1. Boguniewicz M, Leung DY. Atopic dermatitis: a disease of altered skin barrier and immune dysregulation. Immunol Rev. 2011; 242:233–246. PMID:
21682749.

2. Boguniewicz M, Leung DY. Recent insights into atopic dermatitis and implications for management of infectious complications. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:4–13. PMID:
20109729.

3. Hauser C, Wuethrich B, Matter L, Wilhelm JA, Sonnabend W, Schopfer K. Staphylococcus aureus skin colonization in atopic dermatitis patients. Dermatologica. 1985; 170:35–39. PMID:
3972149.
4. Mylonakis E, Calderwood SB. Infective endocarditis in adults. N Engl J Med. 2001; 345:1318–1330. PMID:
11794152.

5. Ahn K. The prevalence of atopic dermatitis in Korean children. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016; 8:1–2. PMID:
26540495.

6. Lee JH, Han KD, Kim KM, Park YG, Lee JY, Park YM. Prevalence of atopic dermatitis in Korean children based on data from the 2008-2011 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2016; 8:79–83. PMID:
26540505.

7. Aly R, Maibach HI, Shinefield HR. Microbial flora of atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol. 1977; 113:780–782. PMID:
141239.

8. Patel D, Jahnke MN. Serious complications from Staphylococcal aureus in atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015; 32:792–796. PMID:
26337792.
9. Harada M, Nishi Y, Tamura S, Iba Y, Abe K, Yanbe Y, et al. [Infective endocarditis with a huge mitral vegetation related to atopic dermatitis and high serum level of infectionrelated antiphospholipid antibody: a case report]. J Cardiol. 2003; 42:135–140. PMID:
14526663.
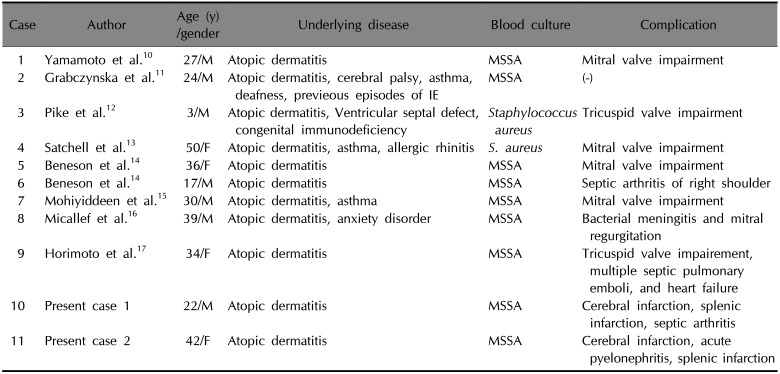
10. Yamamoto T, Yodogawa K, Wakita S, Ogano M, Tokita M, Miyagi Y, et al. Recurrent prosthetic valve endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus colonizing skin lesions in severe atopic dermatitis. Intern Med. 2007; 46:571–573. PMID:
17473491.

11. Grabczynska SA, Cerio R. Infective endocarditis associated with atopic eczema. Br J Dermatol. 1999; 140:1193–1194. PMID:
10354109.
12. Pike MG, Warner JO. Atopic dermatitis complicated by acute bacterial endocarditis. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1989; 78:463–464. PMID:
2741691.

13. Satchell AC, Barnetson RS. Staphylococcal septicaemia complicating treatment of atopic dermatitis with mycophenolate. Br J Dermatol. 2000; 143:202–203. PMID:
10886168.

14. Beneson S, Zimhony O, Dahan D, Solomon M, Raveh D, Schlesinger Y, et al. Atopic dermatitis--a risk factor for invasive Staphylococcus aureus infections: two cases and review. Am J Med. 2005; 118:1048–1051. PMID:
16164895.
15. Mohiyiddeen G, Brett I, Jude E. Infective endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus aureus in a patient with atopic dermatitis: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2008; 2:143. PMID:
18454875.

16. Micallef MJ, Ramphul A. Infective endocarditis in a patient with atopic dermatitis. J Cardiol Cases. 2016; 13:153–154. PMID:
30546632.

17. Horimoto K, Kubo T, Matsusaka H, Baba H, Umesue M. Right-sided infective endocarditis with a ruptured sinus of Valsalva and multiple septic pulmonary emboli in a patient with atopic dermatitis. Intern Med. 2015; 54:797–800. PMID:
25832944.

18. Fukunaga N, Okada Y, Konishi Y, Murashita T, Koyama T. Pay attention to valvular disease in the presence of atopic dermatitis. Circ J. 2013; 77:1862–1866. PMID:
23535217.

19. Ong PY, Ohtake T, Brandt C, Strickland I, Boguniewicz M, Ganz T, et al. Endogenous antimicrobial peptides and skin infections in atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med. 2002; 347:1151–1160. PMID:
12374875.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download