Abstract
Purpose
Materials and Methods
Results
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Expression of NEAT1 is elevated in Aβ-treated SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells. (A and B) The expression of NEAT1 was measured in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells after treatment of different concentrations (0, 5, 10, and 20 µM) of Aβ for 24 h by qRT-PCR. (C and D) The levels of NEAT1 were detected in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells after treatment of 10 µM Aβ for different treatment times (0, 12, 24, and 48 h) by qRT-PCR. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. NEAT1, nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1; Aβ, amyloid β1–42.
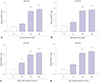
Fig. 2
Knockdown of NEAT1 attenuates Aβ-induced neuronal damage in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells. (A and B) The expression of NEAT1 was measured in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells transfected with si-NEAT1 or si-NC after treatment of 10 µM Aβ for 24 h by qRT-PCR. Cell viability (C and D), Ki67 expression (E and F), and apoptosis (G and H) were detected in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells transfected with si-NEAT1 or si-NC after treatment of 10 µM Aβ for 24 h by MTT, immunocytochemistry, and flow cytometry. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. NEAT1, nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1; Aβ, amyloid β1–42.
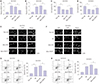
Fig. 3
Interference of NEAT1 weakens Aβ-induced phosphorylation of Tau in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells. The protein levels of phosphorylation of Tau (p-Tau) were measured in SH-SY5Y (A) and SK-N-SH (B) cells transfected with si-NEAT1 or si-NC after treatment of 10 µM Aβ for 24 h by Western blot. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. NEAT1, nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1; Aβ, amyloid β1–42.
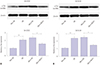
Fig. 4
miR-107 is bound to NEAT1. (A) The putative binding sites of NEAT1 and miR-107 were predicted by StarBase. (B) Luciferase activity was measured in 293T cells co-transfected with NEAT1-WT or NEAT1-MUT and miR-107 or miR-NC. (C and D) The enrichment of NEAT1 was detected in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells transfected with miR-107 or miR-NC after RIP assay. (E and F) The expression of miR-107 was measured in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells transfected with pcDNA, NEAT1, si-NC or si-NEAT1 by qRT-PCR. ***p<0.001. NEAT1, nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1.
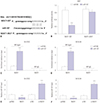
Fig. 5
The levels of miR-107 are decreased in Aβ-treated SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells. (A and B) The expression of miR-107 was measured in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells after treatment of different concentrations of Aβ for 24 h by qRT-PCR. (C and D) The abundance of miR-107 was detected in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells after treatment of 10 µM Aβ for different treatment times by qRT-PCR. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Aβ, amyloid β1–42.
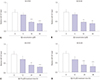
Fig. 6
Abrogation of miR-107 reverses the regulatory effect of NEAT1 knockdown on Aβ-induced neuronal damage in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells. (A and B) The expression of miR-107 was measured in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells transfected with miR-107, miR-NC, si-NEAT1, and anti-miR-NC or anti-miR-107 after treatment of 10 µM Aβ for 24 h by qRT-PCR. Cell viability (C and D) and apoptosis (E and F) were detected in SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells transfected with miR-107, miR-NC, si-NEAT1, and anti-miR-NC or anti-miR-107 after treatment of 10 µM Aβ for 24 h by MTT or flow cytometry. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. NEAT1, nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1; Aβ, amyloid β1–42.
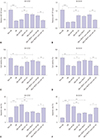
Fig. 7
miR-107 is involved in interference of NEAT1-mediated inhibition of phosphorylation of Tau (p-Tau) in Aβ-treated SH-SY5Y and SK-N-SH cells. The protein levels of p-Tau were detected in SH-SY5Y (A) and SK-N-SH (B) cells transfected with miR-107, miR-NC, si-NEAT1, and anti-miR-NC or anti-miR-107 after treatment of 10 µM Aβ for 24 h by Western blot. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. NEAT1, nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1; Aβ, amyloid β1–42.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: Sha Ke, Fei Yang, Juan Tan, Bo Liao.
Data curation: Juan Tan, Xiaoming Wang, Bo Liao, Fei Yang, Zhaohui Yang.
Formal analysis: Sha Ke, Fei Yang, Juan Tan, Bo Liao.
Funding acquisition: Sha Ke, Juan Tan, Xiaoming Wang, Bo Liao.
Investigation: Bo Liao, Fei Yang.
Methodology: Sha Ke, Bo Liao, Fei Yang.
Project administration: Juan Tan, Fei Yang.
Resources: Sha Ke, Bo Liao.
Software: Sha Ke, Juan Tan.
Supervision: Sha Ke, Fei Yang.
Validation: Fei Yang, Bo Liao.
Visualization: Sha Ke, Juan Tan.
Writing—original draft: Sha Ke, Bo Liao, Fei Yang, Xiaoming Wang.
Writing—review & editing: Sha Ke, Zhaohui Yang, Bo Liao.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download