Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
References
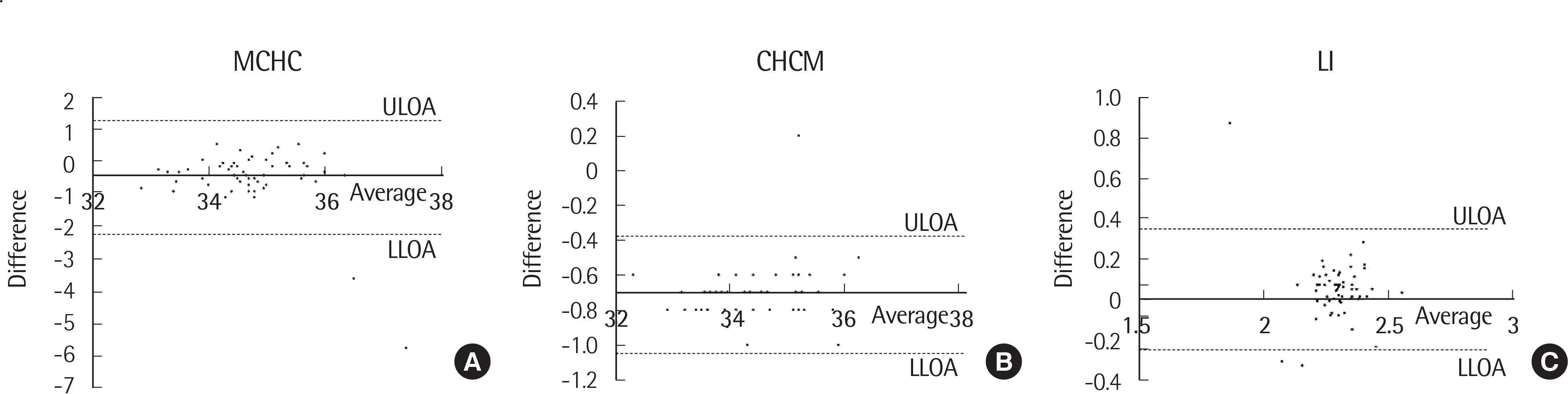 | Fig. 1.Bland-Altman plot of the difference of results between BD Vacutainer and Vacuon (A) mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), (B) cell hemoglobin concentration mean (CHCM), (C) lobularity index (LI). Abbreviations: ULOA, upper limit of agreement; LLOA, lower limit of agreement. |
Table 1.
| BD Vacutainer (mean±SD) | Vacuon (mean±SD) | Mean bias (95% CI) | Difference % | P∗ | r† | Allowable difference range‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WBC, ×103/μL | 6.22±1.49 | 6.3±1.54 | –0.08 (−0.63–0.47) | –1.28 | 0.774 | 0.988 | ±15% |
| RBC, ×106/μL | 4.64±0.61 | 4.66±0.42 | –0.02 (−0.21–0.17) | –0.41 | 0.842 | 0.746 | ±6% |
| Hb, g/dL | 14.53±1.30 | 14.45±1.29 | 0.08 (−0.39–0.55) | –0.54 | 0.742 | 0.988 | ±7% |
| Hct, % | 42.17±3.53 | 41.31±3.58 | 0.87 (−0.42–2.15) | –2.05 | 0.185 | 0.966 | ±6% |
| MCV, fL | 89.98±3.56 | 88.72±3.52 | 1.26 (−0.03–2.54) | –1.39 | 0.055 | 0.874 | ±2.3% |
| MCH, pg | 31±1.51 | 31.07±1.68 | –0.07 (−0.65–0.51) | –0.22 | 0.815 | 0.928 | ±2.7% |
| MCHC, g/dL | 34.44±0.82 | 35±1.11 | –0.56 (−0.91–-0.21) | –1.63 | 0.002 | 0.570 | ±2.2% |
| RDW, % | 12.86±0.67 | 12.86±0.65 | 0.01 (−0.23–0.25) | –0.05 | 0.956 | 0.988 | ±4.6% |
| HDW, % | 02.43±0.19 | 2.46±0.19 | –0.02 (−0.09–0.04) | –1.02 | 0.472 | 0.990 | NA |
| CHCM, g/dL | 34.08±0.84 | 34.79±0.83 | –0.72 (−1.02–-0.41) | –2.1 | 0.000 | 0.978 | NA |
| CH, pg | 30.53±1.49 | 30.74±1.50 | –0.21 (−0.75–0.33) | –0.68 | 0.448 | 0.999 | NA |
| CHDW, % | 3.5±0.22 | 3.55±0.16 | –0.04 (−0.11–0.03) | –1.17 | 0.245 | 0.784 | NA |
| PLT, ×103/μL | 242.77±44.03 | 242.92±44.83 | –0.15 (−16.21–15.91) | –0.06 | 0.985 | 0.970 | ±25% |
| MPV, fL | 7.24±0.66 | 7.15±0.73 | 0.09 (−0.17–0.34) | 1.2 | 0.498 | 0.943 | ±5.8% |
| PDW, fL | 55.71±6.53 | 55.73±6.61 | –0.02 (−2.4–2.36) | –0.04 | 0.987 | 0.810 | NA |
| Pct, % | 0.17±0.03 | 0.17±0.03 | 0.00 (−0.01–0.01) | –1.05 | 0.717 | 0.929 | NA |
| Neutro, % | 57.03±7.93 | 57.07±7.85 | –0.04 (−2.89–2.81) | –0.07 | 0.978 | 0.987 | Target±3SD |
| Lympho, % | 33.1±6.7 | 32.97±6.77 | 0.13 (−2.3–2.57) | 0.4 | 0.914 | 0.985 | Target±3SD |
| Mono, % | 4.9±0.91 | 5.11±0.99 | –0.21 (−0.55–0.13) | –4.29 | 0.230 | 0.833 | Target±3SD |
| Eos, % | 2.48±1.89 | 2.32±1.54 | –0.16 (−0.47–0.78) | –6.33 | 0.620 | 0.679 | Target±3SD |
| Baso, % | 0.47±0.25 | 0.43±0.22 | –0.05 (−0.04–0.13) | –9.51 | 0.298 | 0.744 | Target±3SD |
| LUC, % | 2.02±0.57 | 1.9±0.49 | –0.12 (−0.07–0.31) | –5.78 | 0.230 | 0.781 | NA |
| nRBC/100 WBC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| LI | 2.32±0.11 | 2.27±0.14 | 0.05 (0–0.09) | –2.03 | 0.040 | 0.244 | NA |
| MPXI | –2.13±2.74 | –1.93±2.81 | –0.19 (−1.19–0.81) | –9.02 | 0.706 | 0.832 | NA |
‡ Allowable difference range extrapolated from Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act/College of American Pathologists (CLIA/CAP) participant surveys. Abbreviations: WBC, White blood cell count; RBC, Red blood cell count; Hb, hemoglobin; Hct, hematocrit; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; MCH, mean corpuscular hemoglobin; MCHC, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration; RDW, red cell distribution width; HDW, hemoglobin distribution width; CHCM, cell hemoglobin concentration mean; CH, cellular hemoglobin; CHDW, cell hemoglobin distribution width; PLT, platelet; MPV, mean platelet volume; PDW, platelet distribution width; Pct, platelet-crit; Neutro, neutrophil; Lympho, lymphocyte; Mono, monocyte; Eos, eosinophil; Baso, basophil; LUC, large unstained cell; nRBC, nucleated red blood cell; LI, lobularity index; MPXI, mean peroxidase activity index; SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval.
Table 2.
| BD Vacutainer | Vacuon | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean bias (95% CI) | Difference % | P∗ | Mean bias (95% CI) | Difference % | P∗ | |
| WBC, ×103/μL | 0.02 (−0.51–0.55) | 0.25 | 0.953 | 0.04 (−0.51–0.59) | 0.66 | 0.881 |
| RBC, ×106/μL | –0.06 (−0.25–0.13) | –1.31 | 0.526 | 0.01 (−0.14–0.16) | 0.18 | 0.910 |
| Hb, g/dL | –0.02 (−0.5–0.45) | –0.16 | 0.923 | 0.02 (−0.46–0.50) | 0.15 | 0.929 |
| Hct, % | –0.14 (−1.44–1.17) | –0.32 | 0.836 | –0.1 (−1.39–1.20) | –0.23 | 0.883 |
| MCV, fL | –0.06 (−1.34–1.21) | –0.07 | 0.920 | –0.35 (−1.62–0.91) | –0.40 | 0.582 |
| MCH, pg | 0.03 (−0.49–0.56) | 0.11 | 0.895 | 0.01 (−0.57–0.59) | 0.03 | 0.973 |
| MCHC, g/dL | 0.05 (−0.23–0.34) | 0.15 | 0.719 | 0.14 (−0.21–0.49) | 0.4 | 0.437 |
| RDW, % | 0.05 (−0.18–0.29) | 0.41 | 0.657 | 0.08 (−0.16–0.31) | 0.61 | 0.508 |
| HDW, % | 0.05 (−0.01–0.12) | 2.19 | 0.120 | 0.07 (0.01–0.14) | 2.95 | 0.034 |
| CHCM, g/dL | 0.18 (−0.12–0.48) | 0.53 | 0.231 | 0.36 (0.06–0.65) | 1.02 | 0.018 |
| CH, pg | 0.15 (−0.39–0.68) | 0.48 | 0.589 | 0.2 (−0.35–0.74) | 0.64 | 0.474 |
| CHDW, % | 0 (−0.07–0.07) | –0.11 | 0.914 | 0.03 (−0.03–0.09) | 0.73 | 0.392 |
| PLT, ×103/μL | –11.08 (−27.52–5.35) | –4.57 | 0.184 | –8.92 (−25.44–7.61) | –3.67 | 0.287 |
| MPV, fL | –0.75 (−1.02–-0.49) | –10.38 | 0.000 | –0.88 (−1.17–-0.59) | –12.3 | 0.000 |
| PDW, fL | 0.67 (−1.76–3.09) | 1.20 | 0.587 | –0.16 (−2.52–2.19) | –0.29 | 0.891 |
| Pct, % | –0.03 (−0.04–-0.01) | –14.91 | 0.000 | –0.03 (−0.04–-0.02) | –16.52 | 0.000 |
| Neutro, % | –0.45 (−3.31–2.4) | –0.79 | 0.755 | –0.28 (−3.16–2.6) | –0.49 | 0.847 |
| Lympho, % | 0.94 (−1.48–3.37) | 2.85 | 0.443 | 0.64 (−1.83–3.1) | –1.94 | 0.609 |
| Mono, % | 0.21 (−0.15–0.58) | 4.36 | 0.249 | 0.24 (−0.14–0.62) | –4.67 | 0.214 |
| Eos, % | –0.77 (−1.44–-0.1) | –31.04 | 0.025 | –0.81 (−1.45–-0.17) | –34.94 | 0.014 |
| Baso, % | 0.03 (−0.06–0.12) | 6.69 | 0.474 | –0.07 (−0.16–0.02) | –16.34 | 0.124 |
| LUC, % | 0.02 (−0.19–0.22) | 0.83 | 0.871 | 0.1 (−0.1–0.29) | 5.17 | 0.319 |
| nRBC/100 WBC | 0 | 0 | 0.000 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| LI | 0.75 (0.69–0.81) | 32.3 | 0.000 | 0.7 (0.64–0.76) | 30.89 | 0.000 |
| MPXI | 0.89 (−0.22–1.99) | –41.65 | 0.114 | 0.17 (−0.98–1.31) | –8.53 | 0.775 |
Abbreviations: WBC, White blood cell count; RBC, Red blood cell count; Hb, hemoglobin; Hct, hematocrit; MCV, mean corpuscular volume; MCH, mean corpuscular hemoglobin; MCHC, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration; RDW, red cell distribution width; HDW, hemoglobin distribution width; CHCM, cell hemoglobin concentration mean; CH, cellular hemoglobin; CHDW, cell hemoglobin distribution width; PLT, platelet; MPV, mean platelet volume; PDW, platelet distribution width; Pct, platelet-crit; Neutro, neutrophil; Lympho, lymphocyte; Mono, monocyte; Eos, eosinophil; Baso, basophil; LUC, large unstained cell; nRBC, nucleated red blood cell; LI, lobularity index; MPXI, mean peroxidase activity index; CI, confidence interval.
Table 3.
| BD Vacutainer (mean±SD) | Vacuon (mean±SD) | Mean bias (95% CI) | D ifference % | P∗ | r† | Allowable difference range‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP, mg/dL | 0.10±0.18 | 0.10±0.19 | 0 (−0.07–0.07) | 0.17 | 0.996 | 0.999 | ±30% |
| AST, U/L | 18.56±6.48 | 18.66±6.48 | –0.1 (−2.4–2.21) | –0.52 | 0.934 | 0.982 | ±20% |
| ALT, U/L | 18.94±12.25 | 18.89±12.36 | 0.05 (−4.33–4.42) | 0.26 | 0.983 | 0.998 | ±20% |
| ALP, U/L | 57.61±15.81 | 57.63±15.93 | –0.02 (−5.66–5.63) | –0.03 | 0.995 | 0.992 | ±30% |
| GGT, U/L | 27.63±32.48 | 27.5±32.81 | 0.13 (−11.48–11.74) | 0.47 | 0.982 | 0.999 | ±10% |
| T. Bil, mg/dL | 0.65±0.41 | 0.65±0.41 | 0 (−0.14–0.15) | 0.37 | 0.974 | 0.998 | ±20% |
| D. Bil, mg/dL | 0.25±0.12 | 0.28±0.14 | –0.03 (−0.07–0.02) | –10.3 | 0.262 | 0.991 | ±30% |
| Ca, mg/dL | 9.4±0.31 | 9.39±0.3 | 0.01 (−0.1–0.12) | 0.07 | 0.907 | 0.878 | ±1.00 |
| Mg, mg/dL | 2±0.14 | 2.01±0.15 | –0.01 (−0.07–0.04) | –0.73 | 0.578 | 0.913 | ±25% |
| P, mg/dL | 3.49±0.63 | 3.49±0.63 | 0 (−0.22–0.22) | 0.00 | 0.999 | 0.997 | ±12% |
| Fe, μg/dL | 107.16±44.16 | 106.84±44.17 | 0.32 (−15.38–16.03) | 0.30 | 0.968 | 0.999 | ±20% |
| UIBC, μg/dL | 223.52±61.65 | 224.65±61.95 | –1.13 (−23.1–20.84) | –0.51 | 0.919 | 0.995 | ±25% |
| TP, g/dL | 6.89±1.24 | 6.89±1.25 | 0.01 (−0.43–0.45) | 0.12 | 0.971 | 0.878 | ±10% |
| Alb, g/dL | 4.76±0.24 | 4.77±0.24 | –0.01 (−0.1–0.08) | –0.2 | 0.823 | 0.947 | ±10% |
| Glu, mg/dL | 101.19±16.85 | 101.32±16.8 | –0.13 (−6.11–5.85) | –0.13 | 0.966 | 0.991 | ±10% |
| UA, mg/dL | 5.64±1.47 | 5.63±1.51 | 0.01 (−0.52–0.54) | 0.11 | 0.981 | 0.997 | ±17% |
| LDH, U/L | 175.61±24.14 | 171.9±23.92 | 3.71 (−4.83–12.25) | 2.11 | 0.392 | 0.833 | Target±3SD |
| CK, U/L | 116.23±69.81 | 117.16±70.27 | –0.94 (−25.84–23.97) | –0.8 | 0.941 | 0.999 | ±30% |
| BUN, mg/dL | 12.77±3.56 | 12.87±3.59 | –0.1 (−1.37–1.17) | –0.8 | 0.874 | 0.993 | ±9%0 |
| Cre, mg/mL | 0.82±0.16 | 0.83±0.16 | –0.01 (−0.07–0.04) | –1.6 | 0.646 | 0.980 | ±15% |
| T. Chol, mg/dL | 187.48±37.68 | 188.06±38.17 | –0.58 (−14.06–12.9) | –0.31 | 0.932 | 0.995 | ±10% |
| TG, mg/dL | 141.44±95.55 | 140.87±94.97 | 0.56 (−33.3–34.43) | 0.4 | 0.974 | 0.999 | ±25% |
| HDL, mg/dL | 57.31±16.14 | 57.69±16.32 | –0.39 (−6.16–5.38) | –0.68 | 0.895 | 0.991 | ±30% |
| LDL, mg/dL | 116.6±33.4 | 117.18±33.87 | –0.58 (−12.54–11.38) | –0.5 | 0.924 | 0.999 | ±30% |
| T3, ng/mL | 0.92±0.12 | 0.93±0.11 | 0.00 (−0.05–0.04) | –0.35 | 0.860 | 0.938 | Target±3SD |
| FT4, ng/dL | 1.28±0.16 | 1.26±0.16 | 0.01 (−0.04–0.08) | 1.14 | 0.532 | 0.928 | Target±3SD |
| TSH, μIU/mL | 1.92±1.15 | 1.94±1.14 | –0.02 (−0.41–0.37) | –0.94 | 0.921 | 0.998 | Target±3SD |
‡ Allowable difference in the range extrapolated from Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act/College of American Pathologists (CLIA/CAP) participant surveys.
Abbreviations: CRP, C-reactive protein; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; GGT, gamma-glutamyltransferase; T-Bil, total bilirubin; D-Bil, direct bilirubin; Ca, calcium; Mg, magnesium; P, phosphorus; Fe, ferrous iron; UIBC, unsaturated iron binding capacity; TP, total protein; Alb, albumin; Glu, glucose; UA, uric acid; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; CK, creatine kinase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; Cre, creatinine; T. Chol, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL, high density lipoprotein; LDL, low density lipoprotein; T3, triiodothyronine; FT4, free thyroxine; TSH, thyroid stimulating hormone; SD, standard deviation; CI, confidence interval.
Table 4.
| BD Vacutainer | Vacuon | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean bias (95% CI) | Difference % | P∗ | Mean bias (95% CI) | Difference % | P∗ | |
| CRP, mg/dL | 0 (−0.07–0.07) | –0.17 | 0.996 | 0 (−0.07–0.07) | –1.34 | 0.969 |
| AST, U/L | 18.47 (−2.81–1.84) | –2.61 | 0.682 | –0.6 (−2.91–1.72) | –3.2 | 0.611 |
| ALT, U/L | 18.84 (−3.96–4.74) | 2.04 | 0.861 | 0.21 (−4.19–4.61) | 1.11 | 0.925 |
| ALP, U/L | 57.52 (−6.13–5.13) | –0.87 | 0.861 | –0.44 (−6.04–5.17) | –0.76 | 0.878 |
| GGT, U/L | 27.53 (−11.52–11.58) | 0.12 | 0.996 | 0.03 (−11.58–11.64) | 0.12 | 0.996 |
| T. Bil, mg/dL | 0.56 (−0.13–0.15) | 1.78 | 0.872 | 0.01 (−0.13–0.16) | 1.74 | 0.879 |
| D. Bil, mg/dL | 0.16 (−0.03–0.05) | 4.8 | 0.571 | 0.02 (−0.03–0.06) | 6.21 | 0.474 |
| Ca, mg/dL | 9.3 (−0.27–-0.03) | –1.58 | 0.015 | –0.19 (−0.31–-0.07) | –2.06 | 0.002 |
| Mg, mg/dL | 1.9 (−0.07–0.04) | –0.84 | 0.525 | –0.03 (−0.08–0.03) | –1.26 | 0.360 |
| P, mg/dL | 3.4 (−0.21–0.23) | 0.27 | 0.932 | 0 (−0.22–0.22) | 0.05 | 0.987 |
| Fe, μg/dL | 107.06 (−16.77–14.65) | –0.99 | 0.894 | –1.77 (−17.57–14.02) | –1.66 | 0.824 |
| UIBC, μg/dL | 223.42 (−30.34–13.37) | –3.8 | 0.444 | –8.13 (−30.12–13.86) | –3.62 | 0.466 |
| TP, g/dL | 6.8 (−0.41–0.49) | 0.61 | 0.853 | 0.01 (−0.44–0.46) | 0.09 | 0.977 |
| Alb, g/dL | 4.67 (−0.08–0.09) | 0.14 | 0.878 | 0.01 (−0.08–0.1) | 0.2 | 0.827 |
| Glu, mg/dL | 101.1 (−4.18–7.73) | 1.75 | 0.556 | 1.42 (−4.52–7.36) | 1.4 | 0.637 |
| UA, mg/dL | 5.54 (−0.47–0.58) | 0.94 | 0.842 | 0.06 (−0.48–0.6) | 1.12 | 0.818 |
| LDH, U/L | 175.52 (−12.86–4.19) | –2.47 | 0.316 | –4.84 (−13.36–3.69) | –2.81 | 0.263 |
| CK, U/L | 116.13 (−25.02–24.66) | –0.15 | 0.989 | 0.44 (−24.39–25.26) | 0.37 | 0.972 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 12.67 (−1.77–0.79) | –3.84 | 0.449 | –0.43 (−1.72–0.85) | –3.37 | 0.505 |
| Cre, mg/mL | 0.72 (−0.08–0.04) | –2.36 | 0.501 | –0.01 (−0.07–0.05) | –1.3 | 0.708 |
| T. Chol, mg/dL | 187.39 (−16.13–10.55) | –1.49 | 0.68 | –1.39 (−14.7–11.92) | –0.74 | 0.837 |
| TG, mg/dL | 141.34 (−38.5–31.82) | –2.36 | 0.851 | –1.66 (−35.34–32.02) | –1.18 | 0.922 |
| HDL, mg/dL | 57.21 (−4.52–6.72) | 1.91 | 0.700 | 0.55 (−5.18–6.28) | 0.95 | 0.850 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 116.5 (−11.07–12.75) | 0.72 | 0.889 | 1.21 (−10.75–13.17) | 1.03 | 0.842 |
| T3, ng/mL | –0.06 (−0.09–0.00) | –6.36 | 0.045 | –0.05 (−0.08–0.00) | –5.66 | 0.064 |
| FT4, ng/dL | –0.02 (−0.06–0.06) | –1.2 | 0.915 | 0.01 (−0.05–0.05) | 0.76 | 0.704 |
| TSH, μIU /mL | 0.03 (−0.35–0.42) | 1.67 | 0.863 | 0.03 (−0.35–0.42) | 1.57 | 0.869 |
Abbreviations: CRP, C-reactive protein; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; GGT, gamma-glutamyltransferase; T-Bil, total bilirubin; D-Bil, direct bilirubin; Ca, calcium; Mg, magnesium; P, phosphorus; Fe, ferrous iron; UIBC, unsaturated iron binding capacity; TP, total protein; Alb, albumin; Glu, glucose; UA, uric acid; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; CK, creatine kinase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; Cre, creatinine; T. Chol, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL, high density lipoprotein; LDL, low density lipoprotein; T3, triiodothyronine; FT4, free thyroxine; TSH, thyroid stimulating hormone; CI, confidence interval.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download