Dear Editor:
Tacrolimus ointment is approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for second-line therapy of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis therapy. There are other indications for topical tacrolimus, including contact dermatitis, psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, vitiligo, and rosacea1. Common adverse effects (AEs) include application-site reactions, such as burning sensation, pruritus, and erythema. The incidence of burning sensation after application of 0.1% tacrolimus was 19%~59%, followed by pruritus. However, these are generally transient and have mild to moderate intensity. Primary disease status improvement is associated with relief of AEs, and AE-associated treatment discontinuation is rarely reported. The percentage of patients prematurely discontinuing treatment because of AEs was 1.4%~6.2% with 0.03% tacrolimus ointment and 1.6%~5.3% with 0.1% tacrolimus ointment2.
Topical tacrolimus is relatively safe, but patient compliance can be impacted by AEs at the beginning of treatment. Additional studies are needed to determine whether the incidence of these AEs differ by disease conditions or applied site. Therefore, we conducted a retrospective chart review to assess the incidence patterns.
Data from patients prescribed topical tacrolimus (Protopic®; Astellas Pharma, Tokyo, Japan) from March 2012 to November 2014 were collected retrospectively. Five common diseases treated with topical tacrolimus in our hospital were identified, and these diseases were commonly known to involve the neurogenic pathway in pathogenesis to some extent. AEs such as burning sensation, pruritus, erythema, and skin infection were compared by causative disease and applied site. If the patients refused application of the drug due to AEs, we defined the case as severe AEs, explained the transient character of the AEs, and recommended use of the drug in a cold condition. If the patients continued to refuse application, they were classified as treatment discontinuation. All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS software (version 20.0; IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). The statistical outcomes were deemed significant when the p-value was below 0.05.
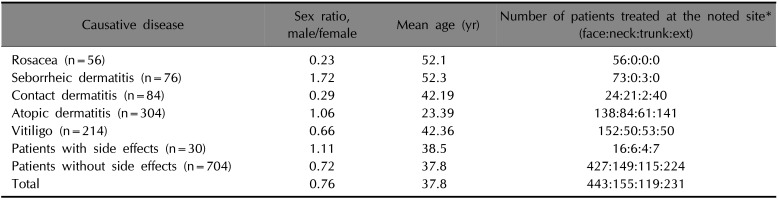
A total of 734 patients were enrolled. Demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. The top five causative diseases were atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, contact dermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and rosacea. Fig. 1A shows the frequency of severe AEs. The incidence of AEs was higher in rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis, and contact dermatitis. Patients with vitiligo showed lower rates of AEs. Of the 30 patients who experienced severe AEs, 21 reported a burning sensation, followed by 6 with pruritus, 2 with erythema, and 1 with folliculitis-like eruption. Treatment discontinuation due to AEs occurred in 6 patients with atopic dermatitis and 4 patients with rosacea. The vitiligo subgroup showed a statistically lower rate of AEs compared to all other subgroups. The incidence of AEs in patients with atopic dermatitis was significantly lower than in patients with rosacea. Fig. 1B demonstrates the differences in rates of severe AEs and treatment discontinuation based on applied site. Based on these results, the application site is not significantly related to the occurrence of AEs.
Currently, tacrolimus ointment is only approved by the FDA for atopic dermatitis treatment. Some reports have indicated that there are additional indications, with various levels of evidence1. Topical tacrolimus is generally well-olerated, except for irritating symptoms during treatment initiation. In this study, the incidence of overall severe AEs was 4.09%, which is lower than previous studies. The proportion of abrupt treatment discontinuation due to AEs was 1.36%, which was also lower than previously reported2. The reason for this low level of reported AEs was likely physician disclosure of the possibility of temporary adverse reactions at the beginning of treatment. Although sex, age, and application sites were not uniformly distributed, the data are representative of the nature of the diseases; studies focused on AEs of topical tacrolimus are limited; therefore, those factors were thought to have no significant effect on the results of this study. Statistical analysis showed that the differences in site of application did not significantly affect the occurrence of AEs.
There are a limited number of articles that address the difference in the incidence of topical tacrolimus AEs according to primary skin disease. In our study, the adverse effects of topical tacrolimus occurred less frequently in vitiligo patients. Stander et al. reported that topical application of a calcineurin inhibitor induced release of substance P (SP) and calcitonin gene-related peptides from primary afferent nerve fibers. These neuropeptides lead to mast cell degranulation. Mast cell mediators, such as histamine and tryptase, could induce pruritus and burning sensation3. Some reports have indicated that SP level is increased in rosacea, contact dermatitis, and atopic dermatitis, but not in vitiligo4567. Although Falabella et al.8 found that SP immunoreactivity was increased in lesional skin of bilateral stable vitiligo compared with bilateral unstable vitiligo, the sample size was relatively small, and no similar trend was observed in unilateral vitiligo. Moreover, this result is difficult to generalize in that there was no comparative study with a normal population. It is known that there is no difference in the activity or skin distribution of SP between vitiligo patients and the normal population79. So, although SP may have a role in the pathogenesis of vitiligo, there is a lack of evidence to conclude that SP is elevated in vitiligo. When inflammation near the area of application is severe, skin irritation symptoms are increased; therefore, because vitiligo has the weakest inflammatory effect, the low incidence of AEs in vitiligo patients is reasonable. The use of topical tacrolimus in atopic dermatitis is generally confined to the chronic phase in which inflammation is relatively mild. For this reason, we think that atopic dermatitis patients have fewer AEs than rosacea patients.
There are some limitations to this study; because the research design was a retrospective chart review, the occurrence of AEs was based on medical chart records of patient statements, and only some of the indications for topical tacrolimus were included. Further analysis is needed, particularly to evaluate the mechanism for the incidence of AEs according to disease.
In conclusion, topical tacrolimus is generally well-tolerated, and patients with vitiligo were less likely to experience adverse events.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The Institutional Review Board of the hospital approved the study (IRB no. KMCIRB 1509-03).
References
1. Luger T, Paul C. Potential new indications of topical calcineurin inhibitors. Dermatology. 2007; 215(Suppl 1):45–54.

2. Rustin MH. The safety of tacrolimus ointment for the treatment of atopic dermatitis: a review. Br J Dermatol. 2007; 157:861–873. PMID: 17854353.

3. Ständer S, Ständer H, Seeliger S, Luger TA, Steinhoff M. Topical pimecrolimus and tacrolimus transiently induce neuropeptide release and mast cell degranulation in murine skin. Br J Dermatol. 2007; 156:1020–1026. PMID: 17388925.

5. Lim YY, Kim HM, Lee HI, Mun SK, Kim CW, Kim MN, et al. A comparison of neuropeptide expression in skin with allergic contact dermatitis in human and mouse. Int J Dermatol. 2012; 51:939–946. PMID: 22788810.

6. Teresiak-Mikołajczak E, Czarnecka-Operacz M, Jenerowicz D, Silny W. Neurogenic markers of the inflammatory process in atopic dermatitis: relation to the severity and pruritus. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013; 30:286–292. PMID: 24353488.

7. Al'Abadie MS, Senior HJ, Bleehen SS, Gawkrodger DJ. Neuropeptide and neuronal marker studies in vitiligo. Br J Dermatol. 1994; 131:160–165. PMID: 7522512.
8. Falabella R, Barona MI, Echeverri IC, Alzate A. Substance P may play a part during depigmentation in vitiligo. A pilot study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2003; 17:355–356. PMID: 12702089.

9. Hristakieva E, Lazarova R, Lazarov N, Stanimirović A, Shani J. Markers for vitiligo related neuropeptides in human skin nerve fibers. Acta Med Croatica. 2000; 54:53–57. PMID: 11028109.
Fig. 1
(A) Adverse effect (AE) incidence rates (%). AE incidence rates are significantly different between atopic dermatitis and rosacea groups (marked with *p=0.033). Patients with vitiligo showed statistically lower AE rates compared to all other subgroups (marked with †p=0.037 with atopic dermatitis, p=0.010 with irritated contact dermatitis, p=0.006 with seborrheic dermatitis, p=0.000 with rosacea subgroup). (B) Side effects and application site. There was no correlation between severe side effects or treatment discontinuation with applied site (p=1.000 between severe side effects and applied site, p=1.000 between treatment discontinuation and applied site).
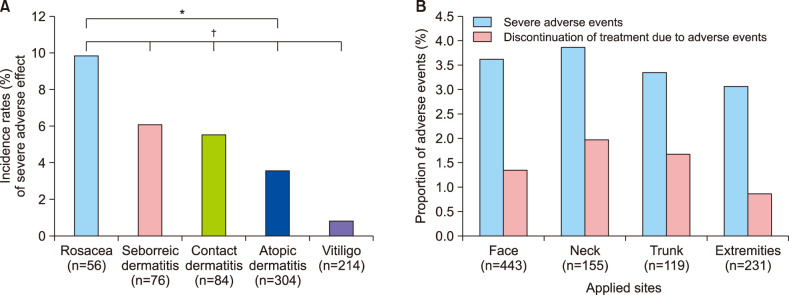
Table 1
Patient demographics




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download