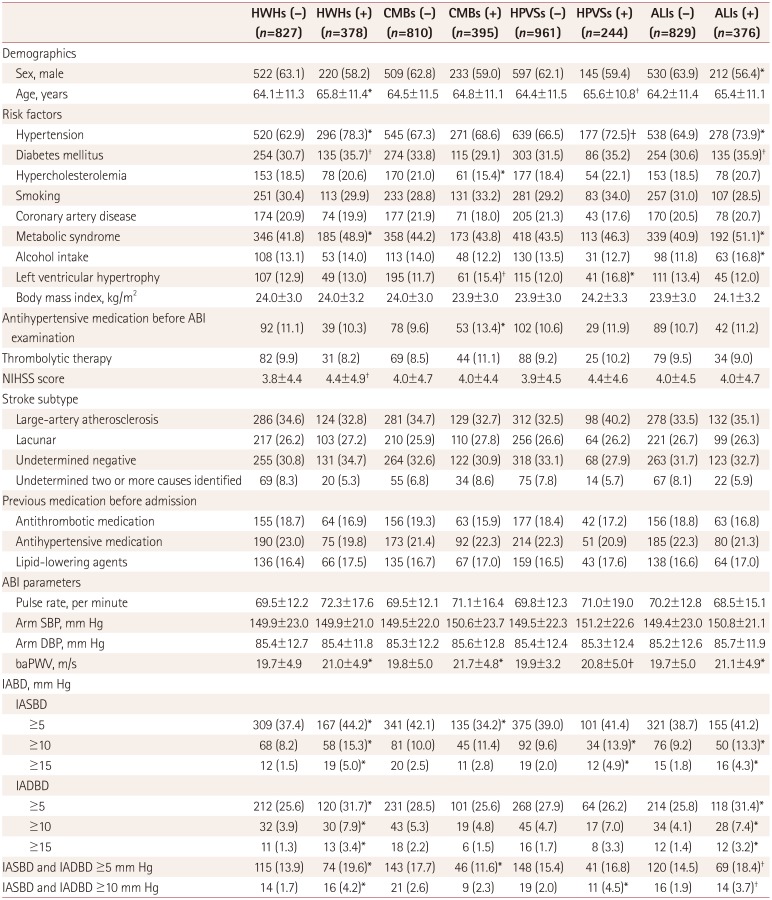
Data are n (%) or mean±SD values.
*p<0.05, †p<0.1.
ABI: ankle-brachial index, ALIs: asymptomatic lacunar infarctions, baPWV: brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity, CMBs: cerebral microbleeds, DBP: diastolic blood pressure, HPVSs: high-grade perivascular spaces, HWHs: high-grade white-matter hyperintensities, IABD: interarm blood pressure difference, IADBD: interarm diastolic blood pressure difference, IASBD: interarm systolic blood pressure difference, NIHSS: National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, SBP: systolic blood pressure, SVDs: small-vessel diseases.
Table 3
Results of the multivariate analysis for the presence of cerebral SVDs according to IASBD and IADBD
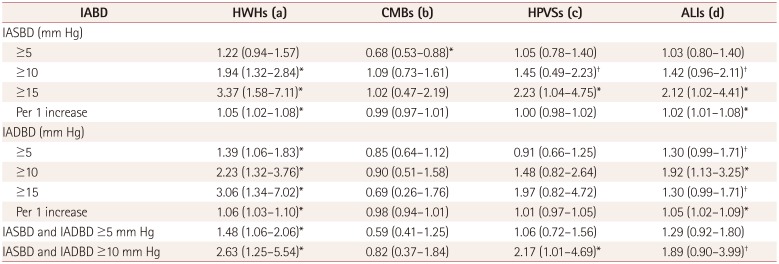
Data are odds ratio (95% CI) values. Adjusted for sex, age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, and baPWV (a), adjusted for sex, age, hypercholesterolemia, left ventricular hypertrophy, antihypertensive medication after admission, and baPWV (b), adjusted for sex, age, hypertension, left ventricular hypertrophy, and baPWV (c), and adjusted for sex, age, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, alcohol intake, and baPWV (d).
*p<0.05, †p<0.1.
ALIs: asymptomatic lacunar infarctions, baPWV: brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity, CMBs: cerebral microbleeds, HPVSs: high-grade perivascular spaces, HWHs: high-grade white-matter hyperintensities, IABD: interarm blood pressure difference, IADBD: interarm diastolic blood pressure difference, IASBD: interarm systolic blood pressure difference, SVDs: small-vessel diseases.
Association between IABD and burden of cerebral SVDs
Table 4
Association of IABD with the total SVD score
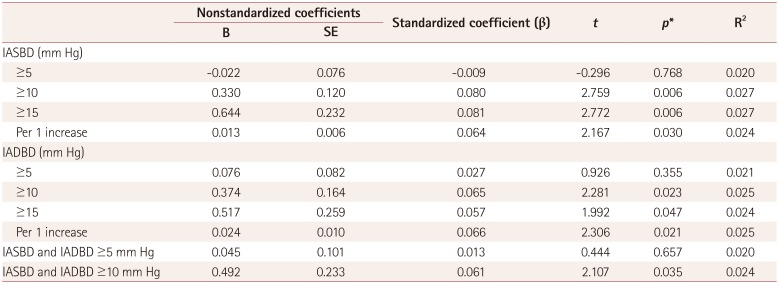
*Results from multivariate linear regression with total SVD score as the dependent variable and with adjustment for sex, age and variables with p<0.1 in the univariate analysis (hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, metabolic syndrome, alcohol intake, left ventricular hypertrophy, and baPWV).
baPWV: brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity, IABD: interarm blood pressure difference, IADBD: interarm diastolic blood pressure difference, IASBD: interarm systolic blood pressure difference, SE: standard error, SVDs: small-vessel diseases.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download