Abbreviations
ATCC
BMP
ECSIT
gAcrp
IB
IKK
IP
IRAK1
MAP3K7
MEF
MyD88
NGF
NOS
PAMP
SQSTM1
TAB1
TAB2
TAK1
TRAF6
WT
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mice
Cells
Antibodies
Luciferase reporter assay
Measurement of pro-inflammatory cytokines and p65- and p50-DNA-binding assays
Plasmids
Western blotting and immunoprecipitation (IP) assay
Ubiquitination assay
RESULTS
p62 negatively regulates the activation of NF-κB induced by TLR4 stimulation
Figure 1
p62 overexpression inhibits the activation of NF-κB induced by TLR4. (A) THP-1 cells were transfected with vector control (Mock) or Myc-p62 vector together with pBIIx-luc and Renilla luciferase vector, untreated or treated with LPS (200 ng/ml) for 6 h, then subjected to the luciferase activity assay. The results are expressed as fold-induction in luciferase activity relative to untreated cells. All error bars represent the mean ± SD of triplicate samples. Western blot analysis was used to measure the expression of transiently transfected Myc-p62 (lower panel). The expression of GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B and C) THP-1 cells were transfected with mock or Myc-p62 vector, untreated or treated with LPS (200 ng/ml) for 6 h, then analyzed for p65-DNA (B) or p50-DNA (C) binding activity. All error bars represent the mean ± SD of triplicate samples. (D-F) THP-1 cells were transfected with mock or Myc-p62 vector, untreated or treated with LPS (200 ng/ml) for 9 h, then subjected to ELISA to determine the levels TNF-α (D), IL-6 (E), and IL-1β (F) produced. All error bars represent the mean ± SD from triplicate samples.
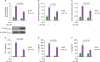
Figure 2
p62−/−MEF cells enhance the activation of NF-κB induced by TLR4. (A) Wild-type (WT) p62+/+MEF and p62−/−MEF cells were transfected with pBIIx-luc and Renilla luciferase vector, untreated or treated with LPS (1 µg/ml) for 6 h, then subjected to the luciferase activity assay. Results are expressed as fold-induction in luciferase activity relative to untreated cells. All error bars represent the mean±SD of triplicate samples. (B and C) WT p62+/+MEF and p62−/−MEF cells were untreated or treated with LPS (1 µg/ml) for 6 h, then analyzed for p65-DNA (B) or p50-DNA (C) binding activity. All error bars represent the mean±SD of triplicate samples. (D-F) WT p62+/+MEF and p62−/−MEF cells were untreated or treated with LPS (1 µg/ml) for 9 h, then subjected to ELISA to determine the levels TNF-α (D), IL-6 (E), and IL-1β (F) produced. All error bars represent the mean±SD from triplicate samples.
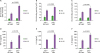
p62−/− MEF cells enhance the activation of TLR4-induced signaling
Figure 3
p62−/−MEF cells enhance TLR4-mediated signals. (A) Wild-type (WT) p62+/+MEF and p62−/−MEF cells were treated with or without LPS (1 µg/ml) for different time periods, as indicated, then subjected to Western blot analyses using anti-TAK1, anti-pho-TAK1, anti-pho-IKKβ, anti-IKKαβ, or anti-GAPDH antibody as a loading control. (B and C) The band intensity of pho-TAK1 (B) or pho-IKKβ (C) was analyzed with the Image J program. The data shown are averages from a minimum of three independent experiments (± SD). (D) WT p62+/+MEF and p62−/−MEF cells were transfected with vector control (Mock) or Myc-p62 vector together with pBIIx-luc and Renilla luciferase vector, untreated or treated with LPS (1 µg/ml) for 6 h, then subjected to the luciferase activity assay. The results are expressed as fold-induction in luciferase activity relative to untreated cells. All error bars represent the mean±SD of triplicate samples. Western blot analysis was used to measure the expression of transiently transfected Myc-p62 (lower panel). The expression of GAPDH was used as a loading control. (E) Model showing how p62 is negatively involved in TLR4-mediated signaling. TLR4 stimulation induces the activation of TRAF6 through upstream signaling molecules. TRAF6 is further associated with ECSIT/TAK1/TAB1/TAB2 molecules for the activation of TAK1, eventually leading to the activation of NF-κB. p62 may be negatively involved in these processes, as indicated.
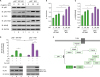
p62 inhibits the association of ECSIT-TRAF6 complex and suppresses the ubiquitination of ECSIT
Figure 4
p62 interacts with ECSIT. (A) HEK293T cells were transfected with mock, Flag-ECSIT WT, and Flag-ECSIT truncated mutants, Flag-ECSIT 1-300 and Flag-ECSIT 1-200, and Myc-p62, as indicated. At 38 h post transfection, the transfected cells were extracted and the cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc antibody followed by IB using anti-Flag or anti-Myc antibody. Model of how p62 interacts with ECSIT (down). (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with mock, Myc-p62, Flag-TRAF6 WT, and Flag-TRAF6 truncated mutants, Flag-TRAF6 110-522, Flag-TRAF6 260-522, and Flag-TRAF6 349-522, as indicated. At 38 h post transfection, transfected cells were extracted and cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody followed by IB using anti-Flag or anti-Myc antibody. Model of how p62 interacts with TRAF6 (down). (C) Model of how ECSIT interacts with TRAF6 and p62. (D) A possible model in which p62 is negatively implicated in TRAF6/ECSIT-mediated activation of NF-κB.
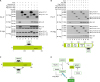
Figure 5
p62 inhibits the interaction of TRAF6-ECSIT and inhibits the ubiquitination of ECSIT. (A) HEK293T cells were transfected with mock, Flag-TRAF6, Myc-ECSIT, and Myc-p62, as indicated. At 38 h post transfection, the transfected cells were extracted and cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody followed by IB using anti-Flag, anti-p62, or anti-ECSIT antibody. (B) HEK293T cells were transfected with mock, Flag-TRAF6, Myc-ECSIT, and different concentrations of Myc-p62, as indicated. At 38 h post transfection, transfected cells were extracted and cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody followed by IB using anti-Flag, anti-p62, or anti-ECSIT antibody. (C) HEK293T cells were transfected with mock, Flag-TRAF6, Myc-ECSIT, HA-Ub, and different concentrations of Flag-p62, as indicated. At 38 h post transfection, transfected cells were extracted and cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Myc antibody followed by IB using anti-HA, anti-Myc, anti-p62, or anti-TRAF6 antibodies.
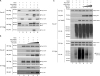
p62−/− mice exhibit high sensitivity to LPS challenge
Figure 6
p62−/− KO mice exhibit a higher mortality rate following LPS challenge. (A and B) Wild-type (WT) p62+/+ and p62−/− KO mice were injected intraperitoneally with 25 mg/kg LPS (n=6 per group) in PBS (A) or 12 mg/kg LPS (n=11–13 per group) in PBS (B). Survival was monitored for 10 days or seven days after LPS challenge. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to compare the differences in mortality rates between the groups. (C) Model of how p62 negatively regulates TLR4-mediated signaling for the activation of NF-κB and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. TLR4 stimulation induces the activation of TRAF6 through upstream signaling molecules, such as MyD88 and IRAK1/2/4. TRAF6 is further associated with ECSIT/TAK1/TAB1/TAB2 molecules for ubiquitination of ECSIT and activation of TAK1 for the activation of NF-κB, eventually leading to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β (left). However, the interaction between p62 and ECSIT may lead to the inhibition of TRAF6-ECSIT interaction and ubiquitination of ECSIT, leading to the inhibition of NF-κB activation and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (right).




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download