Abstract
Objective
Flavopiridol that inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase, can cause cell cycle arrest, induce apoptosis in human tumor cell lines. In the present study, we investigated apoptotic effects of flavopiridol and the underlying molecular mechanisms in human ovarian cancer cell lines.
Methods
We used TOV-21G and TOV-112D cell lines. The cell viability was tested by MTT assay and apoptosis was assessed by TUNEL assay and annexin-V binding. Western blot was used to examine apoptosis related protein levels. MAP kinase activity was analyzed by non-radioactive MAP kinase assay kit.
Results
Treatment of TOV-21G and TOV-112D cells with flavopiridol (50 nM to 1000 nM) led to a dose- and time-dependent inhibition of cell growth and survival. Dose-related induction of apoptosis was also observed in these cell lines. Flavopiridol (500 nM) induced striking decreases in the levels of the antiapoptic proteins Mcl-1, Bcl-XL, and XIAP in both cell lines. In contrast, expression of Bax, Bcl-2, and AIF was not significantly influenced by flavopiridol. Although flavopiridol resulted in accumulation of p53 in both cells, flavopiridol mediated apoptosis was p53 independent because it occurred to the same degree in TOV-112D cells in which p53 was inactivated by mutation. Flavopiridol treatment resulted in enhanced cleavage of pro-caspase 9 and activation of caspase 3. Apoptosis was associated with suppression of ERK activity.
Figures and Tables
Fig. 1
Effect of flavopiridol on the viability of the ovarian cancer cell lines TOV-21G (A) and TOV-112D (B). Cells were treated with flavopiridol at the indicated concentrations 24 hours after plating. At 24, and 48 hours after treatment, cells were stained MTT, and the absorbance was read at 570 nm. Results were presented as percentage of control which was calculated using the equation: (mean absorbance of treated cells/mean absorbance of control cells) ×100. Data were expressed as mean±standard deviation (SD) from four independent experiments. *p<0.05 as compared to corresponding control cells.
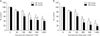
Fig. 2
Ovarian cancer cell lines, TOV-21G (A) and TOV-112D (B) labelled by the TUNEL method. Cells were treated with 100 nM flavopiridol for 24 hours. Nuclear morphology was examined under a fluorescence microscopy. Nuclei of apoptotic cells were green. Live cells were totally blue without green spot. Original magnification, ×200.
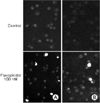
Fig. 3
Induction of apoptosis by flavopiridol in ovarian cancer cell lines TOV-21G. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of flavopiridol (100, 300, and 500 nM) for 24 and 48 hours, respectively. (A) for apoptosis, the externalization of phosphatidylserine was assessed by measuring annexin-V-Fluos binding using propidium iodide as a counterstain. Quadrant rectangular dot grams from a representative of 3 independent experiments is shown. (B) DNA fragmentation were determined using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase for incorporation of fluorescein-12-dUTP at free 3'-OH DNA ends (TUNEL assay). The percentage of TUNEL-positive cells was counted for each condition at 40× magnification in five separate fields of at least 100 cells each. Data were expressed as the mean±standard deviation (SD) from three independent experiments.
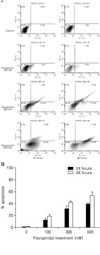
Fig. 4
Induction of apoptosis by flavopiridol in ovarian cancer cell lines TOV-112D. Cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of flavopiridol (100, 300, and 500 nM) for 24 and 48 hours, respectively. (A) For apoptosis, the externalization of phosphatidylserine was assessed by measuring annexin V-Fluos binding using propidium iodide as a counterstain. Quadrant rectangular dot grams from a representative of 3 independent experiments is shown. (B) DNA fragmentation were determined using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase for incorporation of fluorescein-12-dUTP at free 3'-OH DNA ends (TUNEL assay). The percentage of TUNEL-positive cells was counted for each condition at 40× magnification in five separate fields of at least 100 cells each. Data were expressed as the mean±standard deviation (SD) from three independent experiments.
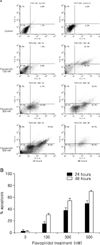
Fig. 5
Activation of caspase 3 by flavopiridol in ovarian cancer cell lines TOV-21G and TOV-112D. Cells were treated with 500 nM flavopiridol for the times indicated. Protein extracts were obtained from aliquots of cells and assayed for caspase 3 activity using the fluorogenic substrate DEVD-AMC.
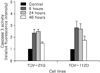
Fig. 6
The effect of flavopiridol on the expression of apoptosis related proteins (AIF, XIAP, p53, Mcl-1, Bcl-XL, Bcl-2, and Bax) in ovarian cancer cell lines TOV-21G and TOV-112D. Cells were treated with flavopiridol (100, 300, and 500 nM) for 24 hours, respectively. Aliquots of cells were transferred and protein extracts were assayed for western blot analysis. The expression of actin were used as the loading control.

Fig. 7
Activation and processing of caspase 9 during flavopiridol induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cell lines TOV-21G and TOV-112D. Cells were treated with flavopiridol (100, 300, and 500 nM) for 24 hours. Aliquots of cells were transferred and lysed in SDS sample buffer and lysates were subjected to western blot analysis with specific antibody, which recognized the pro-form and the active cleaved form of caspase 9, Mr 46 kDa and 34 kDa, respectively.

Fig. 8
Flavopiridol-induced suppression of the activity of ERK, MAP kinase in ovarian cancer cell lines TOV-21G and TOV-112D. Cells were treated with flavopiridol (100, and 500 nM) for 24 hours. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-ERK antibodies before a further incubation with protein A-Sepharose beads. These immune complexes were reacted with myelin basic protein (MBP) as a substrate and then the phosphorylated substrate was analyzed by immunoblot analysis, probing with a monoclonal phospho-MBP antibody.
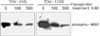
References
1. Kaur G, Stetler-Stevenson M, Sebers S, Worland P, Sedlacek H, Myers C, et al. Growth inhibition with reversible cell cycle arrest of carcinoma cells by flavone L86-8275. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992. 84:1736–1740.

2. Zhai S, Senderowicz AM, Sausville EA, Figg WD. Flavopiridol, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, in clinical development. Ann Pharmacother. 2002. 36:905–911.

3. Worland PJ, Kaur G, Stetler-Stevenson M, Sebers S, Sartor O, Sausville EA. Alteration of the phosphorylation state of p34cdc2 kinase by the flavone L86-8275 in breast carcinoma cells. Correlation with decreased H1 kinase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1993. 46:1831–1840.
4. De Azevedo WF Jr, Mueller-Dieckmann HJ, Schulze-Gahmen U, Worland PJ, Sausville E, Kim SH. Structural basis for specificity and potency of a flavonoid inhibitor of human CDK2, a cell cycle kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996. 93:2735–2740.

5. Carlson B, Lahusen T, Singh S, Loaiza-Perez A, Worland PJ, Pestell R, et al. Down-regulation of cyclin D1 by transcriptional repression in MCF-7 human breast carcinoma cells induced by flavopiridol. Cancer Res. 1999. 59:4634–4641.
7. Melillo G, Sausville EA, Cloud K, Lahusen T, Varesio L, Senderow AM. Flavopiridol, a protein kinase inhibitor, down-regulates hypoxic induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human monocytes. Cancer Res. 1999. 59:5433–5437.
8. Arguello F, Alexander M, Sterry JA, Tudor G, Smith EM, Kalavar NT, et al. Flavopiridol induces apoptosis of normal lymphoid cells, causes immunosuppression, and has potent antitumor activity In vivo against human leukemia and lymphoma xenografts. Blood. 1998. 91:2482–2490.
9. Patel V, Senderowicz AM, Pinto D Jr, Igishi T, Raffeld M, Quintanilla-Martinez L, et al. Flavopiridol, a novel cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, suppresses the growth of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas by inducing apoptosis. J Clin Invest. 1998. 102:1674–1681.

10. Parker BW, Kaur G, Nieves-Neira W, Taimi M, Kohlhagen G, Shimizu T, et al. Early induction of apoptosis in hematopoietic cell lines after exposure to flavopiridol. Blood. 1998. 91:458–465.

11. Achenbach TV, Muller R, Slater EP. Bcl-2 independence of flavopiridol-induced apoptosis. Mitochondrial depolarization in the absence of cytochrome c release. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:32089–32097.
12. Kitada S, Zapata JM, Andreeff M, Reed JC. Protein kinase inhibitors flavopiridol and 7-hydroxy-staurosporine down-regulate antiapoptosis proteins in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 2000. 96:393–397.

13. Raju U, Nakata E, Mason KA, Ang KK, Milas L. Flavopiridol, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, enhances radiosensitivity of ovarian carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2003. 63:3263–3267.
14. Motwani M, Delohery TM, Schwartz GK. Sequential dependent enhancement of caspase activation and apoptosis by flavopiridol on paclitaxel-treated human gastric and breast cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 1999. 5:1876–1883.
15. Shapiro GI. Preclinical and clinical development of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:4270s–4275s.

16. Provencher DM, Lounis H, Champoux L, Tetrault M, Manderson EN, Wang JC, et al. Characterization of four novel epithelial ovarian cancer cell lines. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2000. 36:357–361.

17. Shapiro GI, Koestner DA, Matranga CB, Rollins BJ. Flavopiridol induces cell cycle arrest and p53-independent apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 1999. 5:2925–2938.
18. Samouelian V, Maugard CM, Jolicoeur M, Bertrand R, Arcand SL, Tonin PN, et al. Chemosensitivity and radiosensitivity profiles of four new human epithelial ovarian cancer cell lines exhibiting genetic alterations in BRCA2, TGFbeta-RII, KRAS2, TP53 and/or CDNK2A. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2004. 54:377–383.
19. Wittmann S, Bali P, Donapaty S, Nimmanapalli R, Guo F, Yamaguchi H, et al. Flavopiridol down-regulates antiapoptotic proteins and sensitizes human breast cancer cells to epothilone B-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2003. 63:93–99.
20. Gojo I, Zhang B, Fenton RG. The cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor flavopiridol induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells through transcriptional repression and down-regulation of Mcl-1. Clin Cancer Res. 2002. 8:3527–3538.
21. Ma Y, Cress WD, Haura EB. Flavopiridol-induced apoptosis is mediated through up-regulation of E2F1 and repression of Mcl-1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2003. 2:73–81.
22. Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE, Brothers GM, et al. Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature. 1999. 397:441–446.

23. Cande C, Cecconi F, Dessen P, Kroemer G. Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF): Key to the conserved caspase-independent pathways of cell death? J Cell Sci. 2002. 115:4727–4734.
24. Deveraux QL, Takahashi R, Salvesen GS, Reed JC. X-linked IAP is a direct inhibitor of cell-death proteases. Nature. 1997. 388:300–304.

25. Woo M, Hakem R, Soengas MS, Duncan GS, Shahinian A, Kagi D, et al. Essential contribution of caspase 3/CPP32 to apoptosis and its associated nuclear changes. Genes Dev. 1998. 12:806–819.
26. Laframboise S, Chapman W, McLaughlin J, Andrulis IL. p53 mutations in epithelial ovarian cancers: possible role in predicting chemoresistance. Cancer J. 2000. 6:302–308.




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download