Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Figure 1
Prevalence of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression using two cutoff points, in all patients. (A) The rate of PD-L1 expression was 42% with cutoff Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) 1%. (B) The rate of PD-L1 expression was 21% with cutoff TPS 50%. PD-1: programmed death-1.

Figure 2
Prevalence of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression using the 22C3 pharmDx and SP263 assays. (A) Among the 34 patients analyzed with both the 22C3 and SP263 assays, 27 patients gave positive PD-L1 results for both tests, with a cutoff of Tumor Proportion Score (TPS) ≥1%. (B) Those positive results were found for 20 patients, with a cutoff of TPS ≥ 50%.
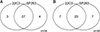
Figure 3
Relationship between programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) immunohistochemical 22C3 pharmDx and SP263 assay. (A) Scatter diagrams illustrating the relationship between expression levels with respect to 22C3 pharmDx and SP263 assays. Each point in the diagram indicates the percentage of positive tumor cells in the 22C3 (x-axis) and SP263 (y-axis) assays. A significantly high relationship was observed between the 22C3 and SP263 assays (r=0.826; 95% confidence interval, 0.736-0.916). (B) Analytic comparison of the percentage of tumor proportion score by case for each assay. Data points expressed the scores on each case (blue points for 22C3 pharmDx and red points for SP263 assay).

Table 1
Baseline demographics
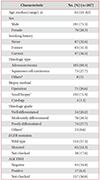
*Other types consisting of small cell lung cancer (5 cases) and large cell lung cancer (3 cases). †Small biopsy specimens were collected via bronchoscopy, endobronchial ultrasound-transbronchial needle aspiration, or transthoracic needle biopsy of the lung. ‡“Others” included specimens for which histologic grade could not be checked.
EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; ALK: anaplastic lymphoma kinase; FISH: fluorescence in situ hybridization.
Table 2
Clinical and pathological characteristics of the 267 patients with PD-L1 expression

Values are presented as mean±SD or number (%).
*Other types included small cell lung cancer (5 cases) and large cell lung cancer (3 cases). †Small biopsy specimens were collected via bronchoscopy, endobronchial ultrasound-trans-bronchial needle aspiration, or transthoracic needle biopsy of the lung. ‡“Others” included specimens for which histologic grade could not be checked.
PD-L1: programmed death-ligand 1; TPS: Tumor Proportion Score; SQC: squamous cell carcinoma; ADC: adenocarcinoma; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; ALK: anaplastic lymphoma kinase; FISH: fluorescence in situ hybridization; SD: standard deviation.
Acknowledgments
Notes
Authors' Contributions
Conceptualization: Oh IJ, Park HY.
Methodology: Oh IJ, Choi YD.
Formal analysis: Park HY, Oh IJ, Choi YD.
Data curation: Park HY, Oh IJ, Kho BG, Kim TO, Shin HJ, Park CK, Kim YC.
Software: Park HY.
Validation: Oh IJ.
Investigation: Park HY, Oh IJ, Park CK, Kim YC, Kwon YS, Kim YI, Lim SC.
Writing - original draft preparation: Park HY.
Writing - review and editing: Oh IJ, Park CK, Kim YC.
Approval of final manuscript: all authors.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download