Abstract
Objective
Homeostasis of the extracellular matrix (ECM) is maintained by the action of a specific system of proteolytic enzymes known as matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP). The MMP/TIMP system regulates the composition and turnover of ECM to control the site and extent of connective tissue remodeling. In pathologic conditions, MMP play a key role in degradation of basement membrane and extracellular matrix, and is responsible for cancer invasion, progression and metastasis. The aim of this study is to evaluate the correlation between expressions of MMP/TIMP and clinicopathologic factors in endometrial cancer.
Methods
Expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 were assessed by immunohistochemistry in a total of 55 endometrial cancers and were analyzed by the correlation between expressions of MMP/TIMP and clinicopathologic factors in endometrial cancer.
Results
Expression rates of MMP-2,-9, TIMP-1, and TIMP-2 were 71.7%, 54.9%, 41.2%, and 76.5% respectively. Expression of MMP-2 was correlated with the group of positive lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer (p=0.04). Specially, coexpression of MMP-2 and TIMP-2 was significantly more frequent in the group of positive lymph node metastasis (p<0.01) and the group of positive peritoneal
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Isolated endometrial tumor glands show focal immunostaining to MMP-2 in tumor cell cytoplasm (×200, MMP-2).
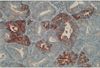
Fig. 2
Endometrial tumor glands show diffuse immunostaining to MMP-9 in tumor cell cytoplasm and stromal cell components (×200, MMP-9).
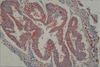
Fig. 3
Isolated endometrial tumor glands show focal immunostaining to MMP-2 in tumor cell cytoplasm (×200, MMP-2).
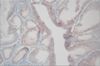
Table 3
The correlation between the expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 and the clinicopathologic parameters in endometrial cancer

Table 4
The correlation between the coexpression of MMP-2 and TIMP-2 and the clinicopathologic factors in endometrial cancer

References
2. Annual report of gynecologic cancer registry program in Korea for 2002 (2002.1.1-2002.12.31). Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2004. 47:1029–1070.
3. Oh SH, Jun CY, Kim JW, Park JS, Kim SJ. Endometrial carcinoma; Clinicopathologic analysis. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1987. 30:1661–1672.
4. Shin SC, Han SW, Kim KL, Kwon JY, Jung IB, Cha DS. Endometrial carcinoma; Clinicopathologic analysis. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 1994. 37:1821–1828.
5. Jeon WJ, Moon EJ, Ryu SY, Kim JH, Kim BG, Park SY, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis of endometrial cancer: A study of 100 cases. Korean J Obstet Gynecol. 2000. 43:1616–1623.
6. Jonathan SB. Berek & Novak's gynecology. 2006. 14th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wikins;1362–1366.
7. Cotran RS, Kumar V, Collins T. Pathologic basis of disease. 1999. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Sauders;106–107.
8. Robert V, Hideaki N. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: Structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res. 2003. 92:827–839.
9. Curry TE, Osteen KG. Cyclic changes in the matrix metalloproteinase system in the ovary and uterus. Biol Reprod. 2001. 64:1285–1296.
10. Stetler-Stevenson WG. Dynamics of matrix turnover during pathologic remodeling of the extracellular matrix. Am J Pathol. 1996. 148:1345–1350.
11. Jones JL, Walker RA. Control of matrix metalloproteinase activity in cancer. J Pathol. 1997. 183:377–379.

12. Heppner KJ, Matrisian LM, Jensen RA, Rodgers WH. Expression of most matrix metalloproteinase family members in breast cancer represents a tumor induced host response. Am J Pathol. 1996. 149:273–282.
13. Kawami H, Toshiba AK, Ohsaki A, Kuroi K, Nishiyama M, Toge T. Stromelysin-3 mRNA expression and malignancy: Comparison with clinicopathologic features and type IV collagenase mRNA expression in breast tumors. Anticancer Res. 1993. 13:2319–2324.
14. Nakagawa T, Kubota T, Kabuto M. Production of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase-1 by human brain tumor. J Neurosurg. 1994. 81:69–77.
15. Stearns ME, Stearns M. Autocrine factors, type IV collagenase secretion and prostatic cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1993. 12:39–52.

16. Takemura M, Azuma C, Kimura T, Kanai T, Saji F, Tanizawa O. Type IV collagenase and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase in ovarian cancer tissues. Inj J Gynecol Obstet. 1994. 46:303–309.
17. Miyajima Y, Nakano R, Morimatsu M. Analysis of expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma by in situ hybridization. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1995. 104:678–684.
18. Ashida K, Nakatsukasa H, Higashi T. Cellular distribution of 92kd type IV collagenase/gelatinase B in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1996. 149:1803–1811.
19. Liotta LA, Steeg PS, Ststler-Stevenson WG. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: An imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991. 64:327–336.

20. Nuovo GJ, MacConnel PB, Simsir A, Valea F, French DL. Correlation of the in situ detection of polymerase chain reaction-amplified metalloproteinase complementary DNAs and their inhibitors with prognosis in cervical carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1995. 55:267–275.
21. Birkedal HH, Moore WG, Bodden MK. Matrix metalloproteinases: A review. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1993. 4:197–250.
22. Greene J, Wang M, Liu YE, Raymond LA, Rosen C, Shi YE. Molecular cloning and characterization of human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 4. J Biol Chem. 1996. 271:30375–30380.
23. Hurskainen T, Hoyhtya M, Tuuttila A, Oikarinen A, Autio-Harmainen H. mRNA expressions of TIMP-1, -2, and -3 and 92-KD type IV collagenase in early human placenta and decidual membrane as studied by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem. 1996. 44:1379–1388.
24. Paloff N, Sraskus PW, Kishmanai NS, Hawkes SP. A new inhibitor of metalloproteinase form chicken. J Biol Chem. 1992. 267:17321–17326.
25. Lokeshwar BL, Selzer MG, Block NL, Gunja-Smith Z. Secretion of matrix metalloproteinase and their inhibitors (tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase) by human protate in explant culture: Reduced tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase secretion by malignant tissues. Cancer Res. 1993. 63:4493–4498.
26. Lindsay CK, Thorgeirsson UP, Tsuda H, Hirohashi S. Expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase and type IV collagenase/gelatinase messanger RNAs in human breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 1977. 28:359–366.
27. Ueno H, Nakamura H, Inoue M. Expression and tissue localization of membrane-type 1, 2 and 3 matrix metallopreoteinase in human invasive breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1997. 57:2055–2060.
28. Maatta M, Soini Y, Liakka A, Autio-Harmainen H. Localization of MT1-MMP, TIMP-1, TIMP-2, and TIMP-3 messenger RNA in normal, hyperplastic, and neoplastic endometrium. Enhanced expression by endometrial adenocarcinoma is associated with low differentiation. Am J Clin Pathol. 2000. 114:402–411.
29. Di Nezza LA, Misajon A, Zhang J, Jobling T, Quinn MA, Ostor AG, et al. Presence of active gelatinases in endometrial carcinoma and correlation of matrix metalloproteinase expression with increasing tumor grade and invasion. Cancer. 2002. 94:1466–1475.

30. Graesslin O, Cortez A, Fauvet R, Lorenzato M, Birembaut P, Darai E. Metalloproteinase-2, -7 and -9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 and -2 expression in normal, hyperplastic and neoplastic endometrium: A clinical-pathological correlation study. Ann Oncol. 2006. 17:637–645.

31. Guo W, Chen G, Zhu C, Wang H. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2, 9 and it's tissue inhibitor-1, 2 in endometrial carcinoma. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2002. 37:604–607.
32. Moser PL, Hefler L, Tempfer C, Neunteufel W, Kieback DG, Gitsch G. Immunohistochemical detection of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 1 and 2, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 (TIMP 2) in stage I and II endometrial cancer. Anticancer Res. 1999. 19:2365–2367.
33. Honkavuori M, Talvensaari-Mattila A, Soini Y, Turpeennierni-Hujanen T, Santala M. MMP-2 expression associates with CA 125 and clinical course in endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 2007. 104:217–221.

34. Aglund K, Rauvala M, Puistola U, Angastrom T, Turpeennierni-Hujanen T, Zackrisson B, et al. Gelatinases A and B (MMP-2 and MMP-9) in endometrial cancer - MMP-9 correlates to the grade and the stage. Gynecol Oncol. 2004. 94:699–704.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print






 XML Download
XML Download