Abstract
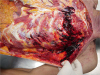
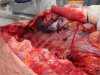
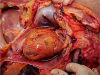
Injuries caused by free-fall from heights represent a specific form of blunt trauma that can be difficult to interpret, especially when the impact medium is water. On autopsy practice, the immersed bodies with rib fractures and internal organ injuries were often encountered and many studies have reported that impact with the water surface could cause skeletal fracture and visceral organ rupture. The height of the fall and body orientation on impact are the most important factors determining the severity and range of these injuries. In the present case, the victim was a 69-year-old male who weighed 48 kg. Following were the autopsy findings: numerous pin-point epidermal injuries on the body surface (like those due to nibbling by fish), a massive soft tissue hemorrhage in the left upper chest, multiple rib fractures (3rd–7th left ribs), ballooning of the lungs, froth in the trachea and bronchus, pericardial tearing in the right anterolateral side (7-cm long), intra-pericardial hemorrhage, and focal hemorrhage in the adventitia of the intra-pericardial aorta. No sign of an external wound was observed in the left chest area. The cause of death was drowning, and the manner of death was suicide. Unfortunately, the site and height of fall were not investigated.
Figures and Tables
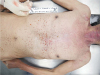 | Fig. 1Numerous pin-point epidermal injury, like nibbling by fish mouth, in the chest and the abdomen. |
References
1. Abel SM, Ramsey S. Patterns of skeletal trauma in suicidal bridge jumpers: a retrospective study from the southeastern United States. Forensic Sci Int. 2013; 231:399.e1–399.e5.

2. Harvey PM, Solomons BJ. Survival after free falls of 59 metres into water from the Sydney Harbour Bridge, 1930–1982. Med J Aust. 1983; 1:504–511.

3. Cetin G, Gunay Y, Fincanci SK, et al. Suicides by jumping from Bosphorus Bridge in Istanbul. Forensic Sci Int. 2001; 116:157–162.
4. Turk EE, Tsokos M. Blunt cardiac trauma caused by fatal falls from height: an autopsy-based assessment of the injury pattern. J Trauma. 2004; 57:301–304.
5. Snyder RG, Snow CC. Fatal injuries resulting from extreme water impact. Aerosp Med. 1967; 38:779–783.
6. Ahn H, Chang BC, Lim SP. Traumatic aneurysm of descending thoracic aorta: report of one case. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1984; 17:67–73.
7. Kikuike K, Uemura S, Miyamoto K, et al. Upper lumbar burst fracture due to recreational high jumping into a river: report of five cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2009; 129:87–90.

8. Teh J, Firth M, Sharma A, et al. Jumpers and fallers: a comparison of the distribution of skeletal injury. Clin Radiol. 2003; 58:482–486.

9. Lau G, Ooi PL, Phoon B. Fatal falls from a height: the use of mathematical models to estimate the height of fall from the injuries sustained. Forensic Sci Int. 1998; 93:33–44.

10. Goodacre S, Than M, Goyder EC, et al. Can the distance fallen predict serious injury after a fall from a height? J Trauma. 1999; 46:1055–1058.

11. Turk EE, Tsokos M. Pathologic features of fatal falls from height. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2004; 25:194–199.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download