Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Flowchart of study cohort construction. *Cohort entry date was matched with the cohort entry date of the cases, ranging from 30 days before or after the entry date.

Fig. 2
Subgroup analyses of the associations between AMD and exposures according to the type of AMD and presence of cerebrovascular diseases. *Adjusted for income level, Charlson comorbidity index, the number of prescriptions, cerebrovascular disease history, complicated or uncomplicated diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension and peripheral vascular disease, and the use of alpha-blockers, alpha-glucosidase, aspirin, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, meglitinide, sulfonylurea, or thiazolidinedione. AMD, age-related macular degeneration; ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARBs, angiotensin II receptor blockers; aORs, adjusted odds ratios; CI, confidence interval.
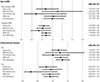
Table 1
Baseline Demographic and Clinical Characteristics of the Study Population
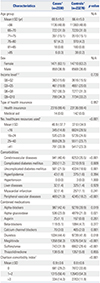
SD, standard deviation; N/A, not applicable.
Variables are presented as a number (percentage) unless otherwise noticed.
*Cases and controls are matched by age, sex, cohort entry date, and follow-up duration; †According to Bonferroni method, the level of significance was adjusted by 0.05/k, where k is the number of groups for each variable; ‡Income levels are classified into 11 groups ranging from 0–10, according to the type of health insurance. Ten of the groups are for employee and district subscribers. Group 0 indicates medical aid.
Table 2
Association between Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Exposure
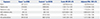
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARBs, angiotensin II receptor blockers.
Variables are presented as a number (percentage) unless otherwise noticed.
*Cases and controls are matched by age, sex, cohort entry date, and follow-up duration; †Adjusted for income level, Charlson comorbidity index, the number of prescriptions, cerebrovascular disease history, complicated or uncomplicated diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension and peripheral vascular disease, and the use of alpha-blockers, alpha-glucosidase, aspirin, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, meglitinide, sulfonylurea, or thiazolidinedione.
Table 3
Association between Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Exposure according to Cumulative Duration
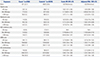
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARBs, angiotensin II receptor blockers; N/A, not applicable.
Variables are presented as a number (percentage) unless otherwise noticed.
*Cases and controls are matched by age, sex, cohort entry date, and follow-up duration; †Adjusted for income level, Charlson comorbidity index, the number of prescriptions, cerebrovascular disease history, complicated or uncomplicated diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension and peripheral vascular disease, and the use of alpha-blockers, alpha-glucosidase, aspirin, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, meglitinide, sulfonylurea, or thiazolidinedione.
Table 4
Association between Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Exposure according to the Time of Administration
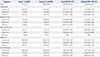
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ACE inhibitors, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; ARBs, angiotensin II receptor blockers, N/A, not applicable.
Variables are presented as a number (percentage) unless otherwise noticed.
*Cases and controls are matched by age, sex, cohort entry date, and follow-up duration; †Adjusted for income level, Charlson comorbidity index, the number of prescriptions, cerebrovascular disease history, complicated or uncomplicated diabetes, hyperlipidemia, hypertension and peripheral vascular disease, and the use of alpha-blockers, alpha-glucosidase, aspirin, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, meglitinide, sulfonylurea, or thiazolidinedione.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: Ju-Young Shin.
Data curation: Hyesung Lee.
Formal analysis: Hyesung Lee.
Funding acquisition: Ju-Young Shin.
Investigation: Hyesung Lee.
Methodology: Ju-Young Shin and Hyesung Lee.
Project administration: Ju-Young Shin.
Resources: Ha-Lim Jeon.
Software: Hyesung Lee.
Supervision: Ju-Young Shin.
Validation: Ju-Young Shin and Ha-Lim Jeon.
Visualization: Hyesung Lee.
Writing—original draft: Hyesung Lee and Ha-Lim Jeon.
Writing—review & editing: Ju-Young Shin and Sang Jun Park.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download