Abstract
Lipoma arborescens or synovial lipomatosis is a rare disorder that is characterized by mature fat infiltration of the hypertrophic synovial villi, most frequently affecting the supra-patellar pouch of the knee. This paper presents a case of lipoma arborescens of the ankle joint bilaterally in an adult patient with involvement of both the intra-articular synovium and the synovial sheath of the tendons around the ankle.
Figures and Tables
 | Figure 1Photographs of the right ankle (A) and the left ankle (B) show soft-tissue swelling around lateral malleolus. Soft and movable mass-like lesion (A: 5×7 cm size, B: 4×6 cm size) was observed. |
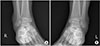 | Figure 2Internal oblique radiographics of the right ankle (A) and the left ankle (B) show soft tissue swelling of the postero-lateral ankle. |
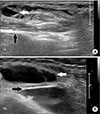 | Figure 3(A, B) Ultrasound scan, longitudinal view, shows encasement of the extensor tendons by the thickened synovium (black arrows). A Large amount of joint effusion in lateral aspect of both ankles (white arrows). |
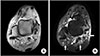 | Figure 4(A) Axial proton density-weighted magnetic resonance image showing high signal intensity within the peroneus brevis tendon at the postero-lateral malleolar level representing longitudinal tear (black arrow). The peroneus longus tendon (white arrow) is normal. (B) Axial T2-weighted fat-suppression magnetic resonance image at the corresponding level shows fluid collection with frond-like proliferations of the synovium of the involved tendon sheaths and ankle joint, with low signal intensity of the hyperplastic fat tissues (white arrows). |
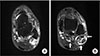 | Figure 5(A) The Anterior talofibular ligament is thin and has irregular margin and suspicious disruption of contour, meaning a chronic partial tear (black arrow). (B) Axial T2-weighted fat-suppression magnetic resonance image at the corresponding level shows fluid collection with frond-like proliferations of the synovium of the involved tendon sheaths and ankle joint, with low signal intensity of the hyperplastic fat tissues (white arrows). |
 | Figure 6(A, B) Intraoperative photographs demonstrate abundant fat within the opened peroneal tendon sheath and partial tear of peroneus longus tendon in both ankles (black arrows). (C) There is a longitudinal split tear of the peroneus brevis tendon (black arrow). |
 | Figure 7Gross photos of mass which are lipoma arborscence with abundant fat tissue and remnant of peroneus longus tendon in left ankle (A: 2×5 cm sized, 3.5 cm sized mass) and in right ankle (B: 2×2.5 cm sized, 6×6 cm sized mass). |
 | Figure 8(A) Photomicrographs of excised synovium showing a lipomatous infiltrate within the synovium. On low power, a fatty infiltrate is seen in the synovium, giving it a lobular or villous contour (H&E stain, ×40). (B) High magnification shows mature adipose cells deep to a hyperplastic layer of synovial cells with scattered inflammatory cells and small plexiform vessels (H&E stain, ×40). |
References
1. Vilanova JC, Barceló J, Villalón M, Aldomà J, Delgado E, Zapater I. MR imaging of lipoma arborescens and the associated lesions. Skeletal Radiol. 2003; 32:504–509.

2. Kakkar N, Vasishta RK, Anand H. Pathological case of the month. Synovial lipomatosis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999; 153:203–204.
3. Laorr A, Peterfy CG, Tirman PF, Rabassa AE. Lipoma arborescens of the shoulder: magnetic resonance imaging findings. Can Assoc Radiol J. 1995; 46:311–313.
4. Arzimanoglu A. Bilateral arborescent lipoma of the knee: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1957; 39-A:976–979.
5. Hallel T, Lew S, Bansal M. Villous lipomatous proliferation of the synovial membrane (lipoma arborescens). J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1988; 70:264–270.

6. Soler T, Rodríguez E, Bargiela A, Da Riba M. Lipoma arborescens of the knee: MR characteristics in 13 joints. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998; 22:605–609.

7. Siva C, Brasington R, Totty W, Sotelo A, Atkinson J. Synovial lipomatosis (lipoma arborescens) affecting multiple joints in a patient with congenital short bowel syndrome. J Rheumatol. 2002; 29:1088–1092.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download